Oral suspensions are heterogeneous disperse systems, and the particle size distribution, crystalline form of the dispersed solid, and composition of the formulation can be listed as parameters that control the drug dissolution rate and its bioavailability.
Voices in Molecular Pharmaceutics: Meet Dr. Bart Hens, A Sociable Scientist Focusing on Multidisciplinary Connections to Unravel the Gaps of Oral Drug Behavior in the Human Gastrointestinal Tract
Bart Hens (Pharm.D., Ph.D.) holds a Ph.D. degree in Pharmaceutical Sciences obtained from KU Leuven (Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Patrick Augustijns - Leuven, Belgium).
Repurposing of Strychnine as the Potential Inhibitors of Aldo–keto Reductase Family 1 Members B1 and B10: Computational Modeling and Pharmacokinetic Analysis
AKR1B1 and AKR1B10 are important members of aldo–keto reductase family which plays a significant role in cancer progression by modulating cellular metabolism.
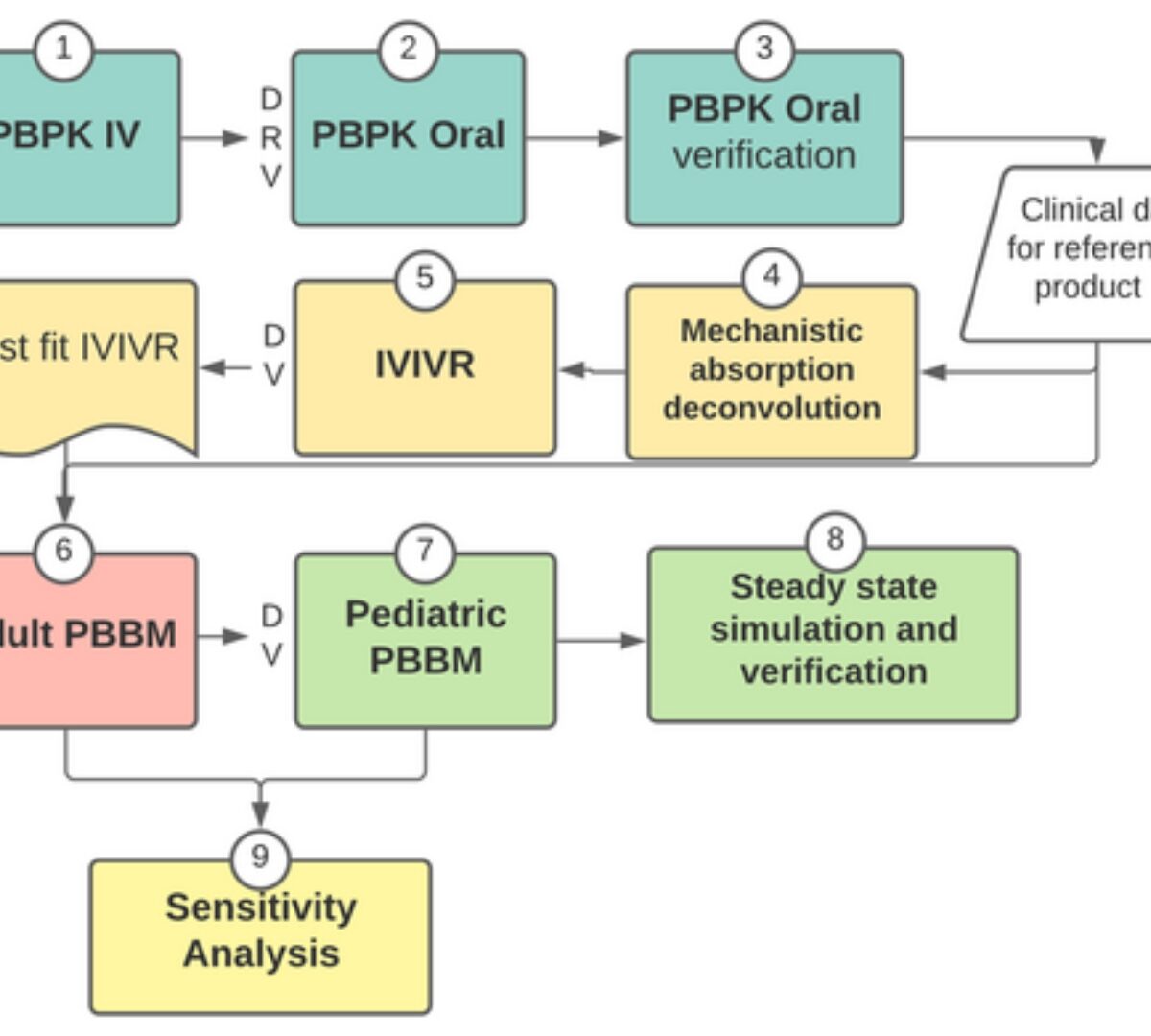
Adult and pediatric physiologically-based biopharmaceutics modeling to explain lamotrigine immediate release absorption process
Physiologically-based biopharmaceutics modeling (PBBM) has potential to accelerate the development of new drug and formulations.
Quercetin-encapsulated magnetoliposomes: Fabrication, optimization, characterization, and antioxidant studies
Quercetin (QU) faces challenges in its therapeutic efficacy due to its hydrophobic nature and limited oral bioavailability.
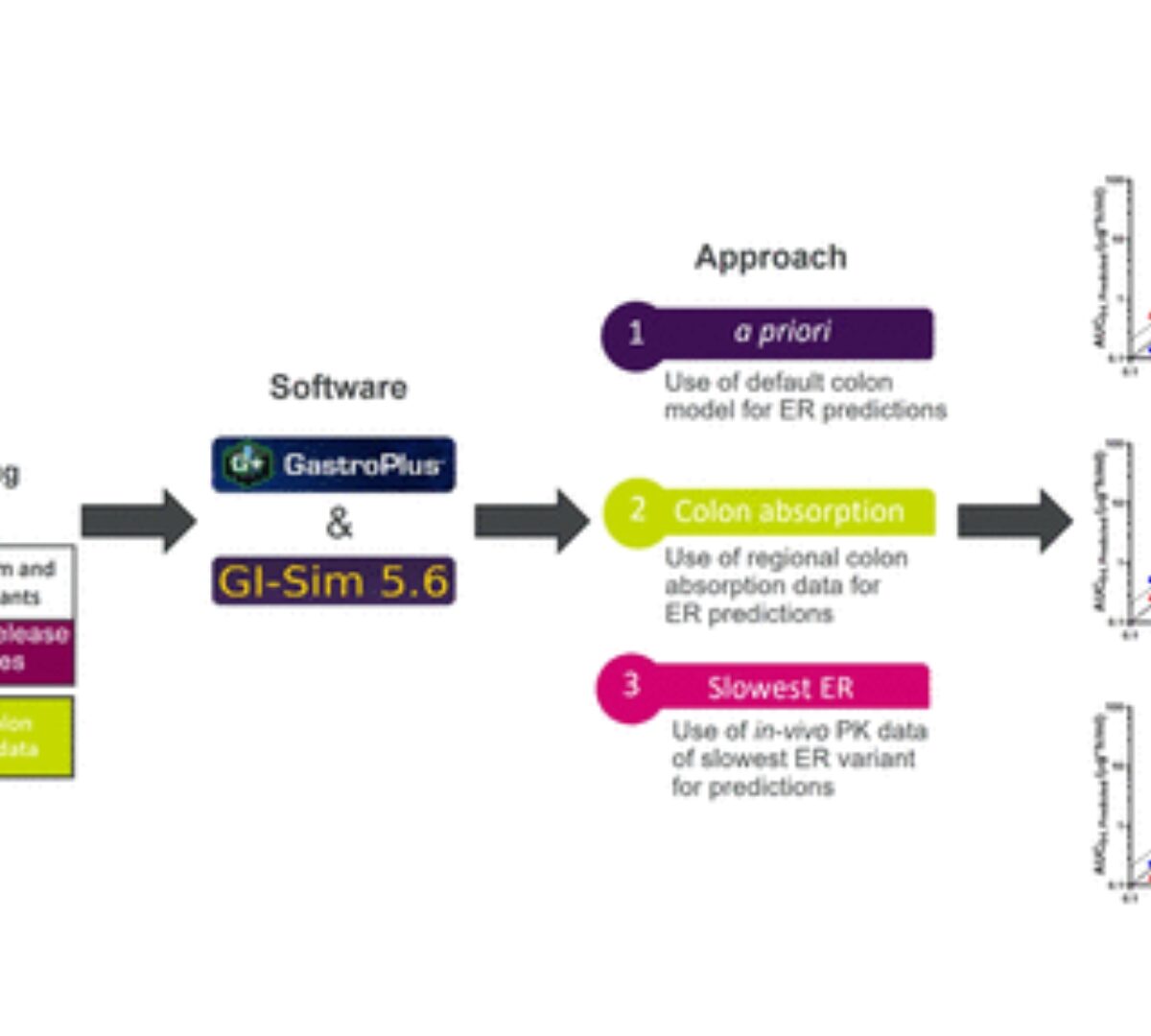
Approaches to Account for Colon Absorption in Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling of Extended-Release Drug Products
The rate and extent of colon absorption are important determinants of the in vivo performance of extended-release (ER) drug products.

ADME characterization and PBK model development of 3 highly protein-bound UV filters through topical application
Estimating human exposure in the safety assessment of chemicals is crucial. Physiologically based kinetic (PBK) models which combine information on exposure, physiology...
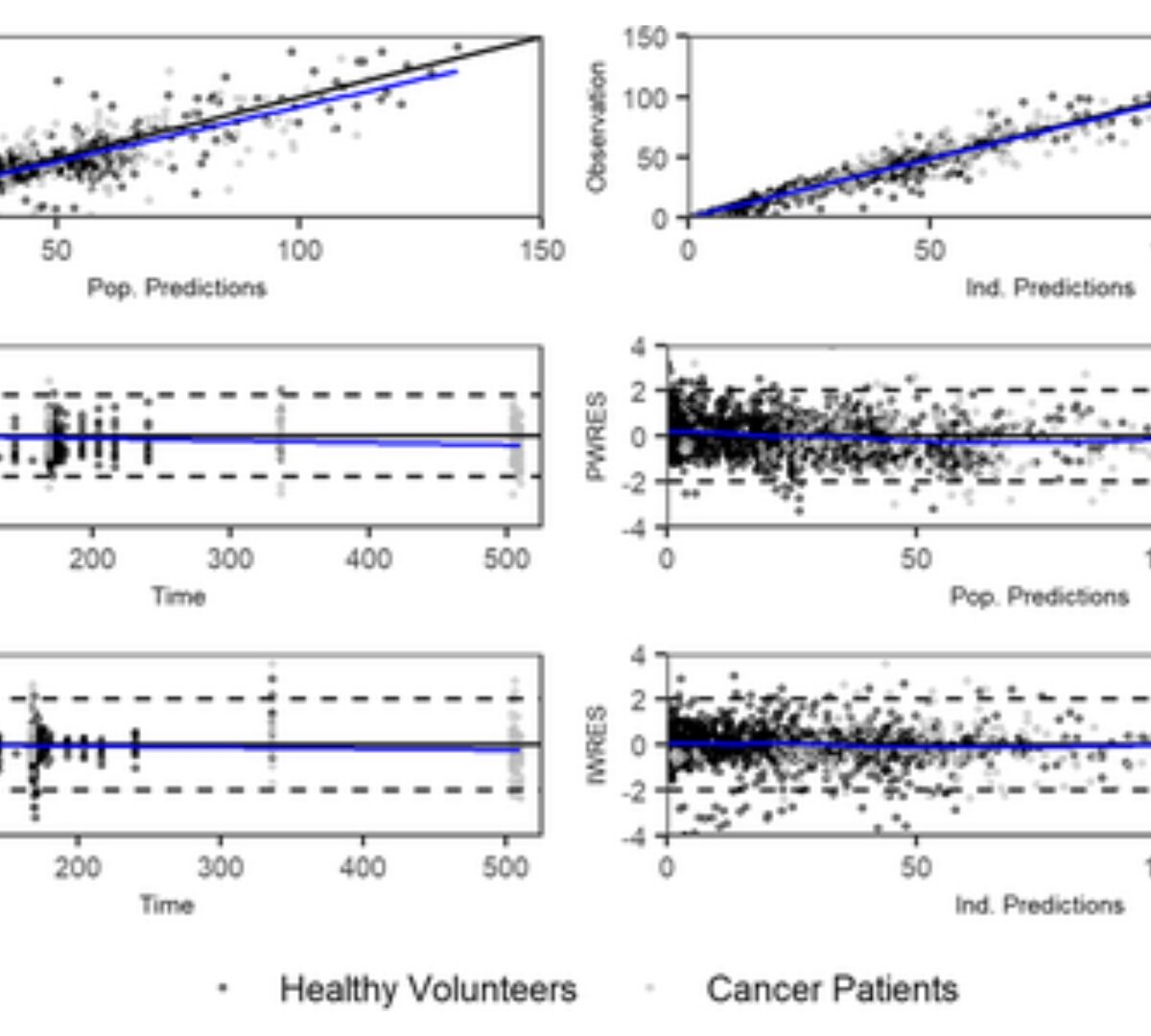
Bridging population pharmacokinetic and semimechanistic absorption modeling of APX3330
APX3330 ((2E)-2-[(4,5-dimethoxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-cyclohexadien-1-yl)methylene]-undecanoic acid), a selective inhibitor of APE1/Ref-1, has been investigated in treatment of hepatitis, cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and macular edema.
In vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetic characterization, chiral conversion and PBPK scaling towards human PK simulation of S-MRI-1867, a drug candidate for Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome pulmonary fibrosis
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder that affects lysosome-related organelles, often leading to fatal pulmonary fibrosis (PF)

Predicting absolute aqueous solubility by applying a machine learning model for an artificially liquid-state as proxy for the solid-state
In this study, we use machine learning algorithms with QM-derived COSMO-RS descriptors, along with Morgan fingerprints, to predict the absolute solubility of drug-like compounds.
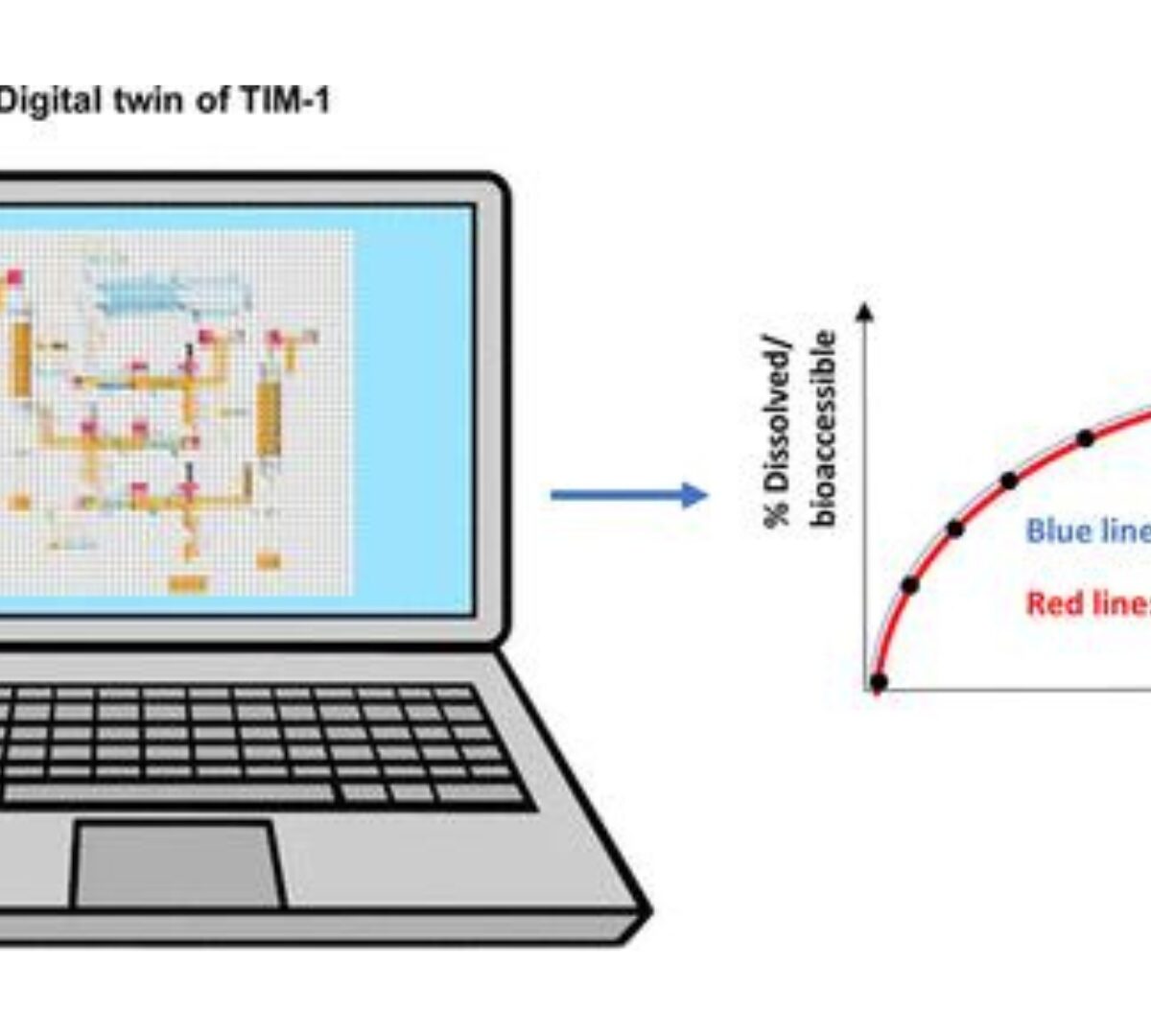
Digitalizing the TIM-1 Model Using Computational Approaches─Part Two: Digital TIM-1 Model in GastroPlus
A TIM-1 model is an in vitro gastrointestinal (GI) simulator considering crucial physiological parameters that will affect the in vivo drug release process.
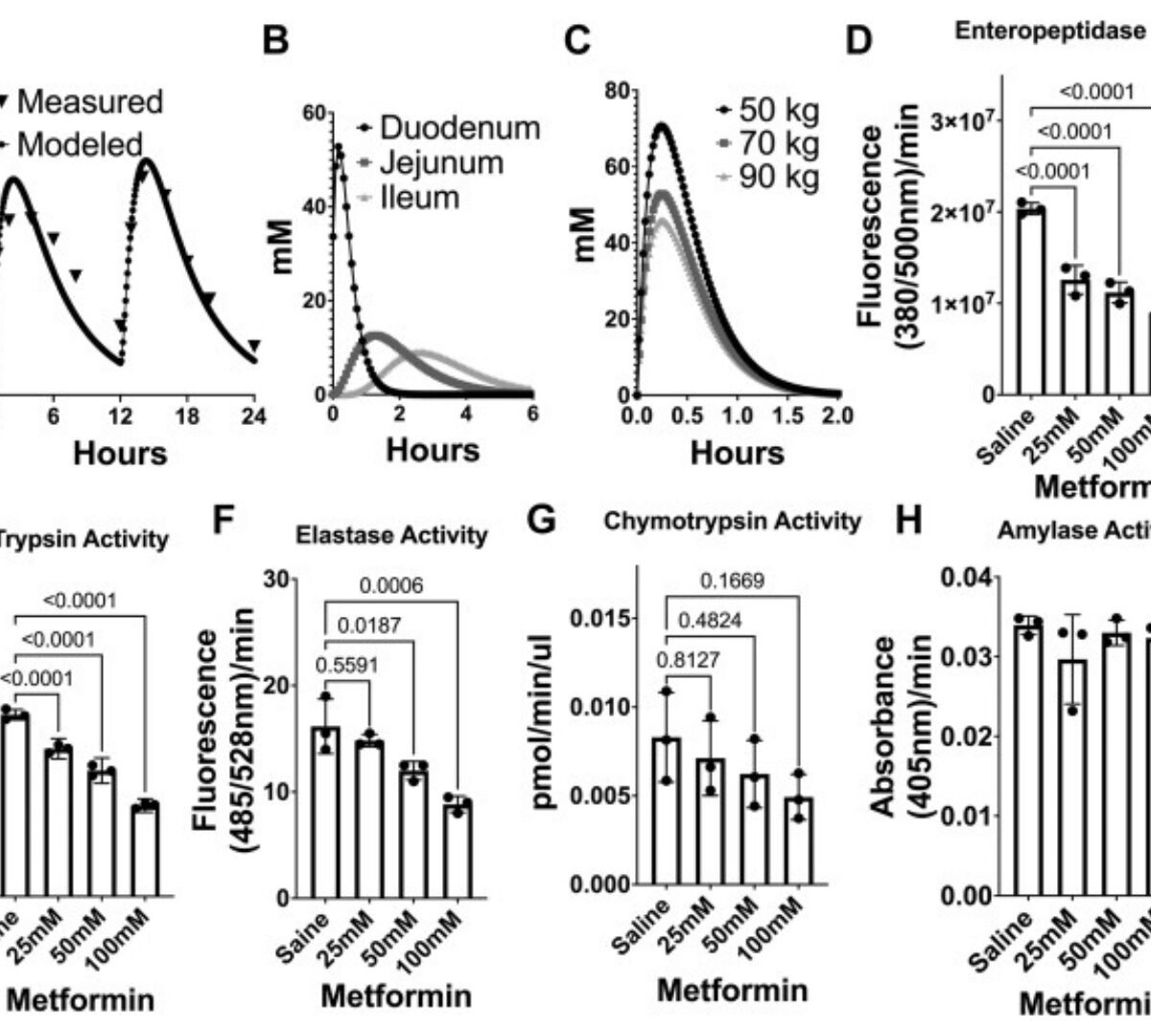
Metformin inhibits digestive proteases and impairs protein digestion in mice
Metformin is among the most prescribed medications worldwide and the first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes.
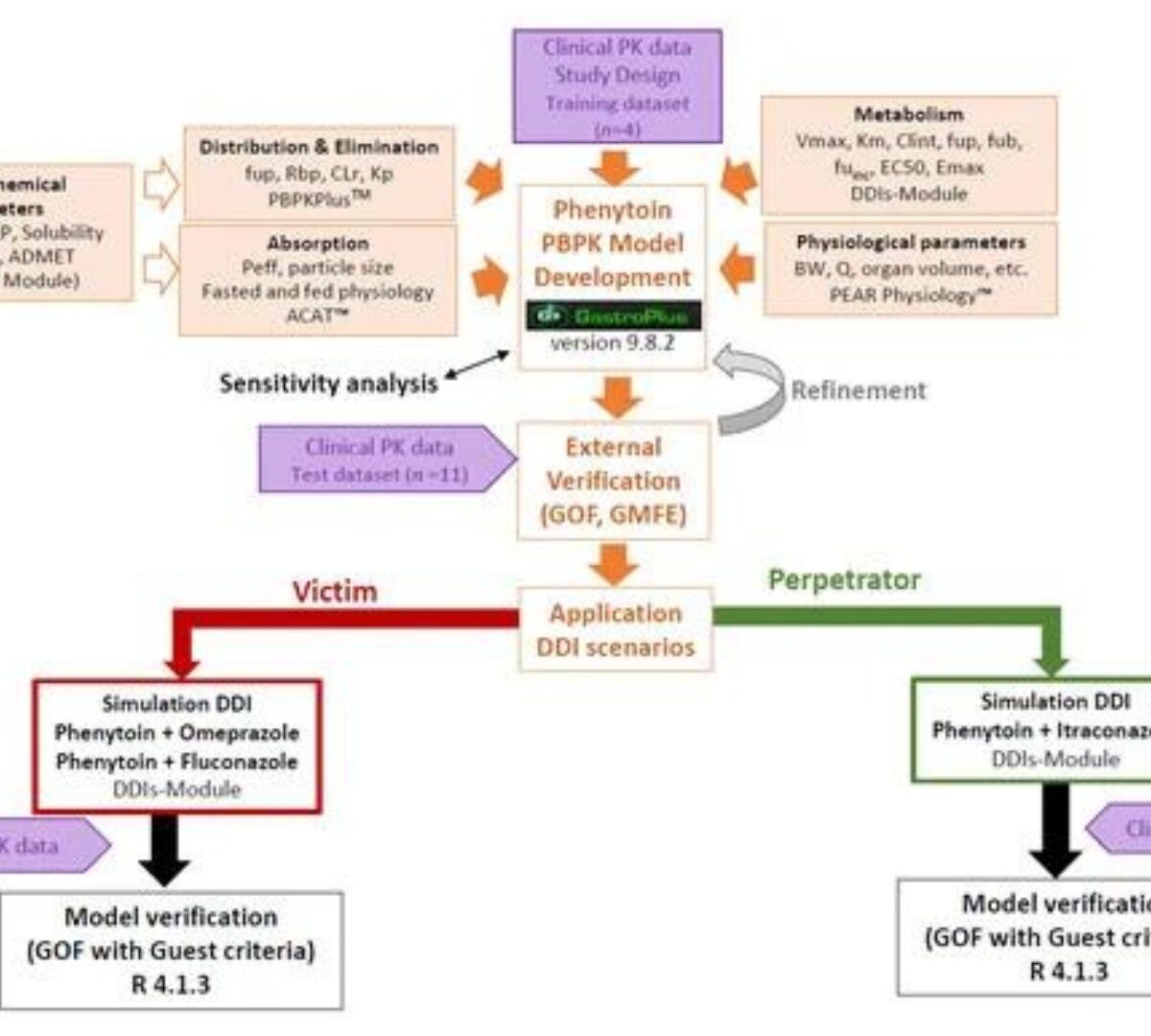
Comprehensive Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model to Assess Drug–Drug Interactions of Phenytoin
Regulatory agencies worldwide expect that clinical pharmacokinetic drug–drug interactions (DDIs) between an investigational new drug...
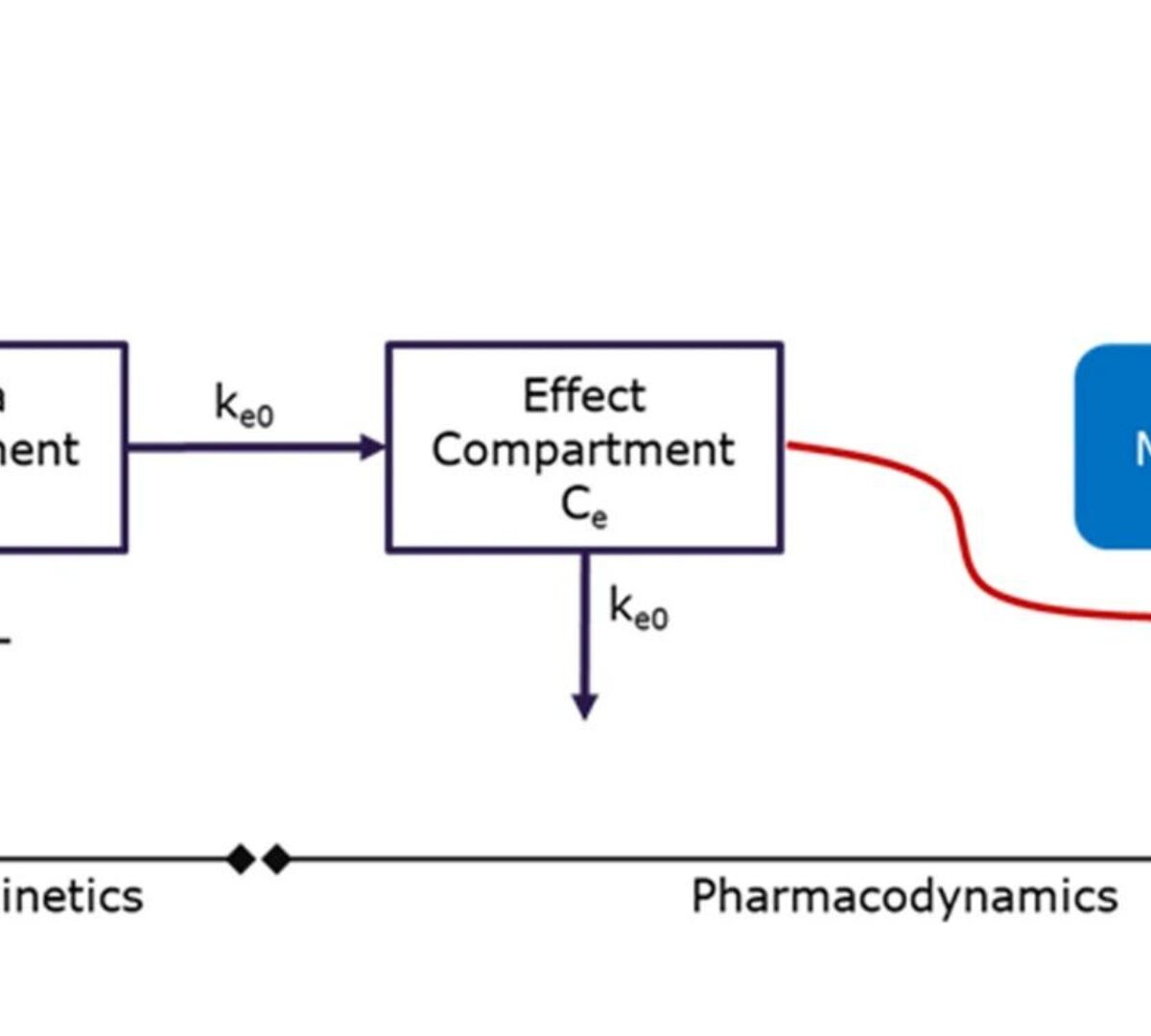
Preclinical Pharmacokinetics and Translational Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modeling of M8891, a Potent and Reversible Inhibitor of Methionine Aminopeptidase 2
M8891 is a selective and reversible inhibitor of methionine aminopeptidase 2 (MetAP2).

Pharmacokinetics of the novel 5-HT4 receptor agonist, DA-6886, in dogs
The pharmacokinetics of a new 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 agonist, DA-6886, intended for the treatment of constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome...
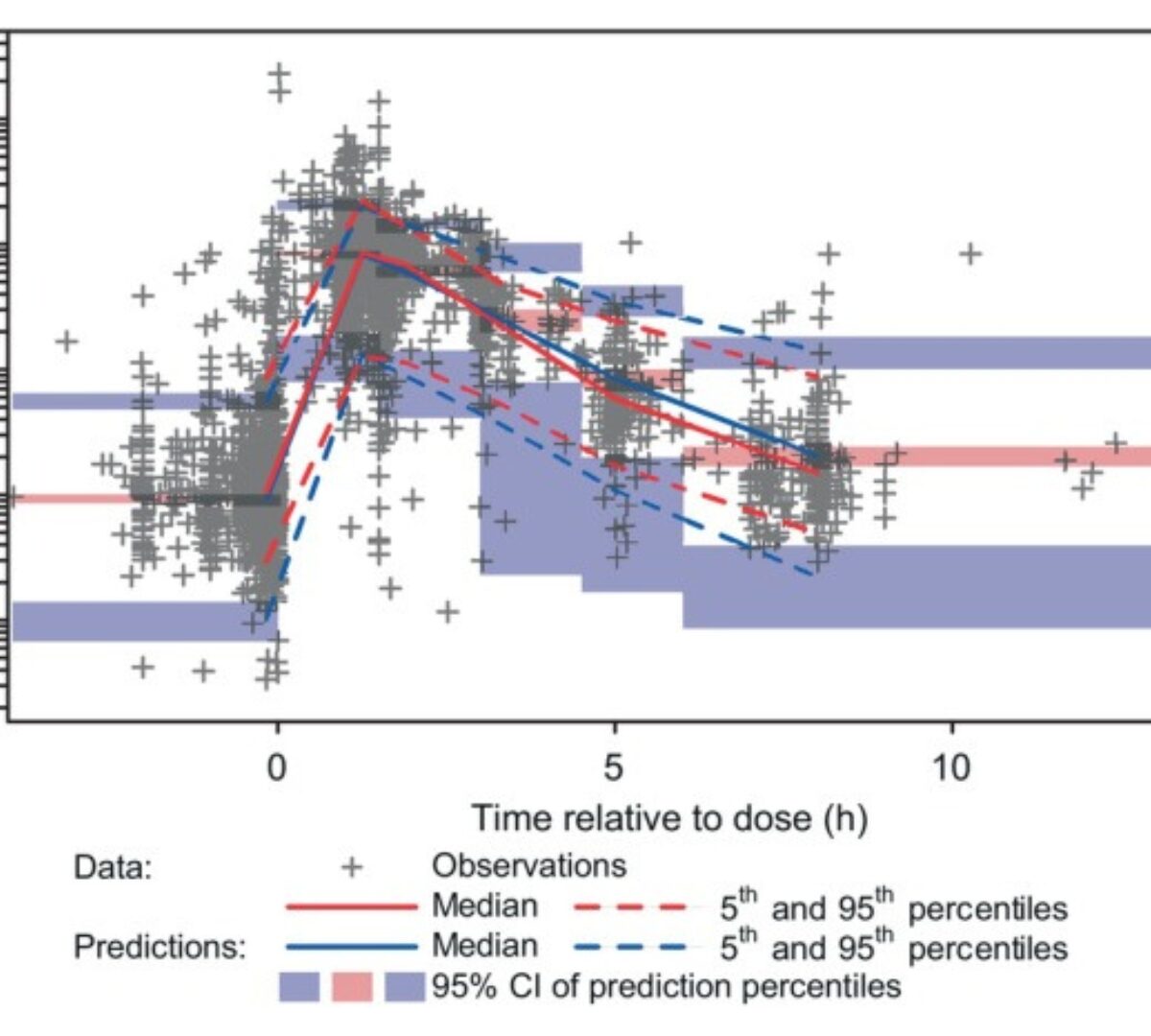
Population Pharmacokinetics of Molnupiravir in Adults With COVID-19: Lack of Clinically Important Exposure Variation Across Individuals
Effective antiviral treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are needed to reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, particularly...
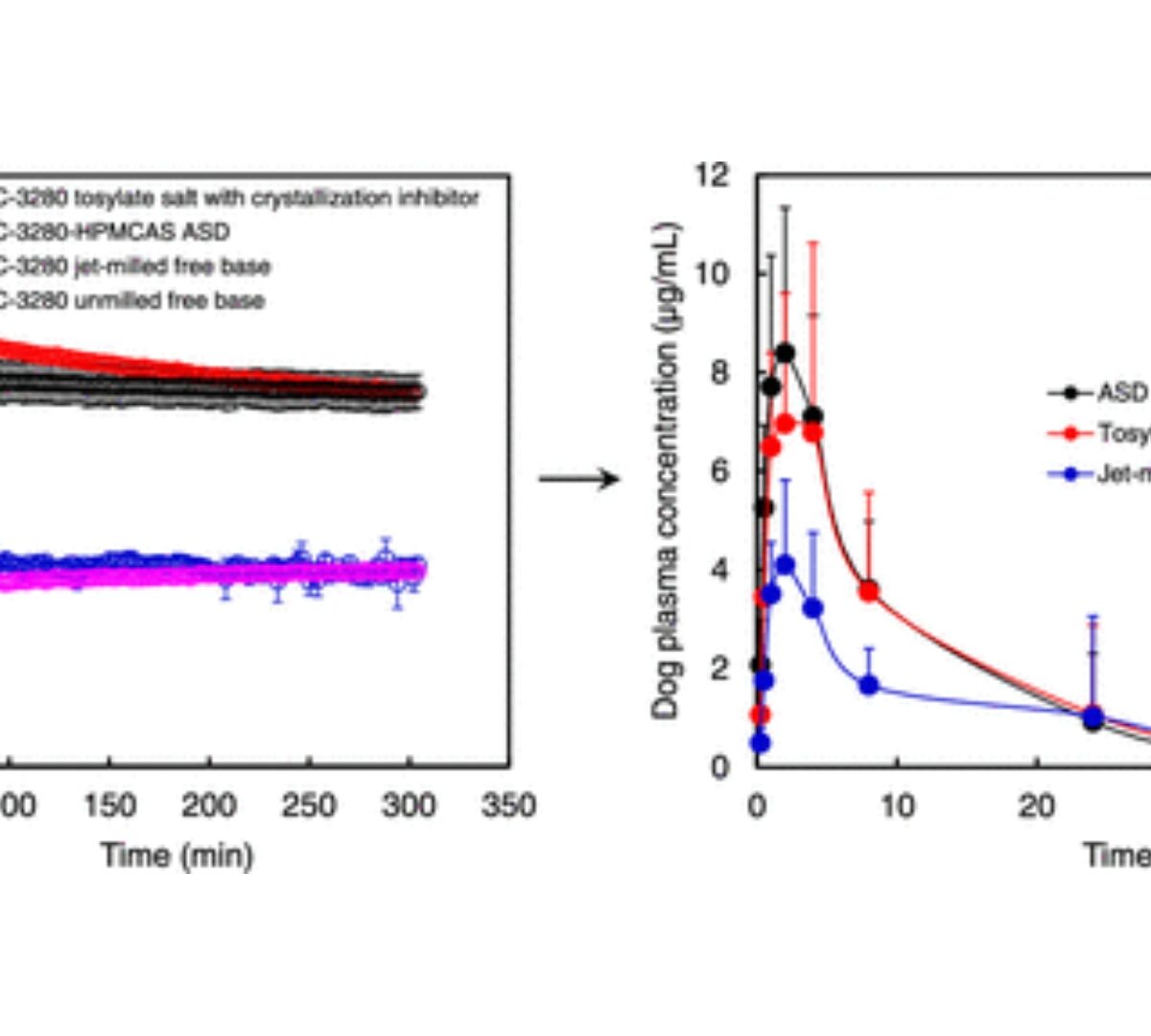
Comparative Evaluation of Particle Size Reduction, Salt Formation, and Amorphous Formulation on the Biopharmaceutical Performance of a Weak Base Drug Candidate
Various approaches have been developed to enhance the solubility or dissolution rate for the delivery of poorly water-soluble molecules.
Virtual Docking, design and in silico ADMET profiling of novel Rho-associated protein kinases-1 (ROCK1) inhibitors
Overexpression of Rho-associated protein kinases has been associated with various diseases, including tumors.
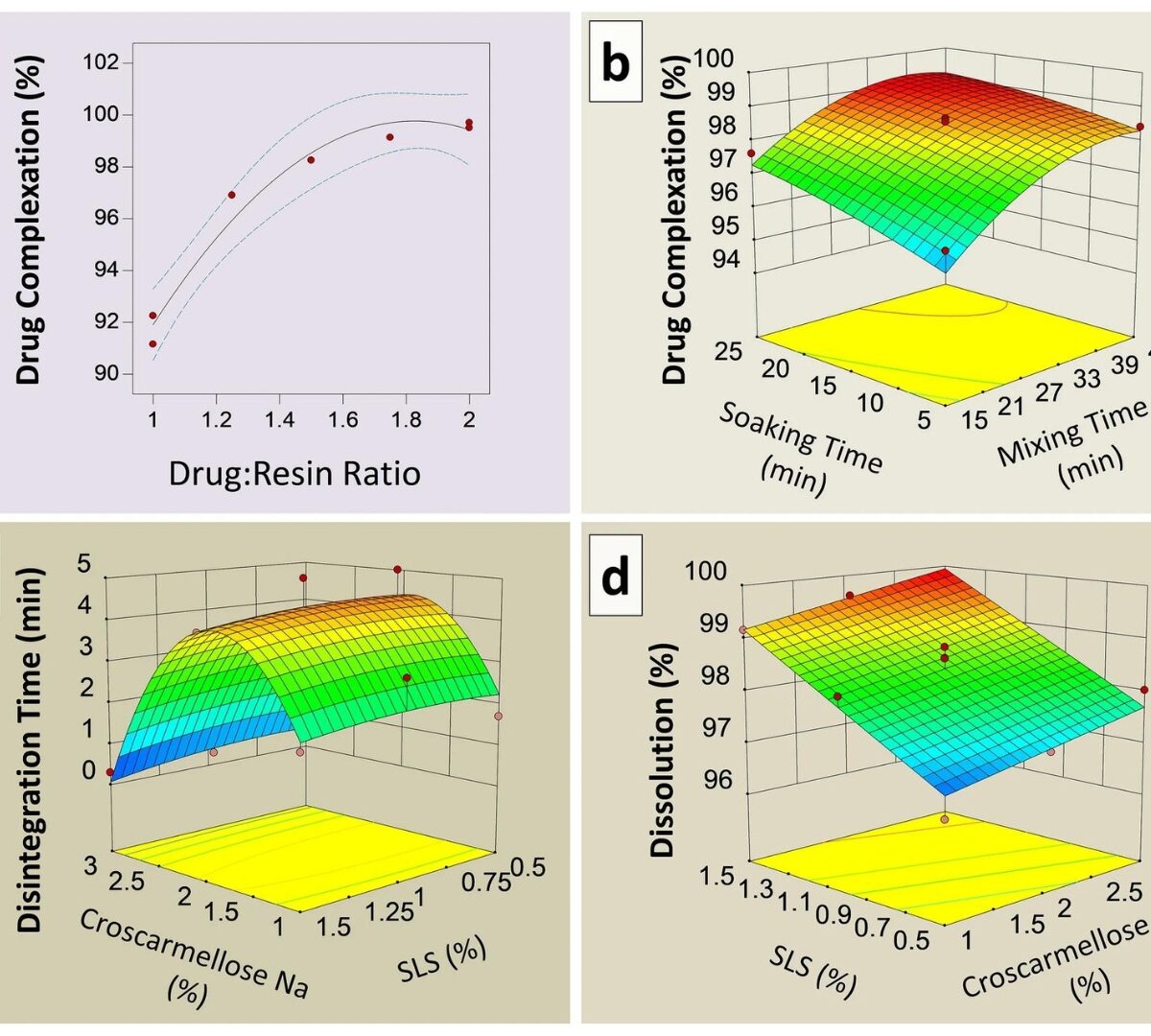
Formulation development, in vivo bioequivalence and pediatric PBPK modeling studies of taste-masked ciprofloxacin chewable tablets
A taste-masked chewable tablet of ciprofloxacin using ion exchange resin Kyron T-134 for enhancing compliance for the paediatric population was developed.

Combined data-driven and mechanism-based approaches for human-intestinal-absorption prediction in the early drug-discovery stage
It is important to precisely predict the intestinal absorption ratio (Fa) at an early stage in the discovery of orally available drugs because it directly influences drug efficacy.