We are pleased to offer PBPK models for large molecules (biologics). The Biologics Module simulates the systemic absorption and pharmacokinetics of biologics – for both monoclonal antibodies (mAb) and NEW! antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). In the current implementation, both mAbs and ADCs administered as an intravenous bolus dose, intravenous infusion, subcutaneous (SQ), and NEW! intramuscular (IM) injections (both bolus and controlled release) can be modeled.
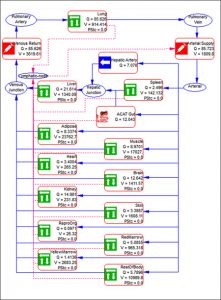
As with other GastroPlus modules, there is no equation or code writing required. A schematic diagram of how the different organs are connected to one another is shown below. All major organs are connected in an anatomical fashion with plasma flow represented by blue solid arrows and lymph flow by red dashed arrows.
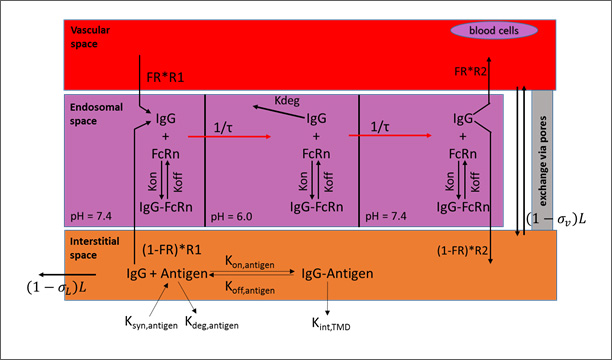
The lymph node collects the lymphatic drainage from organs and lymph fluid is returned to the systemic circulation. Each organ in the PBPK model is divided into three major compartments representing the vascular, endosomal, and interstitial spaces.