Trifluoromethylated N-benzamide enaminones have been identified as potential anticonvulsants for the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy.
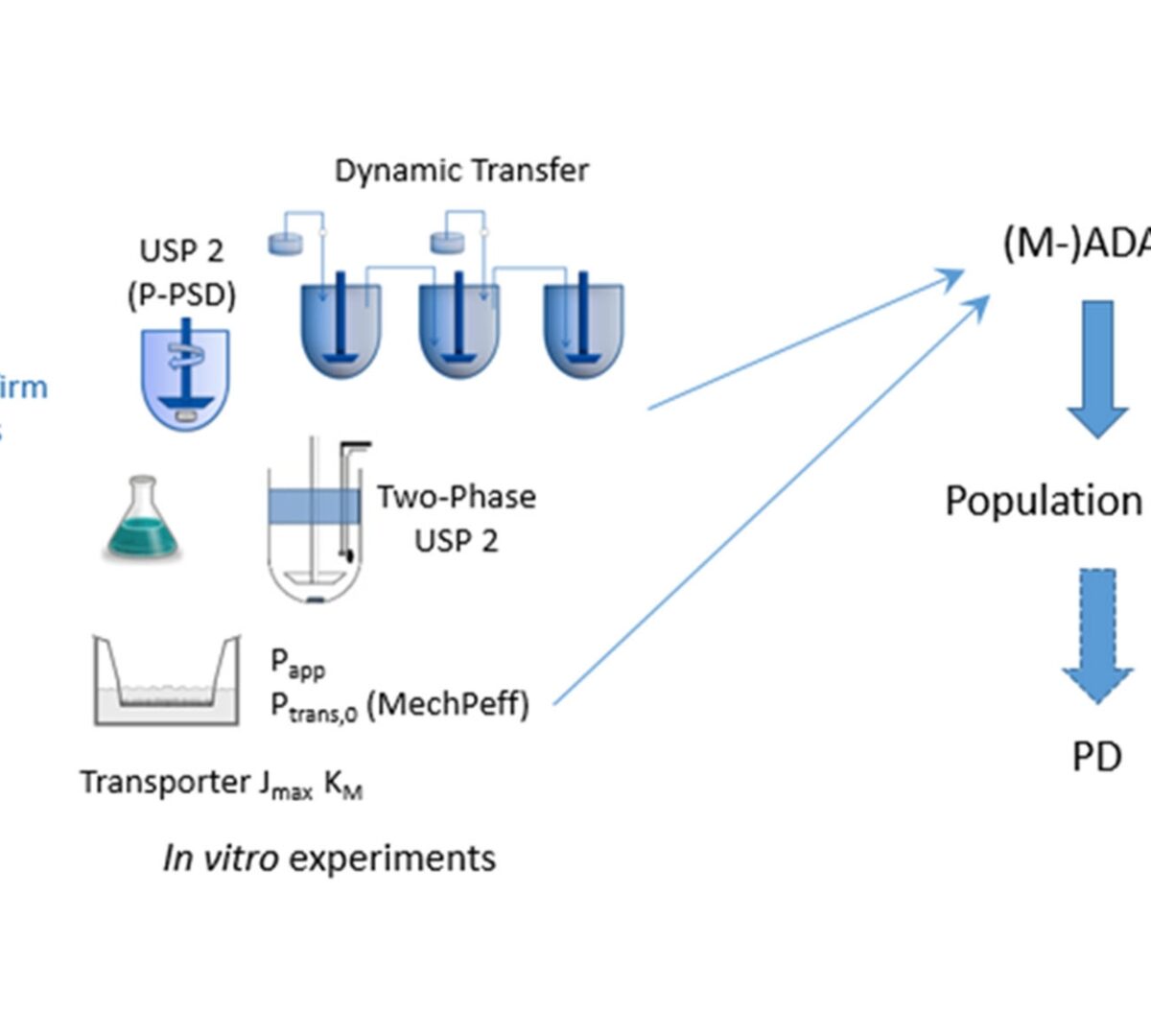
Developing Clinically Relevant Dissolution Specifications (CRDSs) for Oral Drug Products: Virtual Webinar Series
A webinar series that was organised by the Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences Biopharmaceutics focus group in 2021 focused on the challenges of developing clinically relevant...

Comparison of toxicological effects and exposure levels between triclosan and its structurally similar chemicals using in vitro tests for read-across case study
Read-across based on structural and biological similarities is expected to be a promising alternative method for assessing systemic toxicity.
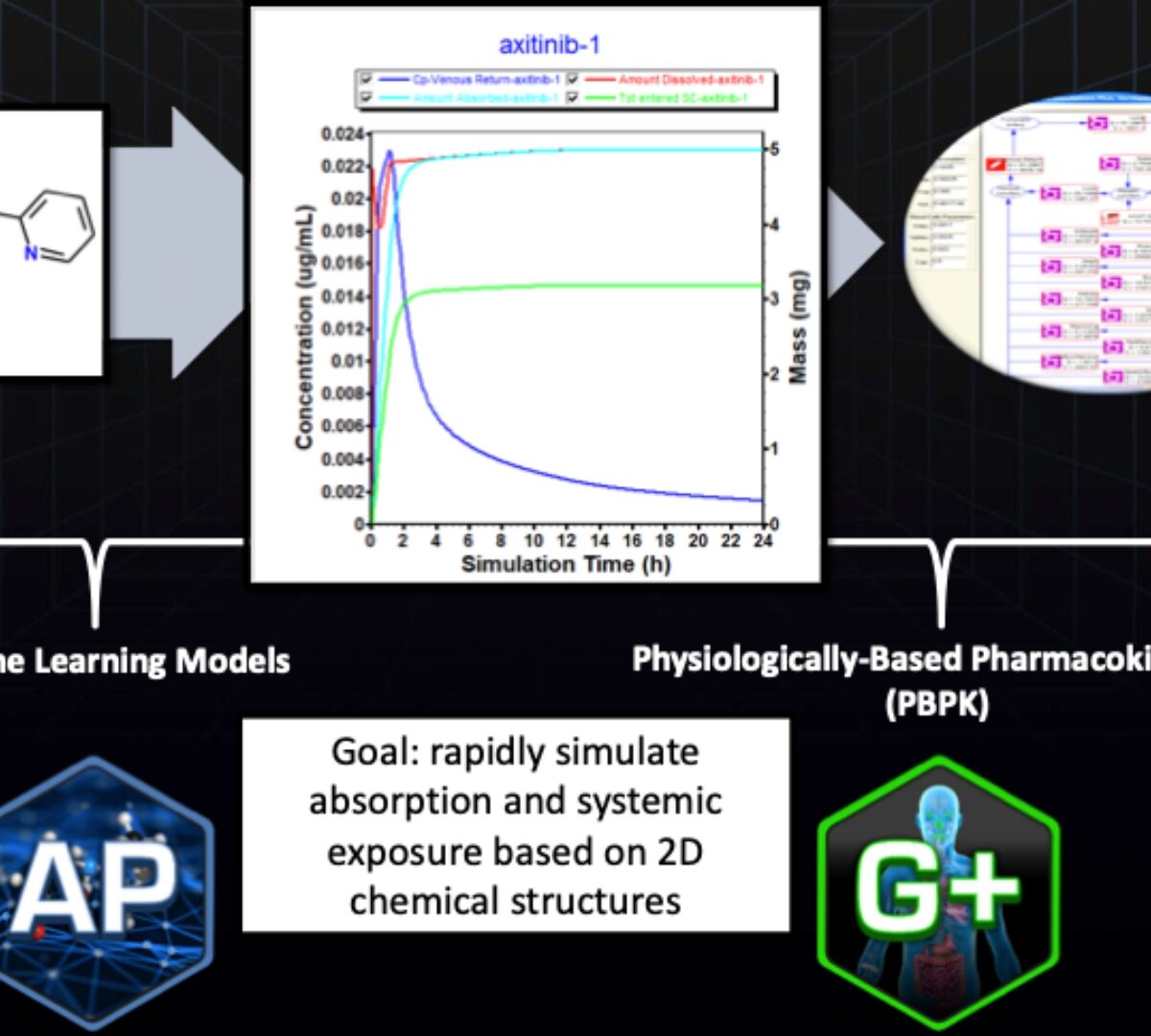
API Enabled HTPK Deployment of Early PK Assessments for Drug Discovery
Mechanistic High-Throughput PK

Discovery of 2-((2-methylbenzyl)thio)-6-oxo-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile as a novel and effective bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) inhibitor for the treatment of sepsis
Sepsis has long been a major health problem worldwide.

Clinical Ocular Exposure Extrapolation Using PBPK Modeling and Simulation: Moxifloxacin Solution Case Study
Development of generic ophthalmic drug products is challenging due to the complexity of the ocular system and a lack of sensitive...

Evaluating the pharmacokinetics of intrapulmonary administered ciprofloxacin solution for respiratory infections using in vivo and in silico PBPK rat model studies
Respiratory antibiotics have been proven clinically beneficial for the treatment of severe lung infections such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa.

A Mechanistic Absorption and Disposition Model of Ritonavir to Predict Exposure and Drug-Drug Interaction Potential of CYP3A4/5 and CYP2D6 Substrates
Due to health authority warnings and the recommended limited use of ketoconazole as a model inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 in clinical drug–drug interaction...

Simulations Plus Successfully Delivers FDA-Funded Project
Collaboration with the US FDA and Center for Research on Complex Generics to Establish the Suitability of Model-Integrated Evidence to Demonstrate Bioequivalence for Long-Acting Injectables

Membrane Plus v3 Release Webinar
Learn about new, improved, and enhanced features to drive advances to in vitro-in vivo extrapolation (IVIVE) for permeability, hepatocyte, skin penetration, and release assay systems.

Evaluation of the Success of High-Throughput Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (HT-PBPK) Modeling Predictions to Inform Early Drug Discovery
Minimizing in vitro and in vivo testing in early drug discovery with the use of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling and machine learning (ML) approaches...

Exposure-efficacy analyses support optimal dosing regimens of ceftolozane/tazobactam in participants with hospital-acquired/ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia in ASPECT-NP
An exposure-efficacy analysis of the phase 3 ASPECT-NP trial was performed to evaluate the relationship between plasma exposure of ceftolozane and tazobactam and

Influence of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the P2Y12 receptor antagonist selatogrel
Selatogrel is a potent and selective reversible P2Y12 receptor antagonist in development for early treatment of acute myocardial infarction via subcutaneous (s.c.)self-injection.

Comprehensive interpretation of in vitro micronucleus test results for 292 chemicals: from hazard identification to risk assessment application
Risk assessments are increasingly reliant on information from in vitro assays.

Simulations Plus Enters New Collaboration to Advance DDDPlus™ Software
Funded partnership with large pharmaceutical company will enhance mechanistic dissolution models for injectable formulations

Prediction of CYP-mediated DDIs involving inhibition: Approaches to address the requirements for system qualification of the Simcyp Simulator
Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling is being increasingly used in drug development to avoid unnecessary clinical...

Introducing ILDsym, a New Tool to Facilitate Development of Drugs to Treat Interstitial Lung Disease
Systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma, is a rare connective tissue and autoimmune disease associated with inflammation and fibrosis of the skin and/or internal organs.
