The NAFLDsym modeling software is a mechanistic, mathematical model of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which can be used to predict efficacy for treatment modalities developed for MASLD and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), formerly known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NAFLDsym has been utilized to evaluate a number of compounds from several large pharmaceutical companies, supporting clinical trial design optimization and clinical development decision making.

-
Examples of NAFLDsym use within collaborative projects
We apply the NAFLDsym modeling software in proprietary services projects by performing simulations of compounds to evaluate and model their efficacy and other effects on key characteristics related to MASLD (NAFLD). NAFLDsym is also available for in-house use through corporate software licensing.
Examples of NAFLDsym use within collaborative projects that have been presented publicly include:
- BFKB8488A (agonist anti-FGFR1/KLB bispecific antibody) analysis in collaboration with Genentech;
- Target analysis of AMP Kinase activation in collaboration with Pfizer;
- Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC) inhibition analysis in collaboration with Gilead;
- Virtual patient development in collaboration with BMS;
- Response to dietary intervention analysis in collaboration with Pfizer.
-
MASLD is a prevalent, worldwide disease with few available treatment options
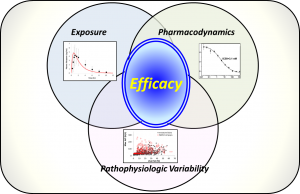
MASLD (NAFLD) is a prevalent, worldwide disease with few available treatment options. Accumulating lipids within the liver cause steatosis and impose lipotoxicity upon hepatocytes that can lead to declining liver function and ultimately liver transplant. Bringing effective treatments rapidly to market is paramount to improve patient health. QSP modeling has been demonstrated to accelerate clinical development, and we anticipate NAFLDsym will contribute to accelerating the clinical development of effective treatments for MASLD patients. NAFLDsym employs the QSP modeling practices of combining predictions of compound exposure with the pharmacodynamic characteristics of a compound and how they can produce efficacy across a range of patients with pathophysiologic variability.
-
Leverage our quantitative systems toxicology (QST) expertise
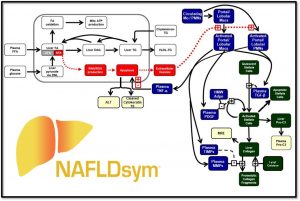
We have significant quantitative systems toxicology (QST) expertise in the area of drug-induced liver injury (DILI), and has employed this expertise to develop and apply DILIsym to evaluate the safety risk of numerous drug candidates. We also have noteworthy experience in the area of metabolic diseases and has leveraged this expertise to develop the quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) modeling software, NAFLDsym v2B. We apply this QSP platform to assist with clinical development in collaborative partnerships and offer access to the software via corporate software licenses.
-
NAFLDsym v2B includes the mechanistic underpinnings associated with:
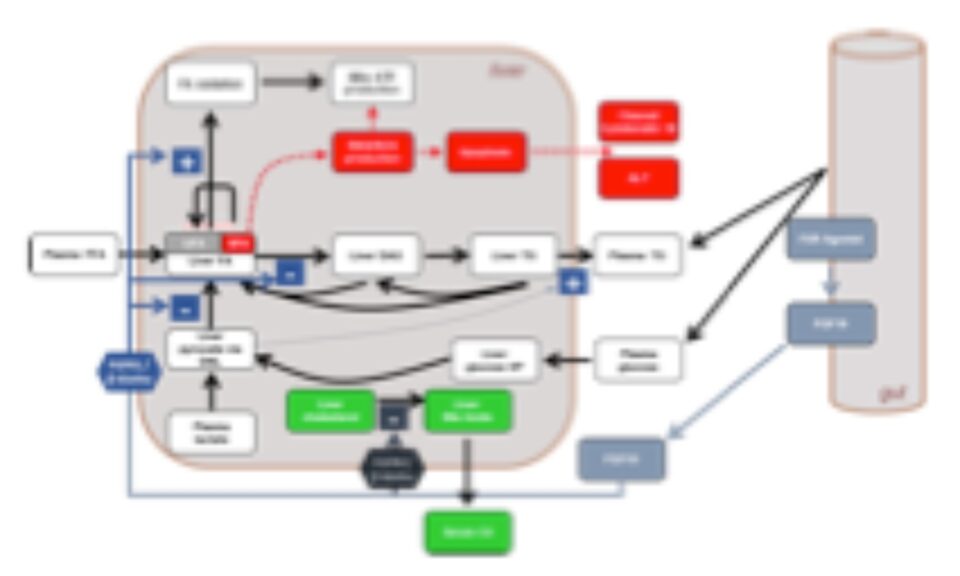
NAFLDsym v2B includes the mechanistic underpinnings associated with steatosis and lipotoxicity, chronic inflammation, and fibrosis within the liver. It is useful for evaluating the efficacy of potential new drug candidates to treat MASLD/MASH in each of these areas, including the powerful capability to evaluate combination treatment approaches. It is a powerful tool for understanding and predicting disease progression and the complications associated with clinical trial design for MASH/MASLD studies, including predictions for weight-stable, weight-loss, and weight-gaining patients. Weight loss and gain are dynamically represented with a state-of-the-art body weight model (Hall 2010). 4 large pharmaceutical companies have sponsored the development of version 2A.
A number of key biomarkers or endpoints are incorporated into NAFLDsym v2B, such as
- Plasma TG, free fatty acids, and adiponectin
- Plasma ALT and cytokeratin-cleaved 18 (cK18)
- Phasma TNF-alpha and TNF-beta
- Plasma Pro-C3
- The NAFLD Activity Score (NAS)
- Steatosis and ballooning score
- Inflammation score
- Fibrosis stage
- Liver fat percentage (MRI) and stiffness (MRE)
- and many more…
-
The heterogeneity of MASLD/MASH is a major challenge in the quest for new treatments
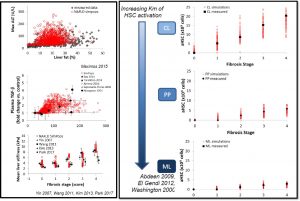
The heterogeneity of MASLD/MASH is a major challenge in the quest for new treatments. To this end, NAFLDsym v2B includes well over 1,000 simulated patients with varying stages of MASLD and MASH. The simulated patients, or SimPops®, can be used to optimize clinical trial protocols by determining favorable measurement frequencies and dosing levels, evaluating targets using key internal laboratory or mechanistic clinical data, testing combination treatment approaches across varying patient backgrounds, and comparing efficacy in different patient groups (e.g. stratification by NAS, etc.). The SimPops has been validated against a large backdrop of key data sets, such as those shown below for liver fat and ALT, Plasma TGF-beta and ALT, activation of stellate cells by liver zone, and mean liver stiffness versus fibrosis stage.
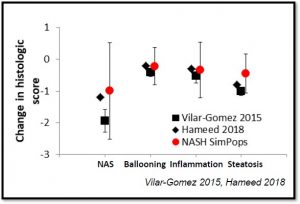
Validation of the various relationships within NAFLDsym v2B working in harmony comes from predicted efficacy when body weight is applied as a treatment. The results below were predicted from the first principle mechanisms included (emergent behavior from the model) during 5% weight loss over the course of a year. Several other validations have been completed and/or are on-going in the context of confidential consulting projects.
NAFLDsym v2B is available for in-house use through corporate software licenses. Contact us today for more information on license terms and pricing.
NAFLDsym v2B is a computational model of MASLD and can be used to predict efficacy for treatment modalities developed for treating MASLD and MASH. NAFLDsym v2B includes many of the primary components of MASLD and MASH pathophysiology such as:
- Steatosis
- Regulation of liver triglyceride and fatty acids
- Lipotoxicity
- Fibrosis
- Inflammation
- Liver injury and proliferation
- Hepatocellular bioenergetics
- Dynamic body weight and its effects on lipids
- Biomarkers (e.g., ALT, AST, cytokeratin cleaved K18, NAS, MRI, MRE, fibrosis score)
NAFLDsym® is computer software, namely, downloadable computer software for conducting simulations of compounds such as drugs or chemicals to evaluate and model their effects on liver disease, namely, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
These mechanistic components have been combined to generate >1000 simulated MASLD/MASH (NAFLD/NASH) patients in NAFLDsym v2B. Reflecting the variability in clinical patient populations, these populations of simulated patients (SimPops®) have a range of liver fat levels (steatosis), mediator levels (inflammation), collagen production levels (fibrosis), body weight, and many also have liver injury (e.g., elevated ALT). The SimPops responds diversely to simulated treatments such as weight loss.

NAFLDsym applications have been conducted to address important questions for Pfizer and Gilead and also several other pharmaceutical companies.
Key features of NAFLDsym v2B Beta within Julia include:
- Integration with a modern C++ based graphical user interface (GUI)
- Integration with the open-source Julia Scientific and Machine Learning (SciML) toolkit to solve simulations efficiently
- Results viewer that can open previously exported results files
- Pre-compiled Julia dependencies so users do not need to install a separate Julia environment
- An interactive console application for editing and appending to existing NAFLDsym QSP model equations