Physiologically based kinetics (PBK) modelling provides (internal) exposure concentrations. We used a PBK model parameterized exclusively with in silico and in vitro data in a bottom-up approach to predict the pharmacokinetics of oxybenzone, a UV filter, present in two formulations (for which dose-normalized Cmax and AUC from clinical studies were different).

Emerging Perspectives on Leveraging Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) for BCS Class III Biowaivers: a Webinar Summary
The regulatory framework for Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) class III drug products provides a pathway for streamlined biowaivers in drug development, eliminating the need for expensive...

QSAR-based Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling for 34 Fentanyl Analogs: Model Validation, Human Pharmacokinetic Prediction and Abuse Risk Insights
Fentanyl analogs, as emerging new psychoactive substances (NPS), pose a global public health threat due to widespread abuse, high toxicity, and frequent overdose fatalities.

Development of Co-Amorphous Systems for Inhalation Therapy—Part 2: In Silico Guided Co-Amorphous Rifampicin–Moxifloxacin and –Ethambutol Formulations
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global health challenge due to long treatment durations, poor adherence, and growing drug resistance. Inhalable co-amorphous systems (COAMS) offer a promising strategy for targeted pulmonary delivery...

Formulation and Evaluation of Poly(Jasmine Lactone) Based Micelles for Improving the Oral Permeability of Acyclovir
Acyclovir (ACV), an antiviral drug, belongs to the BCS class III drug with intermediate solubility and low permeability.

Simulation-Guided Dissolution Testing: Coupling DDDPlus™ and GastroPlus® to Predict Aripiprazole Oral Bioperformance
Orally administered weakly basic compounds like aripiprazole (ARI) can precipitate in the small intestine due to limited solubility at intestinal pH.

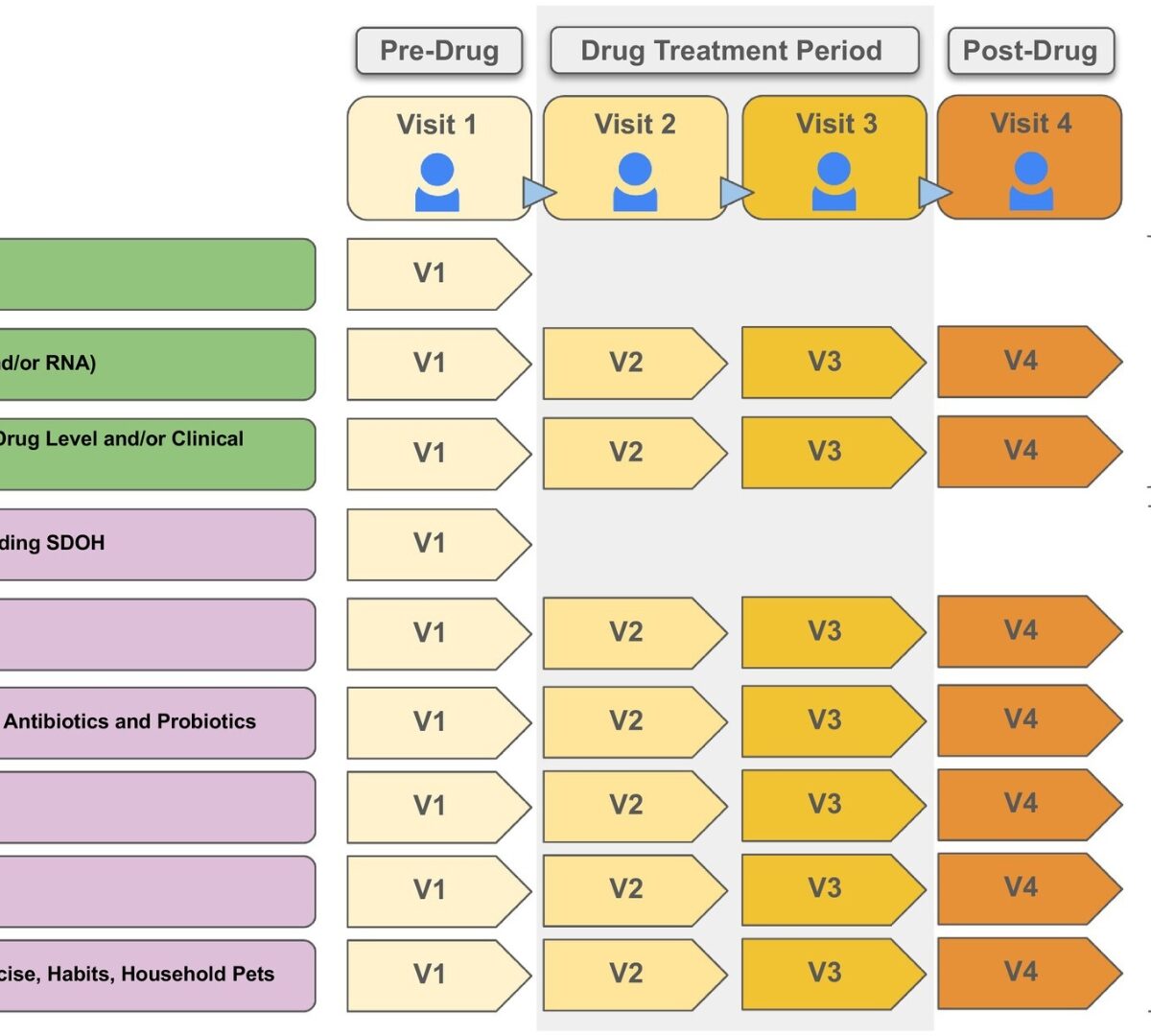
Sensitivity Analysis of the Inputs for Bioactivity-Exposure Ratio Calculations in a NAM-based Systemic Safety Toolbox
To support regulatory decision-making without animal testing, Next-Generation Risk Assessment (NGRA) frameworks leverage New Approach Methodologies (NAM).

Applications of PBPK Models to Predict Tissue Residues and Extralabel Withdrawal Times of Drugs in Food Animals: Perspectives from the Food Animal Residue Avoidance Databank (FARAD) Program
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models are commonly used in human drug discovery and development and human health risk assessment of environmental chemicals.
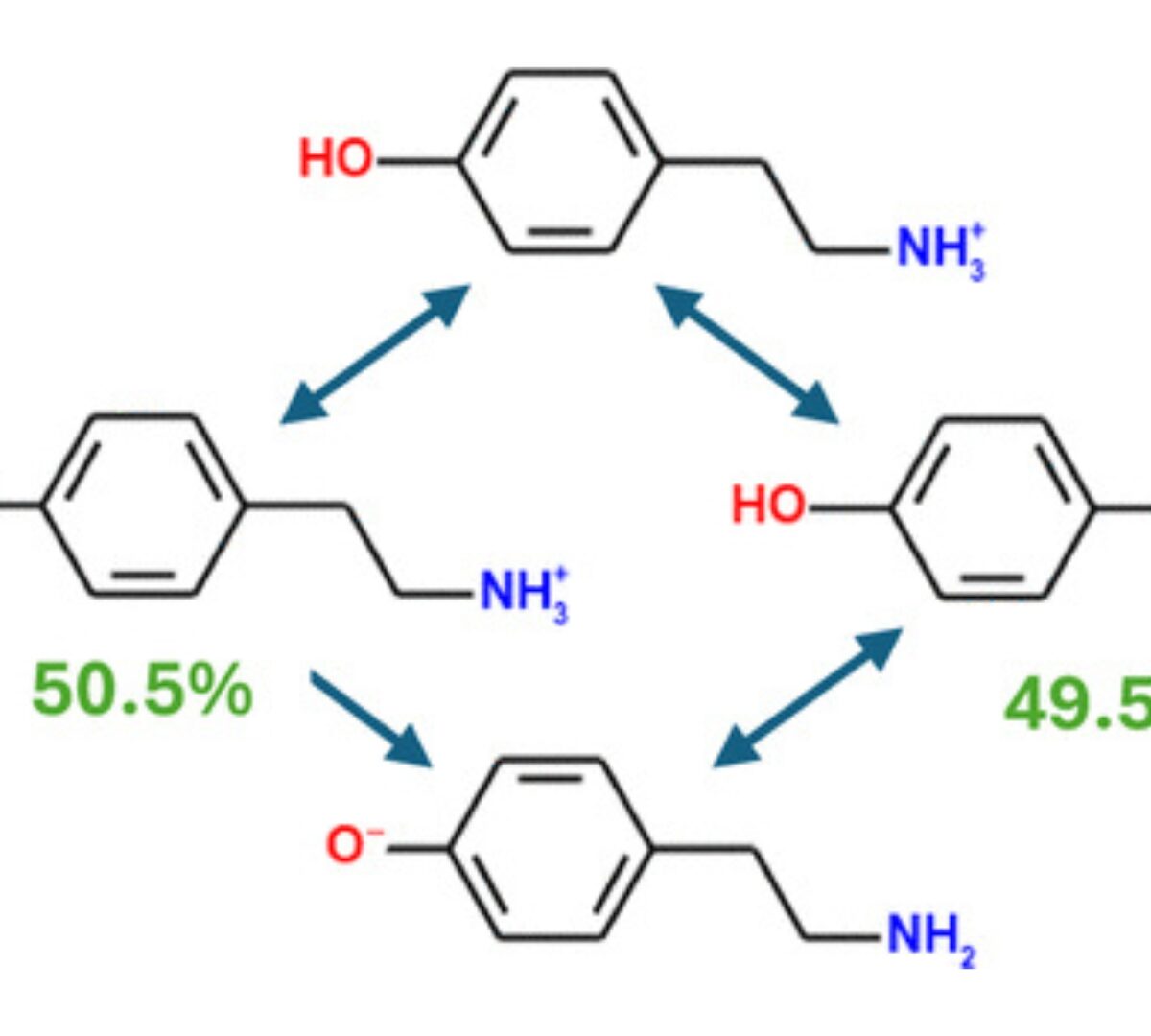
What, This “Base” Is Not a Base? Common Misconceptions about Aqueous Ionization That May Hinder Drug Discovery and Development
The challenges of modern medicinal chemistry increase with the complexity of the chemical compounds studied.
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Hydroxyurea: Implications for Dose Adjustment in Patients with Renal Insufficiency
Hydroxyurea is widely used in the management of sickle cell anemia.
Pharmacomicrobiomics
Oral medications encounter gut commensal microbes that participate directly and indirectly in drug effects through metabolism, interactions with drug metabolites, or production of substrates that compete with drugs for drug-metabolizing enzymes, consequently influencing drug pharmacokinetics.

AI-driven ANN and RSM-CCD integrated optimization of cinnarizinedomperidone bilayer tablet: In-vitro evaluation and in-silico PBPK modeling using GastroPlus®
Response surface methodology coupled with the design of experiments identifies the optimal response surface function related to selected independent factors.
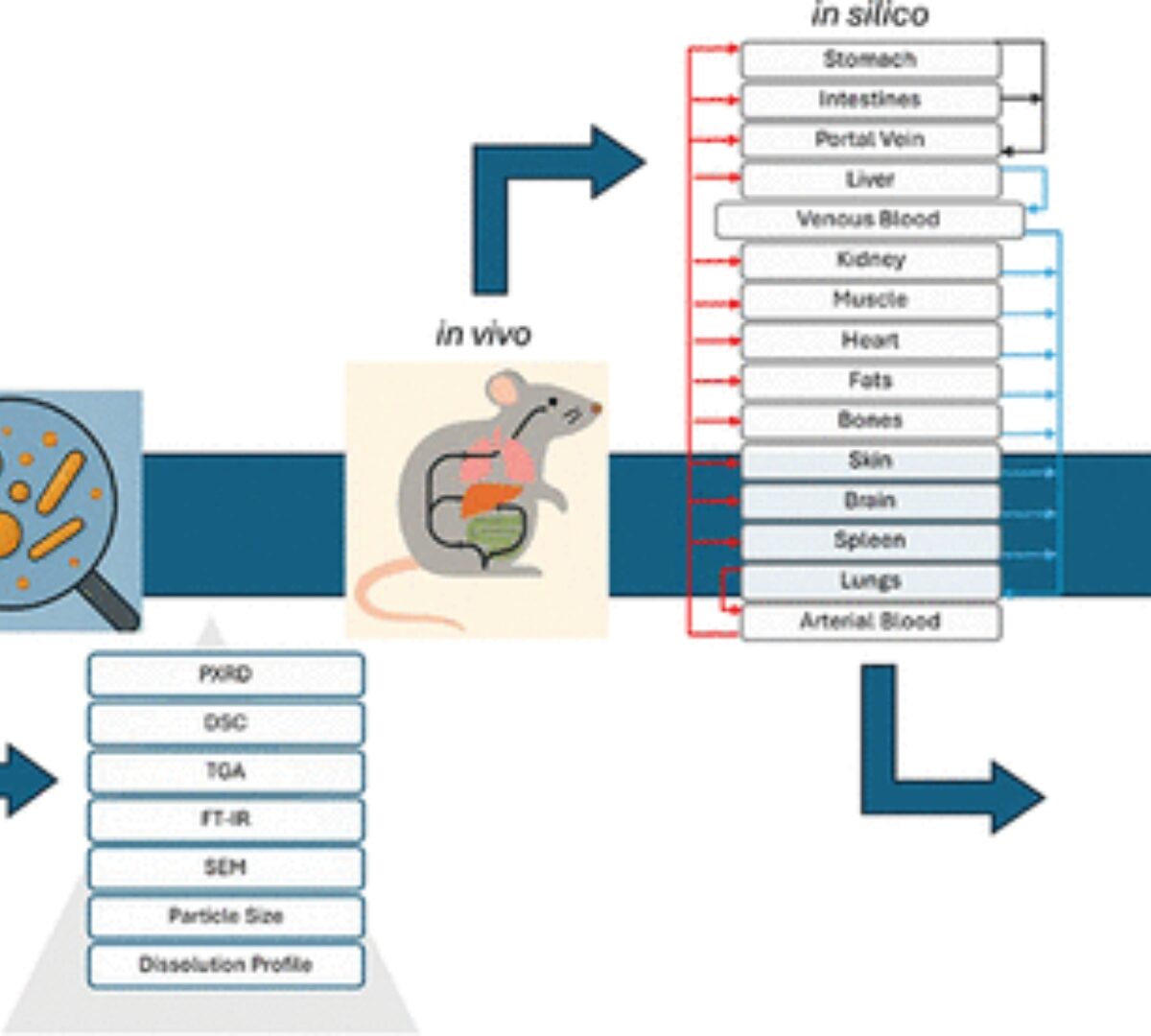
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Efavirenz Nanoparticles: from Animal Model to Human Extrapolation
The present work aims to establish a formulation-specific, physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for efavirenz (EFV) nanocrystals that have shown increased dissolution and were produced ...
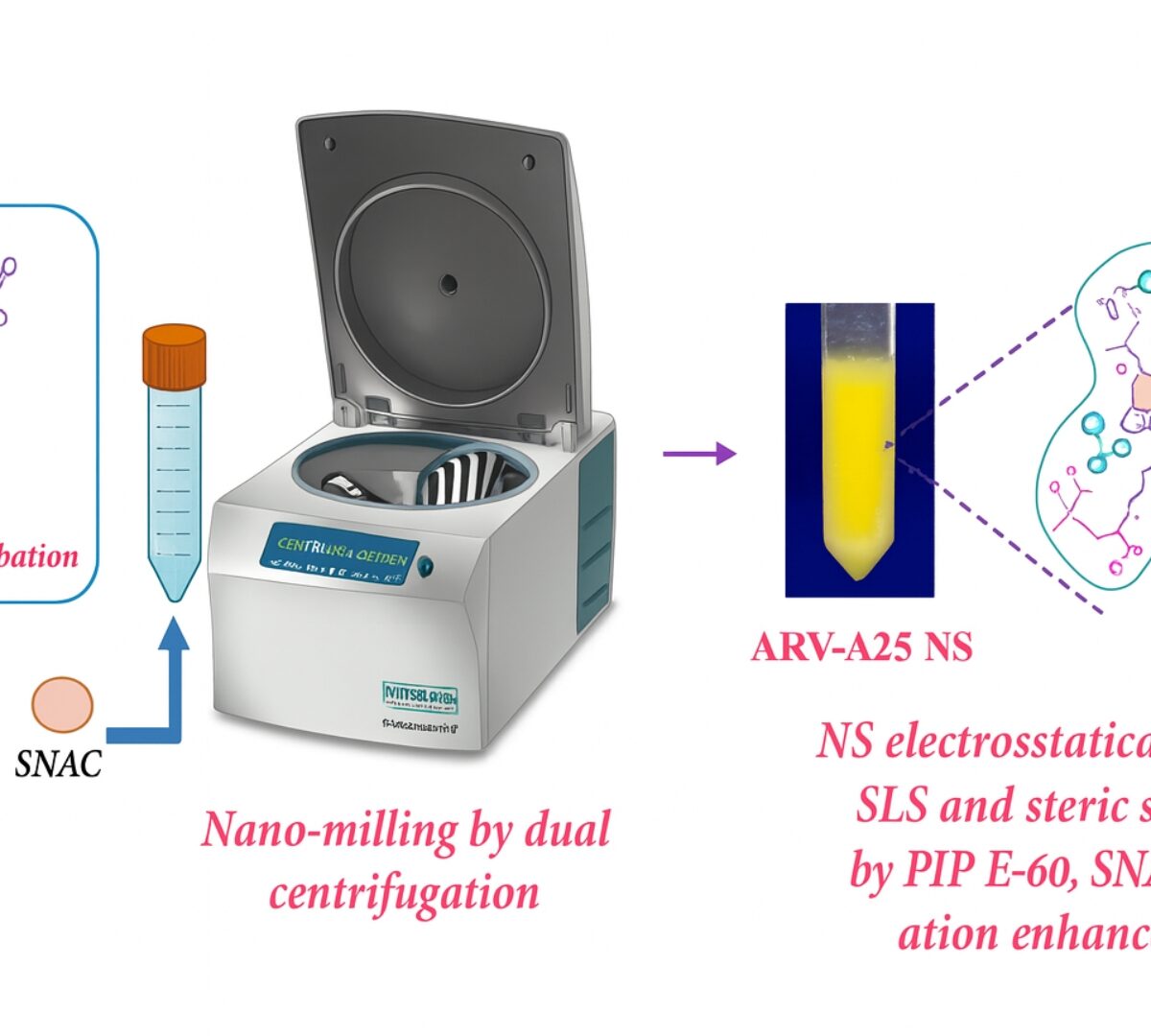
Permeability Enhancer Incorporated Oral Nanosuspension of ARV-825 PROTAC for Glioblastoma Treatment
Glioblastoma(GBM) is an aggressive brain tumor with dismal prognosis, necessitating innovative therapeutic strategies.

Indirect Modeling of Post-Prandial Intestinal Lymphatic Uptake of Halofantrine Using PBPK Approaches: Limitations and Implications
Despite the recognized importance and distinctive characteristics of the intestinal lymphatic pathway in drug absorption, its pharmacokinetic modeling remains largely unexplored.

Innovative Triamcinolone Acetonide Microsuspension for Non-Invasive Ocular Management of Inflammation
Enhancing the bioavailability of insoluble active agents in the eye through topical administration is a key focus in formulation science.

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Dose Optimization of Linezolid in Pediatric Patients With Renal Impairment
Linezolid (LZD), a commonly used antimicrobial agent in clinical practice, has not undergone adequate pharmacokinetic (PK) assessment in pediatric populations with renal impairment (RI).

Differential Cannabinoid-Like Effects, Receptor Affinity and Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetics of the Synthetic Cannabinoids 4F-MDMB-BINACA, 4F-MDMB-BICA and 5F-MDMB-PICA in Mice: A Comparative Study
Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists (SCRAs) 4F-MDMB-BINACA, 4F-MDMB-BICA, and 5F-MDMB-PICA share a “tail” group but differ in indazole/indole cores and N-fluoroalkyl chain lengths (C4 vs. C5).

In Vivo Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Assessment of Cannabidiol-loaded Camel Milk Exosomes in Doxorubicin-Resistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Xenografts
Cannabidiol (CBD) suffers from poor aqueous solubility and extensive first-pass metabolism, which significantly limits its oral bioavailability.
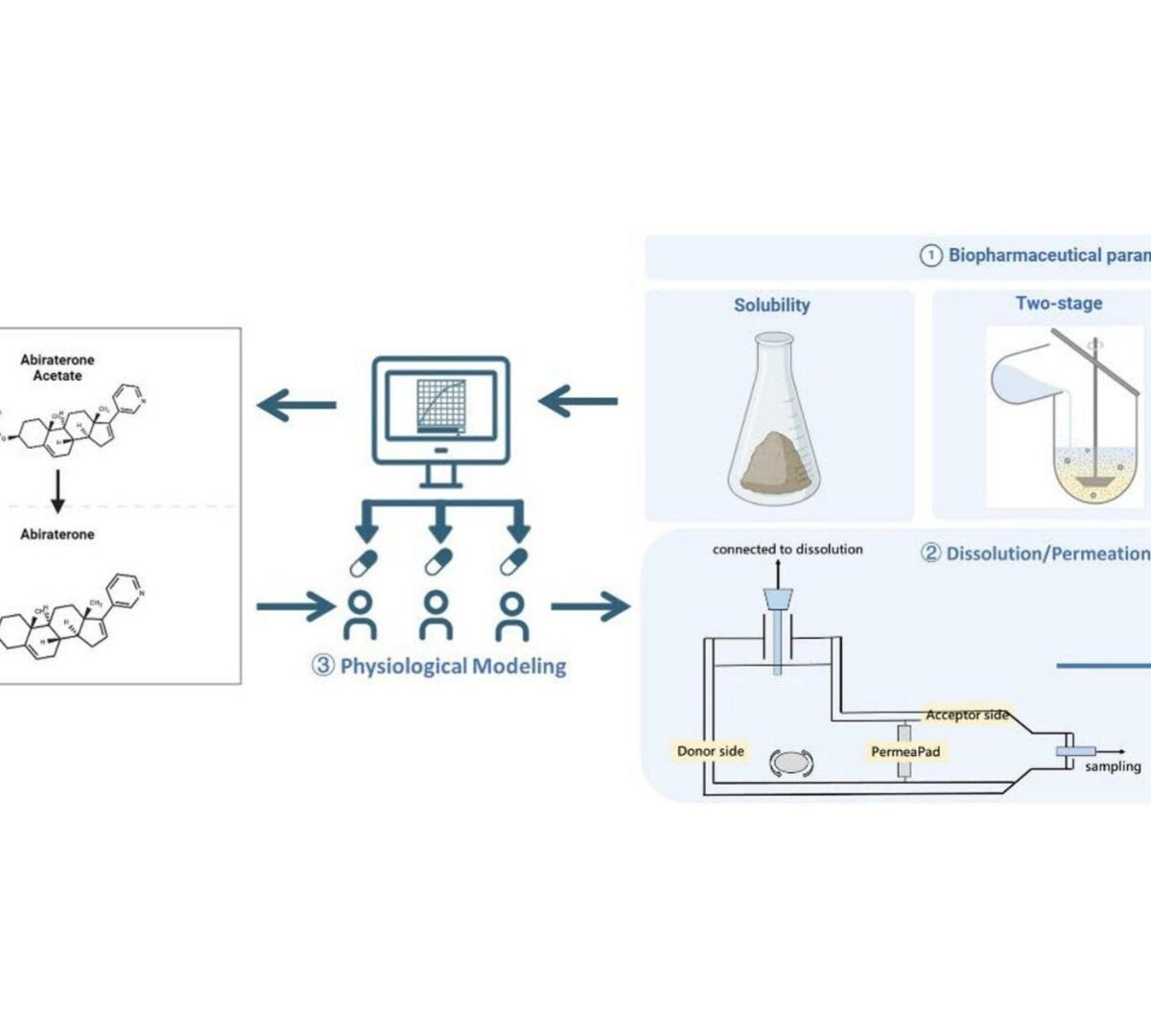
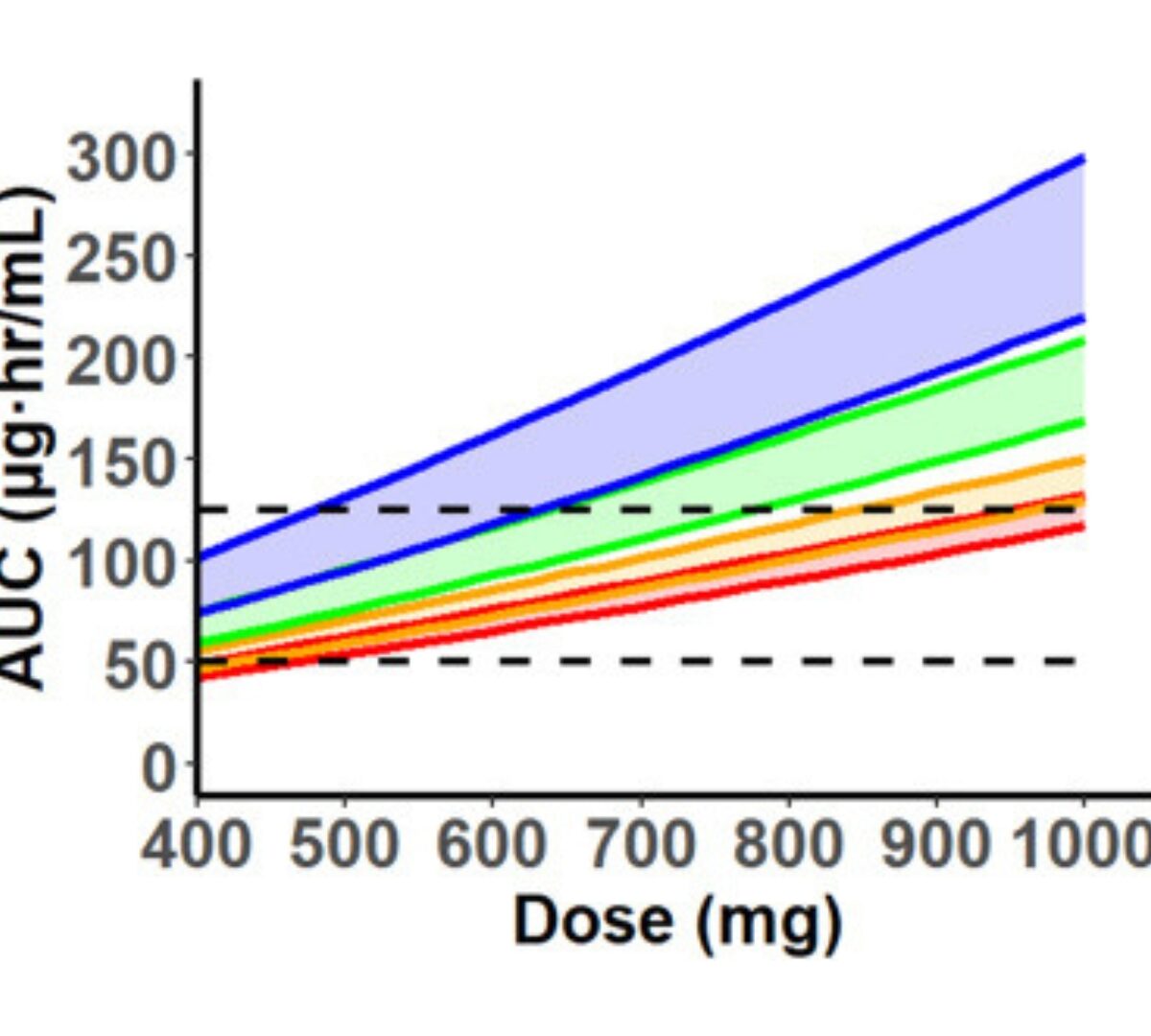
Establishing Clinically Relevant Dissolution Specifications for Prodrug Bioequivalence Risk Assessment: Integration of a Dissolution/Permeation System with Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling in Abiraterone Acetate
Prodrugs with enzymatic activation requirements, such as the weakly basic biopharmaceutical classification system (BCS) class IV compound...
