Risk assessment related to bioequivalence study outcome is critical for effective planning from the early stage of drug product development.

Modeling time‐delayed concentration‐QT effects with ACT ‐1014‐6470, a novel oral complement factor 5a receptor 1 (C5a 1 receptor) antagonist
The novel oral complement factor 5a receptor 1 antagonist ACT- 1014- 6470 was well tolerated in single- and multiple- ascending dose studies, including 24 h Holter electro-cardiogram (ECG) recordings evaluating its cardiodynamics based on data from singledoses of 30– 200 mg and twice- daily (b.i.d.) dosing of 30– 120 mg for 4.5 days.

Gastroplus and HSPiP Oriented Predictive Parameters as the Basis of Valproic Acid Loaded Mucoadhesive Cationic Nanoemulsion Gel for Improved Nose-To-Brain Delivery to Control Convulsion in Human
Oral and parenteral delivery of first-line anticonvulsant Valproic cid (VA) are associated with serious adverse effects, high hepatic metabolism, high clearance, and low bioavailability in brain.

Development of a 2D-QSAR Model for Tissue-to-Plasma Partition Coefficient Value with High Accuracy Using Machine Learning Method, Minimum Required Experimental Values, and Physicochemical Descriptors
The demand for physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model is increasing currently.
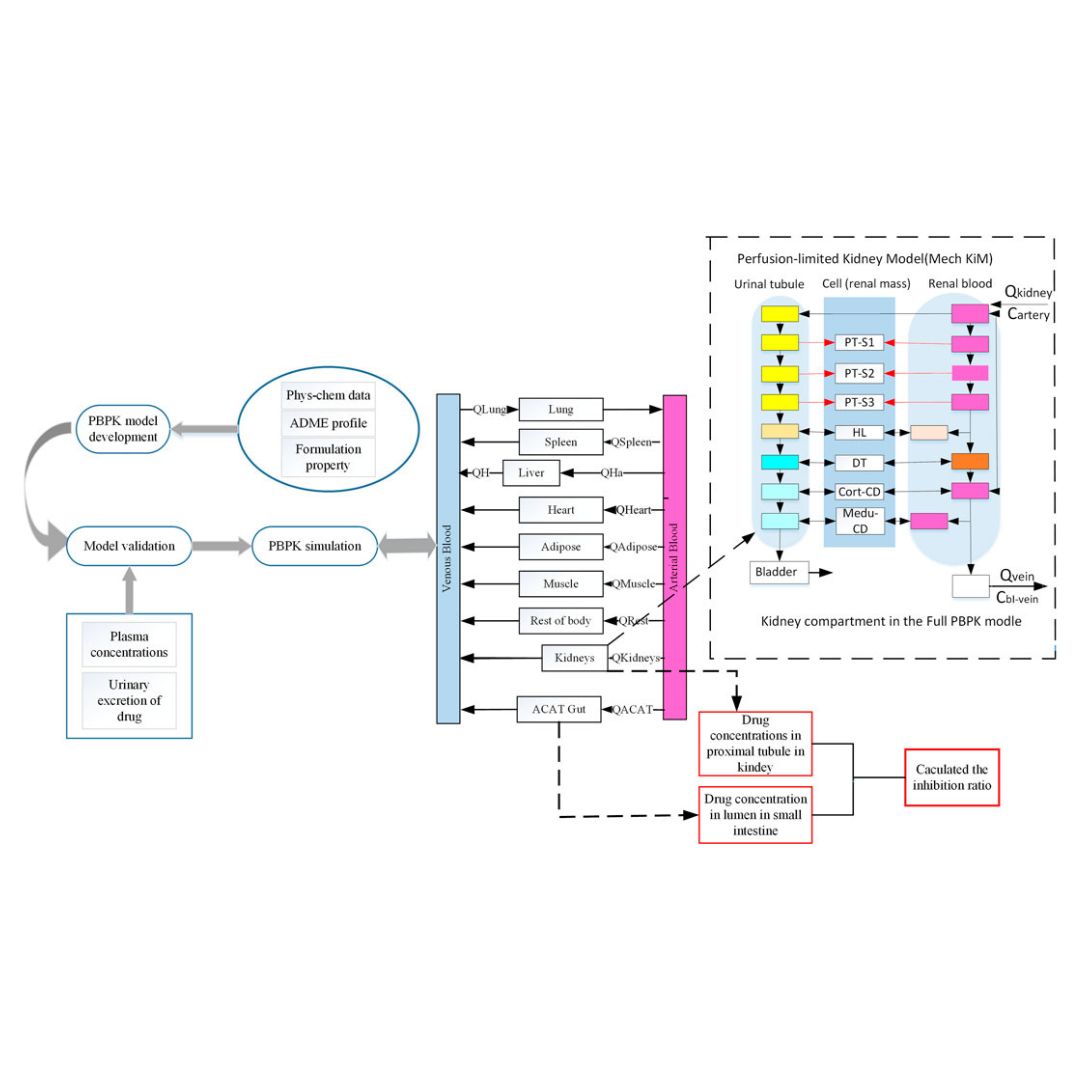
Mechanistic evaluation of the inhibitory effect of four SGLT-2 inhibitors on SGLT 1 and SGLT 2 using physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling approaches
Sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT 2, gliflozins) inhibitors are potent orally active drugs approved for managing type 2 diabetes.
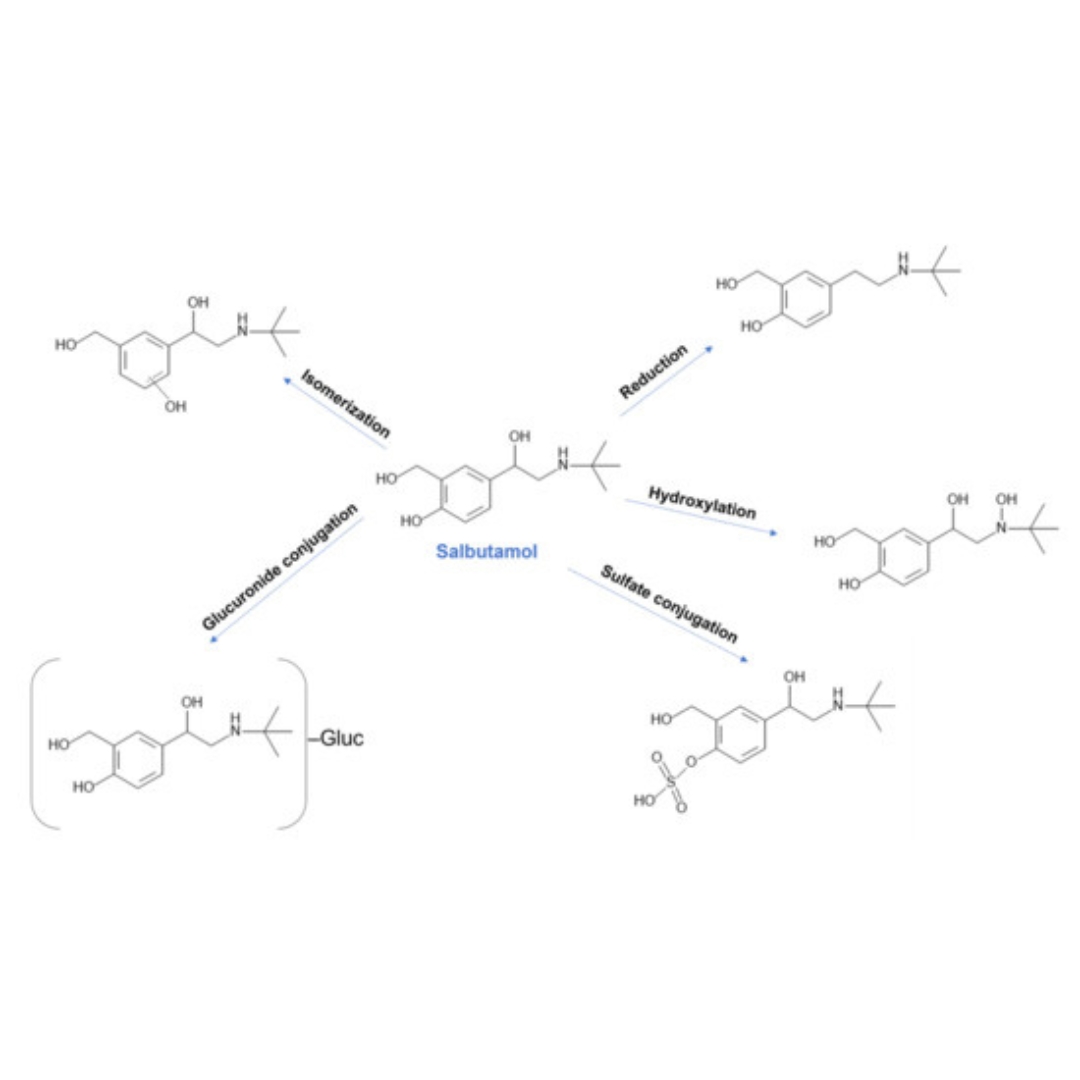
Prediction of CYP-Mediated Drug Interaction Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling: A Case Study of Salbutamol and Fluvoxamine
Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) represent a significant concern in healthcare, particularly for patients undergoing polytherapy.
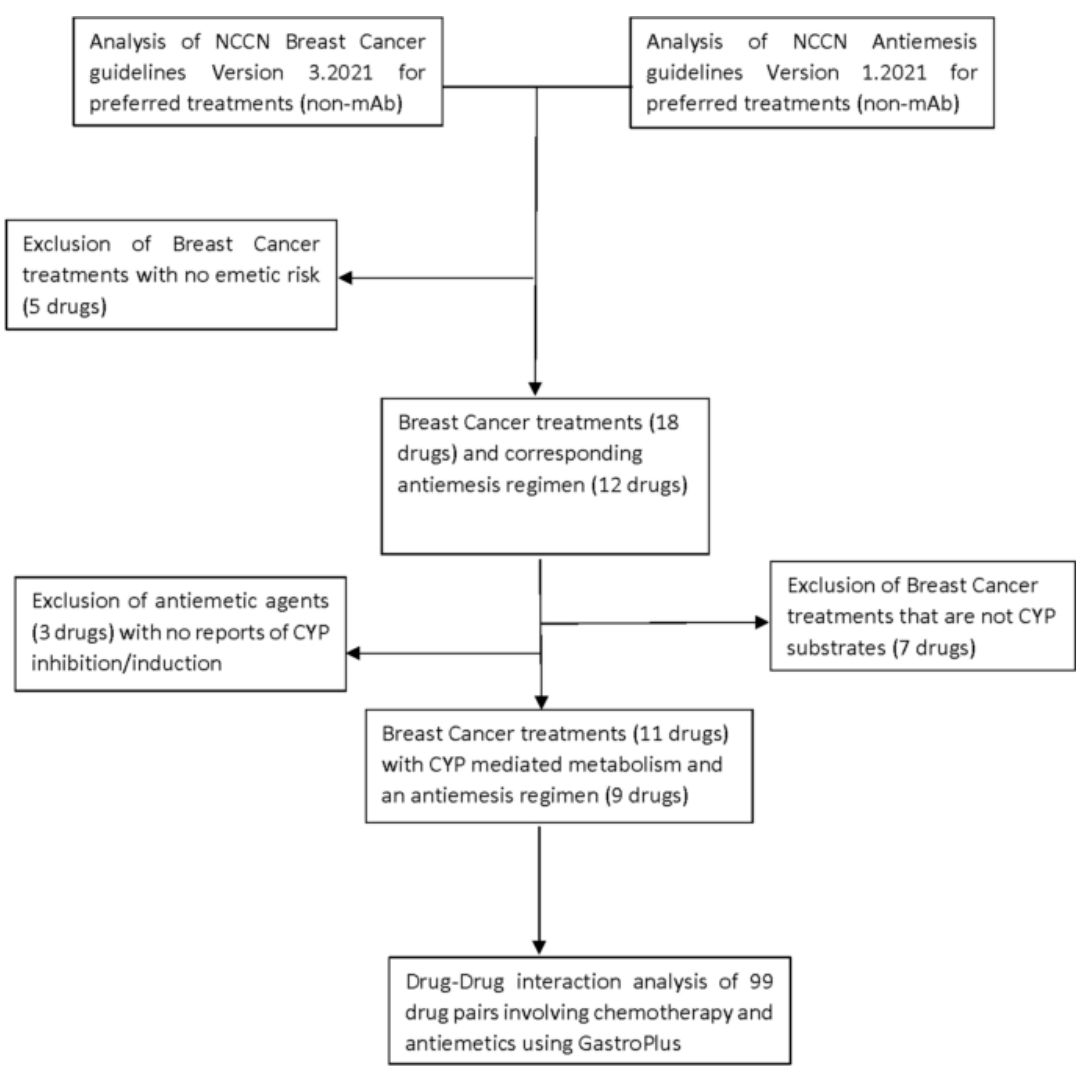
Simulation of drug-drug interactions between breast cancer chemotherapeutic agents and antiemetic drugs
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting are commonly experienced side effects in breast cancer (BCa) patients.
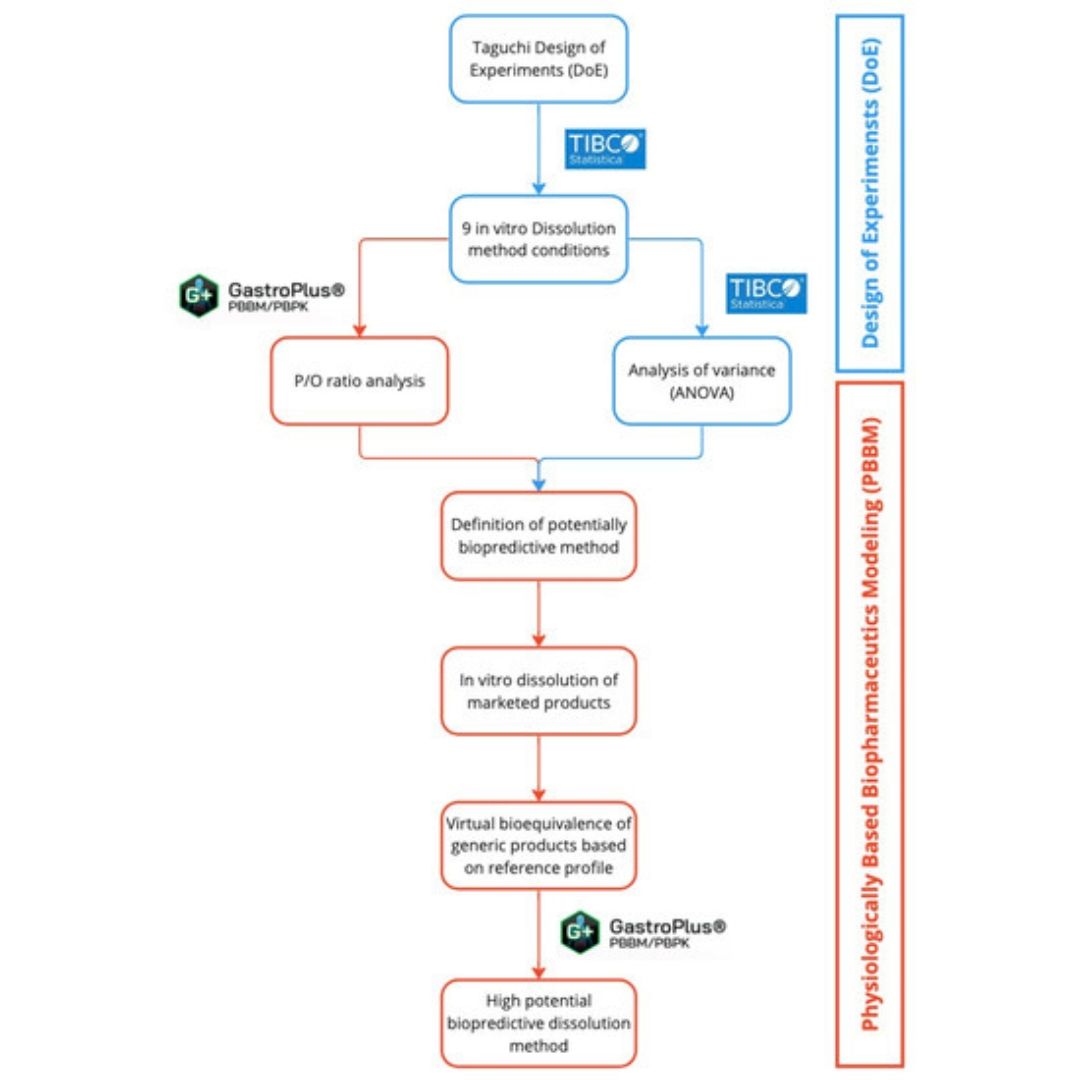
Development of Biopredictive Dissolution Method for Extended-Release Desvenlafaxine Tablets
This study aimed to develop a biopredictive dissolution method for desvenlafaxine ER tablets using design of experiments (DoE)...
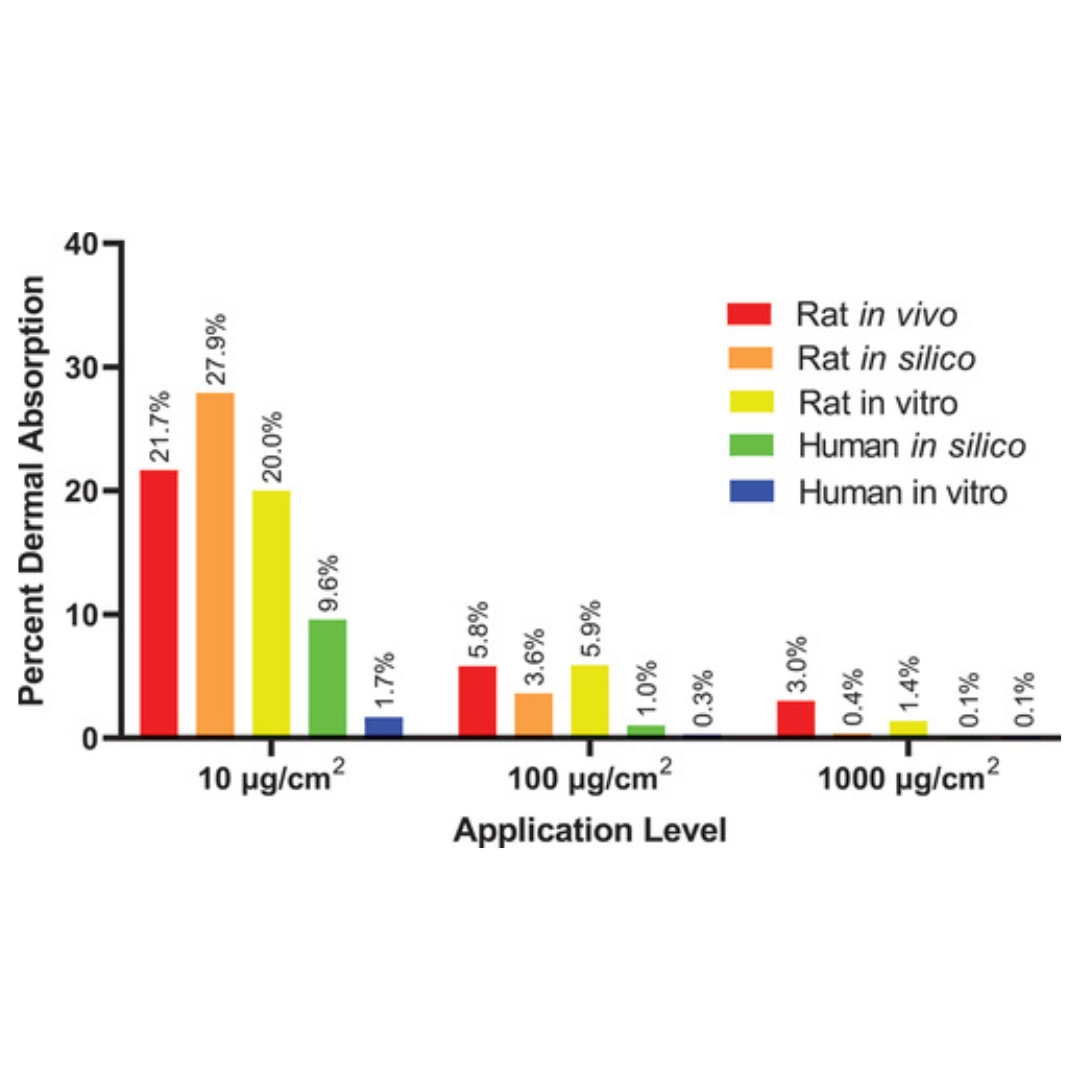
Estimated Dermal Penetration of Tetrachlorvinphos (TCVP) in Humans Based on In Silico Modeling and In Vitro and In Vivo Data
Tetrachlorvinphos (TCVP) is the pesticidal active ingredient in some collars for dogs and cats.
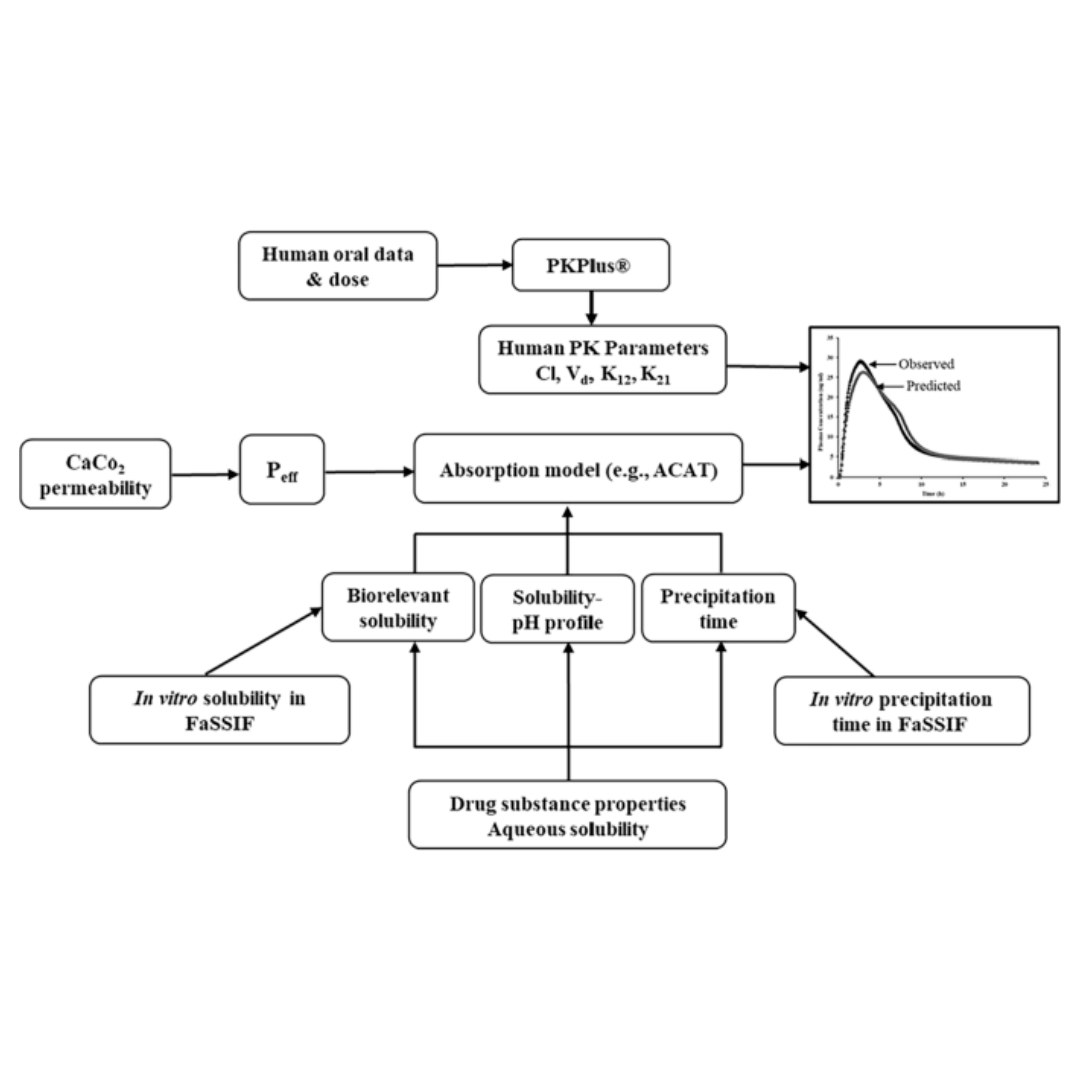
A Combined In-Vitro and GastroPlus® Modeling to Study the Effect of Intestinal Precipitation on Cinnarizine Plasma Profile in a Fasted State
Poorly water-soluble weak base molecules such as cinnarizine often exhibit pH-dependent solubility within the gastrointestinal tract.
Subtractive sequence-mediated therapeutic targets from the conserved gene clusters of Campylobacter hyointestinalis and computational inhibition assessment
Campylobacter hyointestinalis is a causative agent of enteritis, proctitis, human gastroenteritis, and diarrhea.
Pan-genome mediated therapeutic target mining in Kingella kingae and inhibition assessment using traditional Chinese medicinal compounds: an informatics approach
Kingella kingae causes bacteremia, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, meningitis, spondylodiscitis, and lower respiratory tract infections in pediatric patients
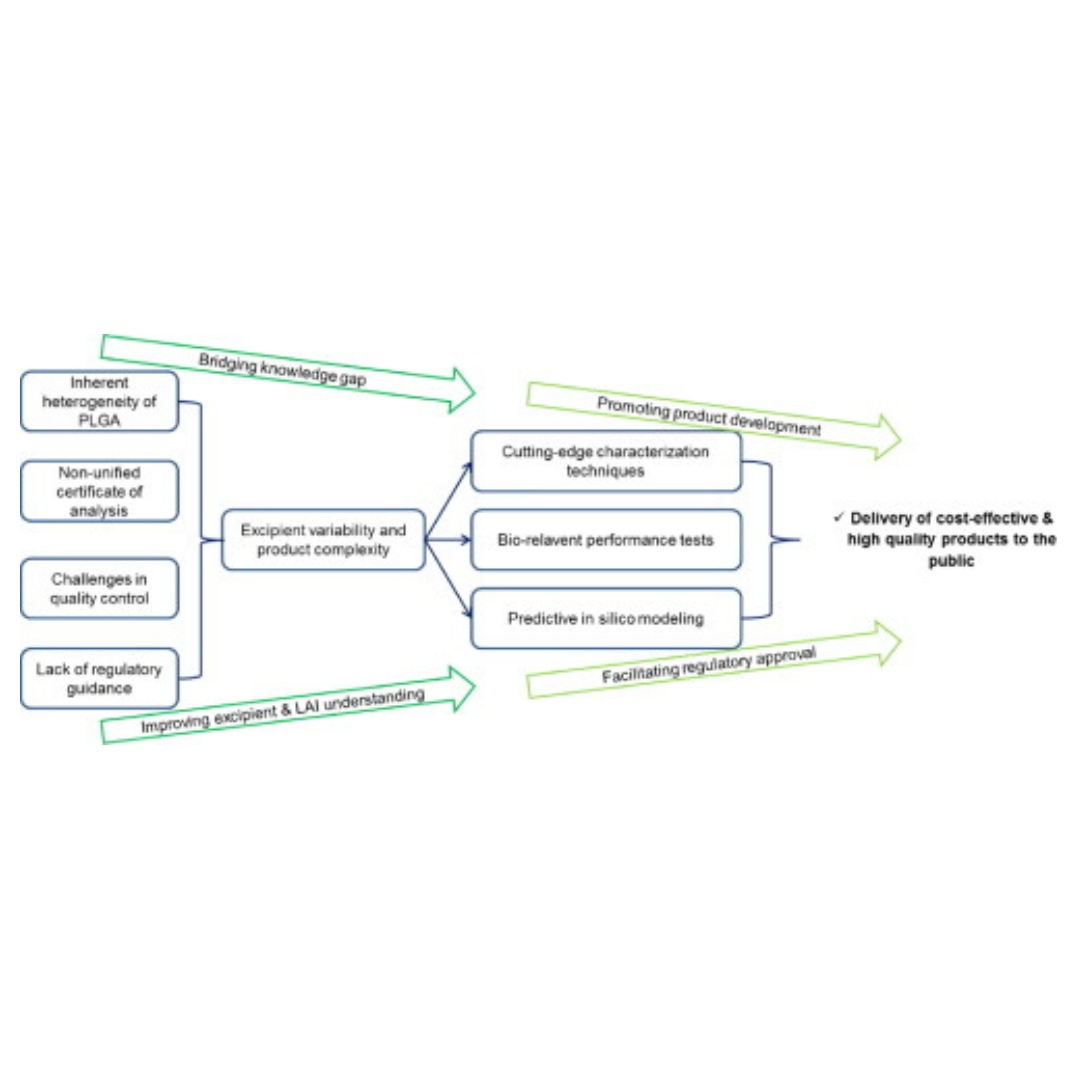
Long-acting PLGA microspheres: Advances in excipient and product analysis toward improved product understanding
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres are a sustained-release drug delivery system with several

Rapid emergence of potentially transmissible SARS-CoV-2 with resistance to combination monoclonal antibody therapy
Prolonged COVID-19 may generate new viral variants.
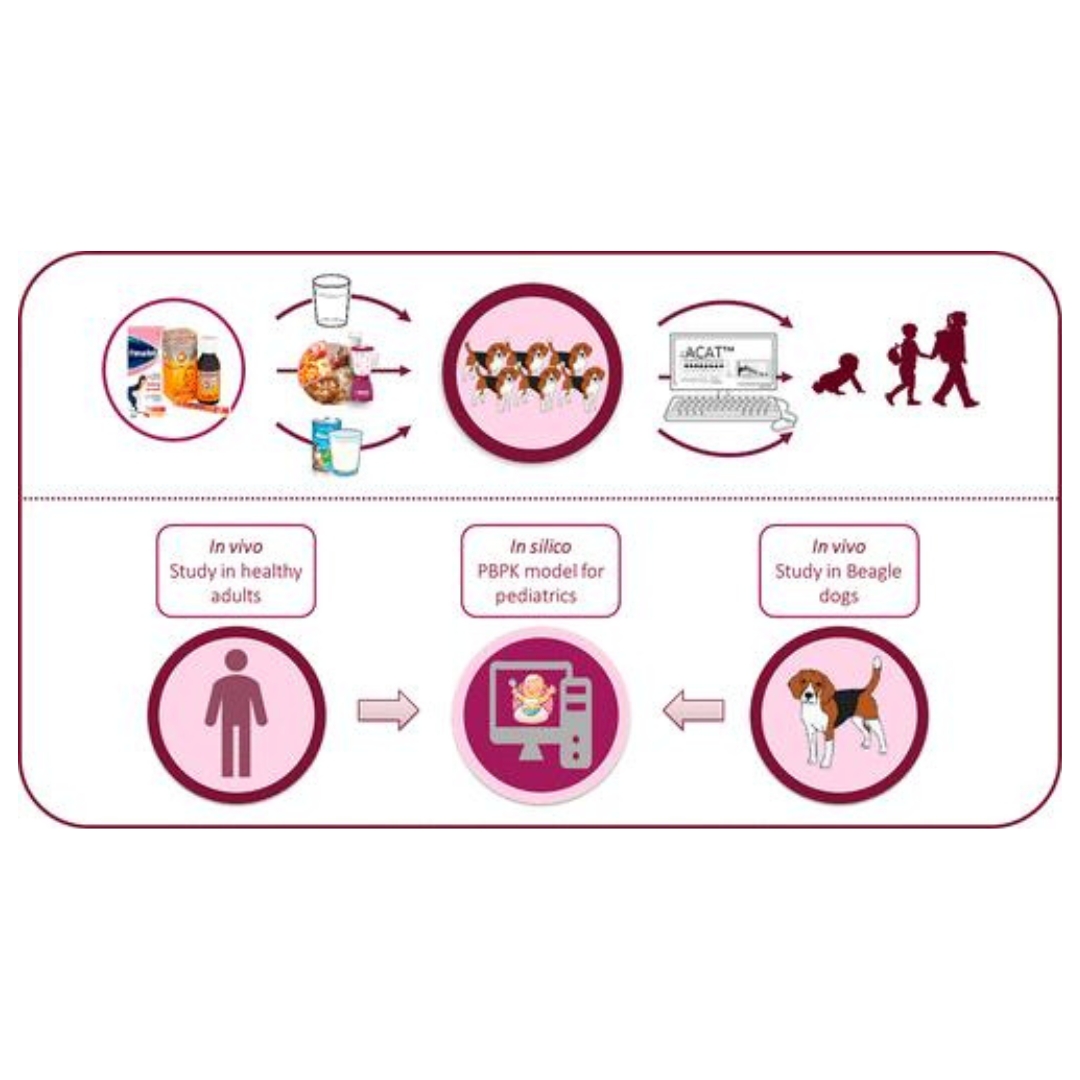
Usefulness of the Beagle Model in the Evaluation of Paracetamol and Ibuprofen Exposure after Oral Administration to Pediatric Populations: An Exploratory Study
The present study aimed to explore the usefulness of beagle dogs in combination with physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling...
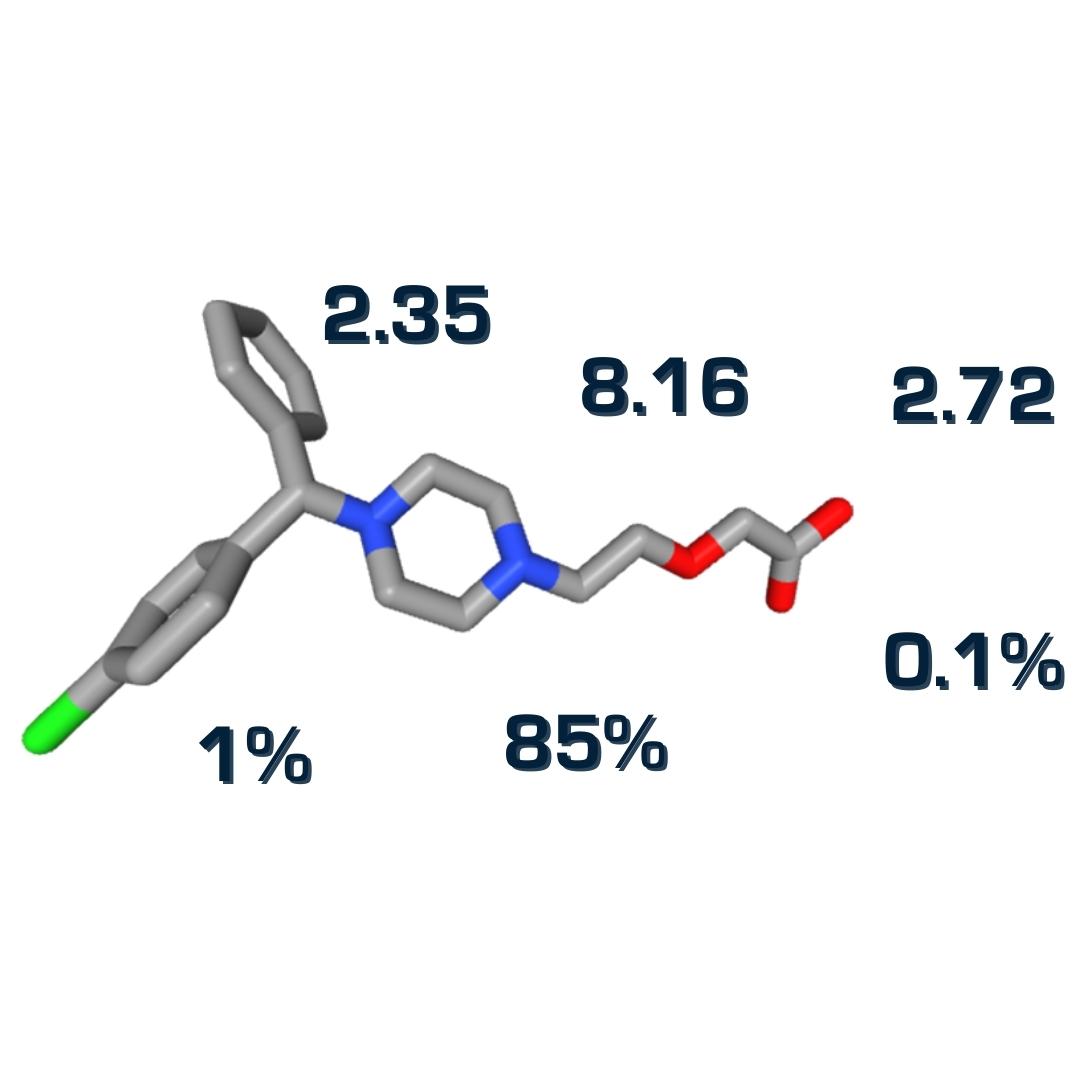
pK50─A Rigorous Indicator of Individual Functional Group Acidity/Basicity in Multiprotic Compounds
In this work, we show that the apparent pKa measured by standard titration experiments is an insufficient measure of acidity...
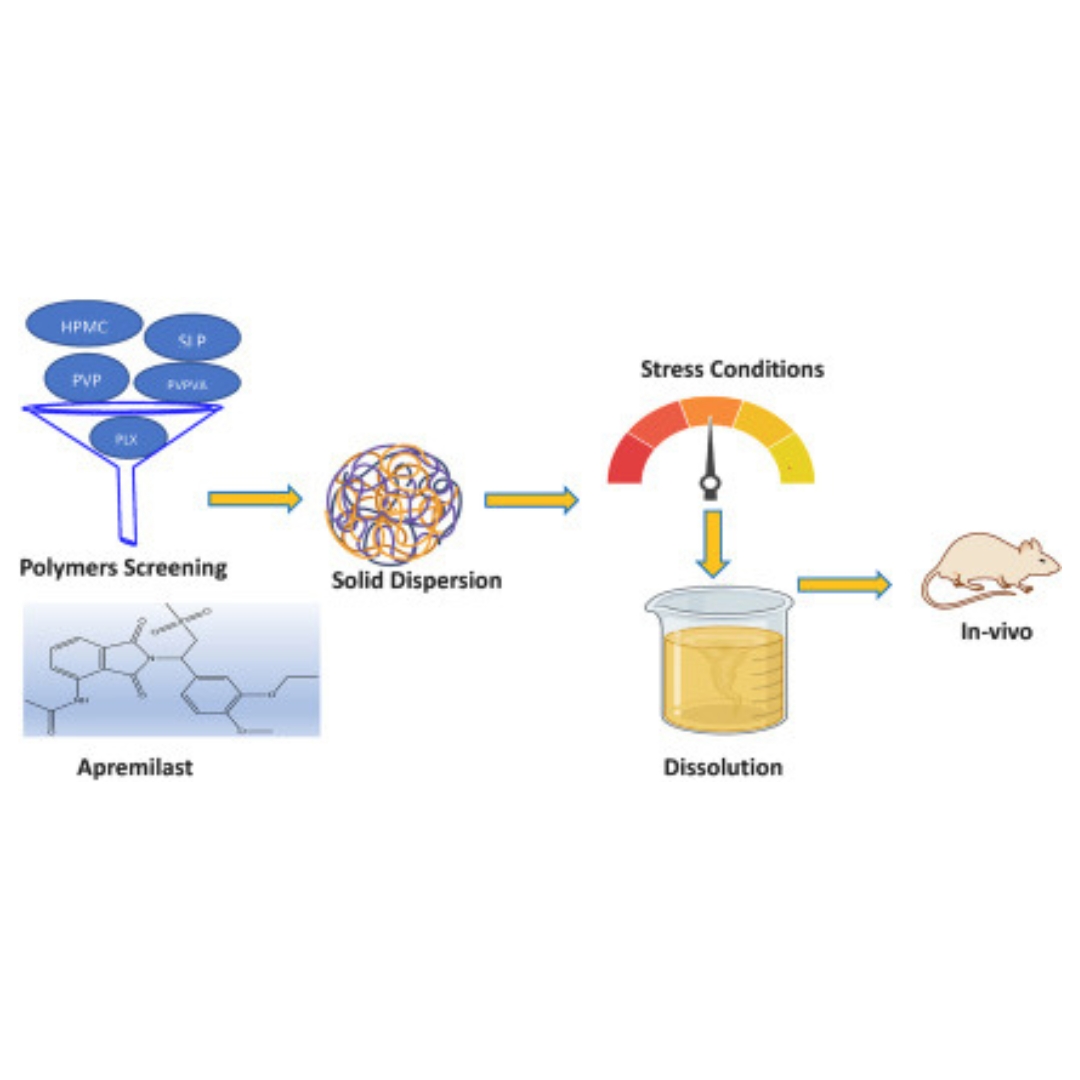
Investigating the influence of the type of polymer on sustaining the supersaturation from amorphous solid dispersions of Apremilast and its pharmacokinetics
Apremilast, a BCS class IV drug, has minimal solubility in aqueous medium which results in poor bioavailability.

Next generation risk assessment of human exposure to estrogens using safe comparator compound values based on in vitro bioactivity assays
In next generation risk assessment (NGRA), the Dietary Comparator Ratio (DCR) can be used to assess the safety of chemical exposures to humans in a 3R compliant approach.
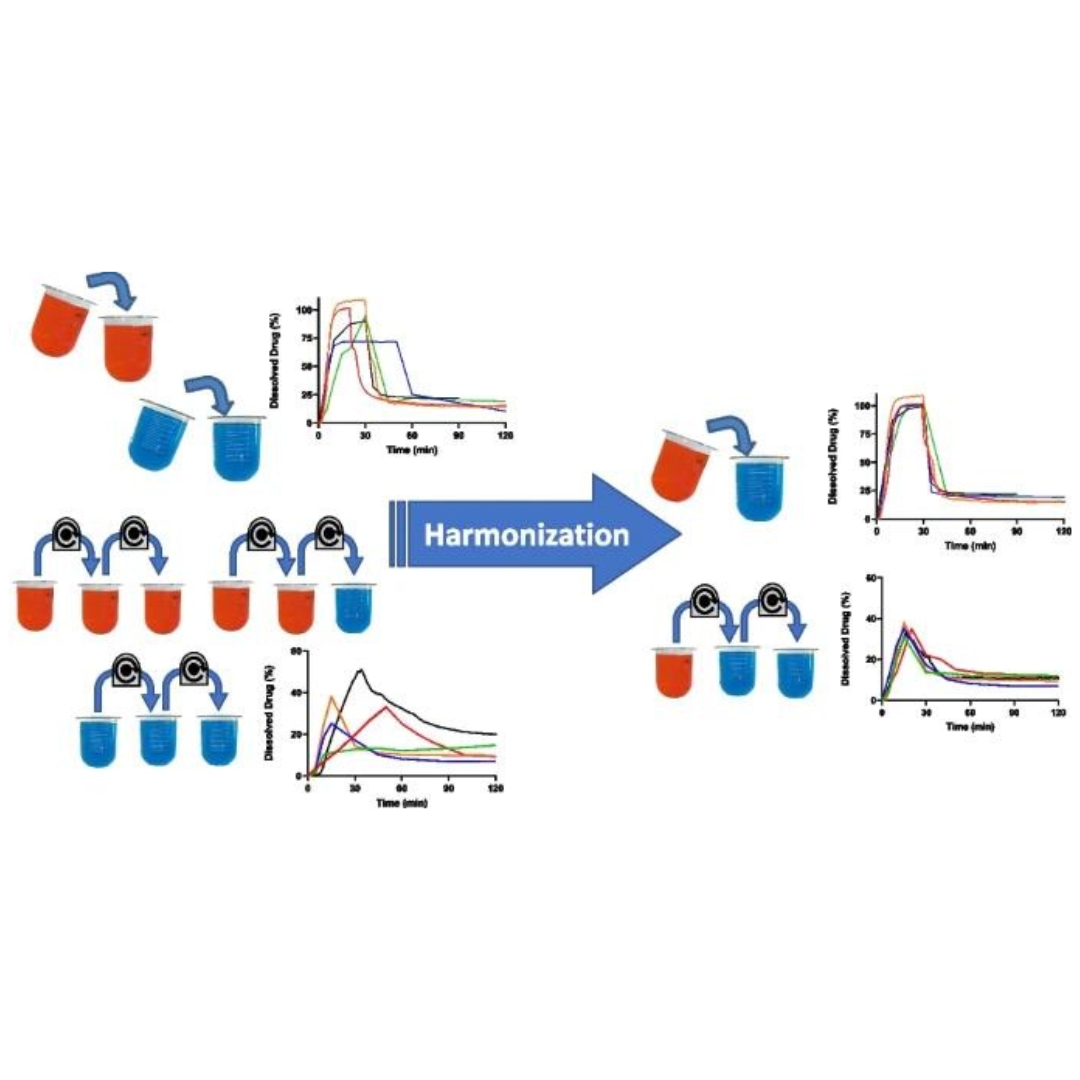
Harmonizing Biopredictive Methodologies Through the Product Quality Research Institute (PQRI) Part I: Biopredictive Dissolution of Ibuprofen and Dipyridamole Tablets
Assessing in vivo performance to inform formulation selection and development decisions is an important aspect of drug development.
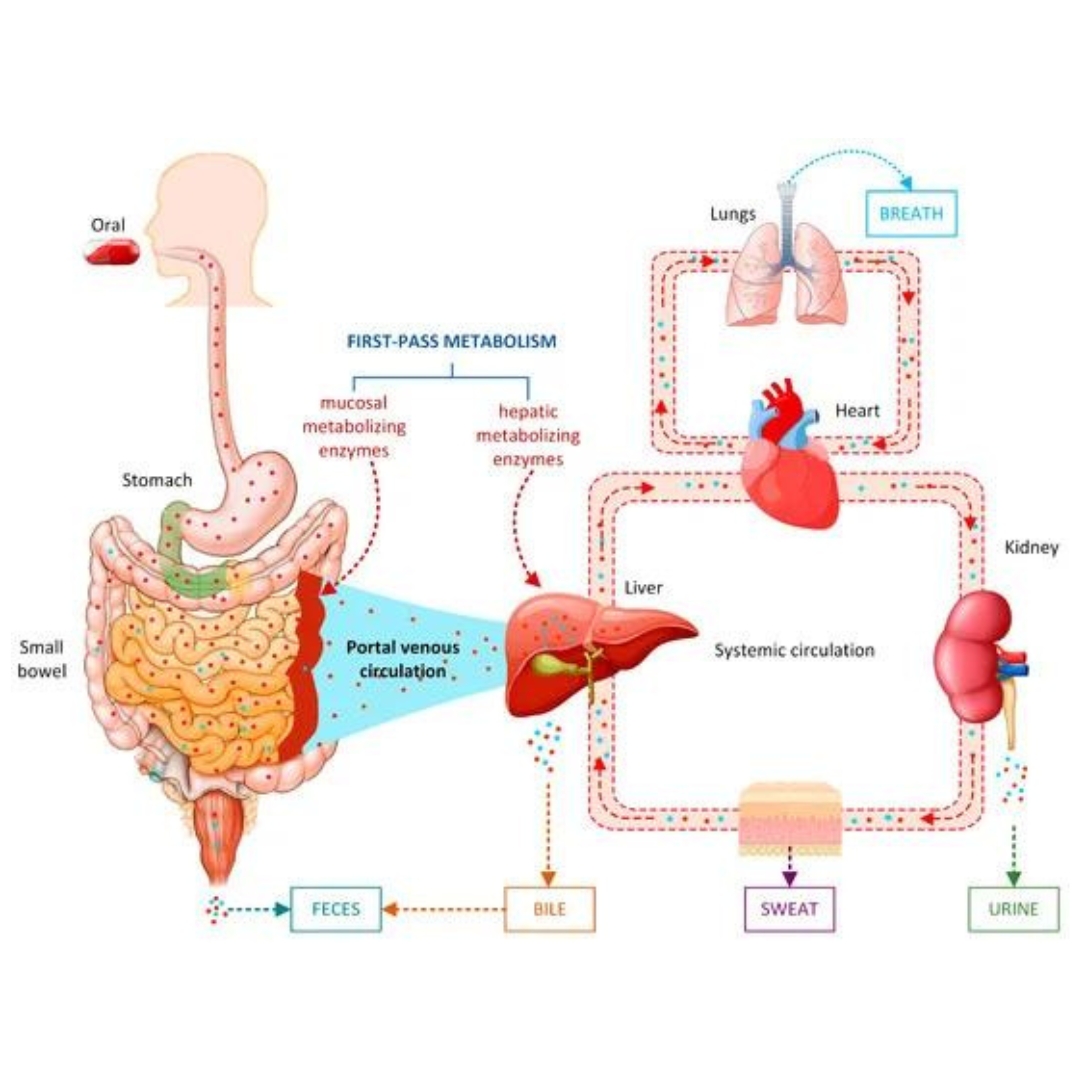
Artificial Intelligence in Drug Metabolism and Excretion Prediction: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Drug metabolism and excretion play crucial roles in determining the efficacy and safety of drug candidates, and predicting these processes is an essential part of drug discovery and development.
