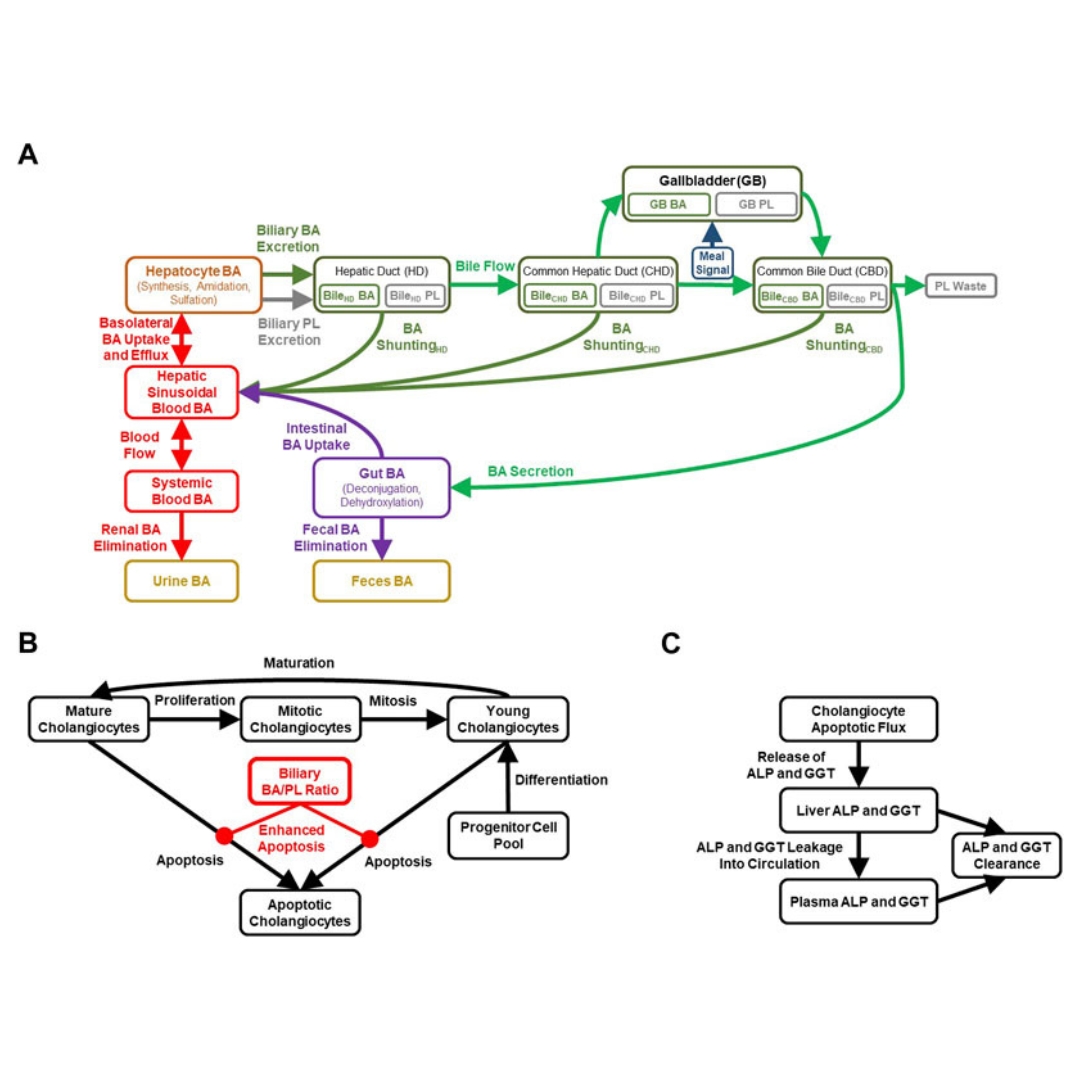
Inhibition of the canalicular phospholipid floppase multidrug resistance protein 3 (MDR3) has been implicated in cholestatic drug-induced liver injury (DILI), which is clinically...

N-Derivatives of (Z)-Methyl 3-(4-Oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-5-ylidene)methyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxylates as Antimicrobial Agents—In Silico and In Vitro Evaluation
Herein, we report the experimental evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of seventeen new (Z)-methyl 3-(4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-5-ylidene)methyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxylate derivatives.
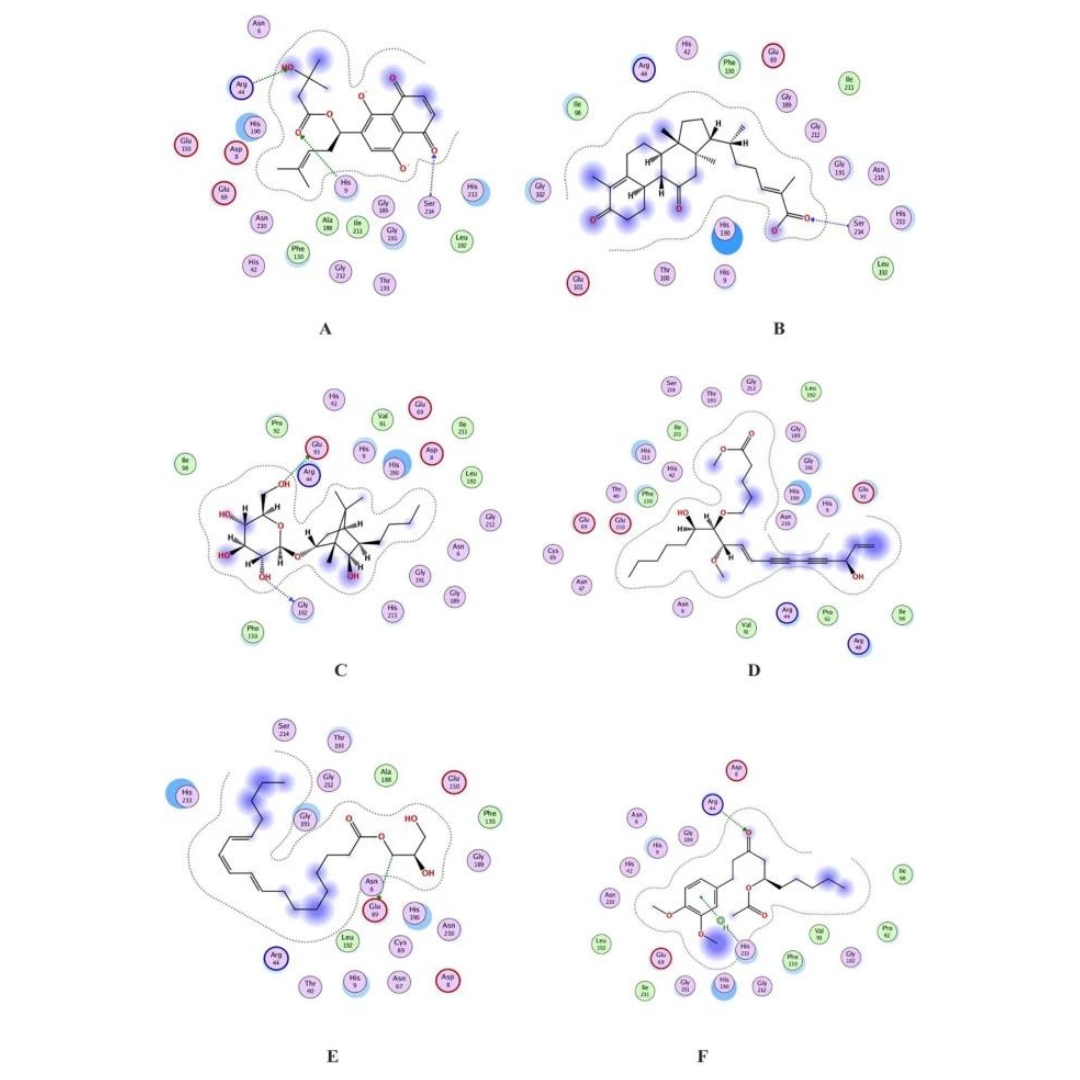
Therapeutic target mapping from the genome of Kingella negevensis and biophysical inhibition assessment through PNP synthase binding with traditional medicinal compounds
Kingella negevensis belongs to the Neisseriaceae family. It is implied that it has significant virulence potential due to RTX toxin production, which can cause hemolysis.
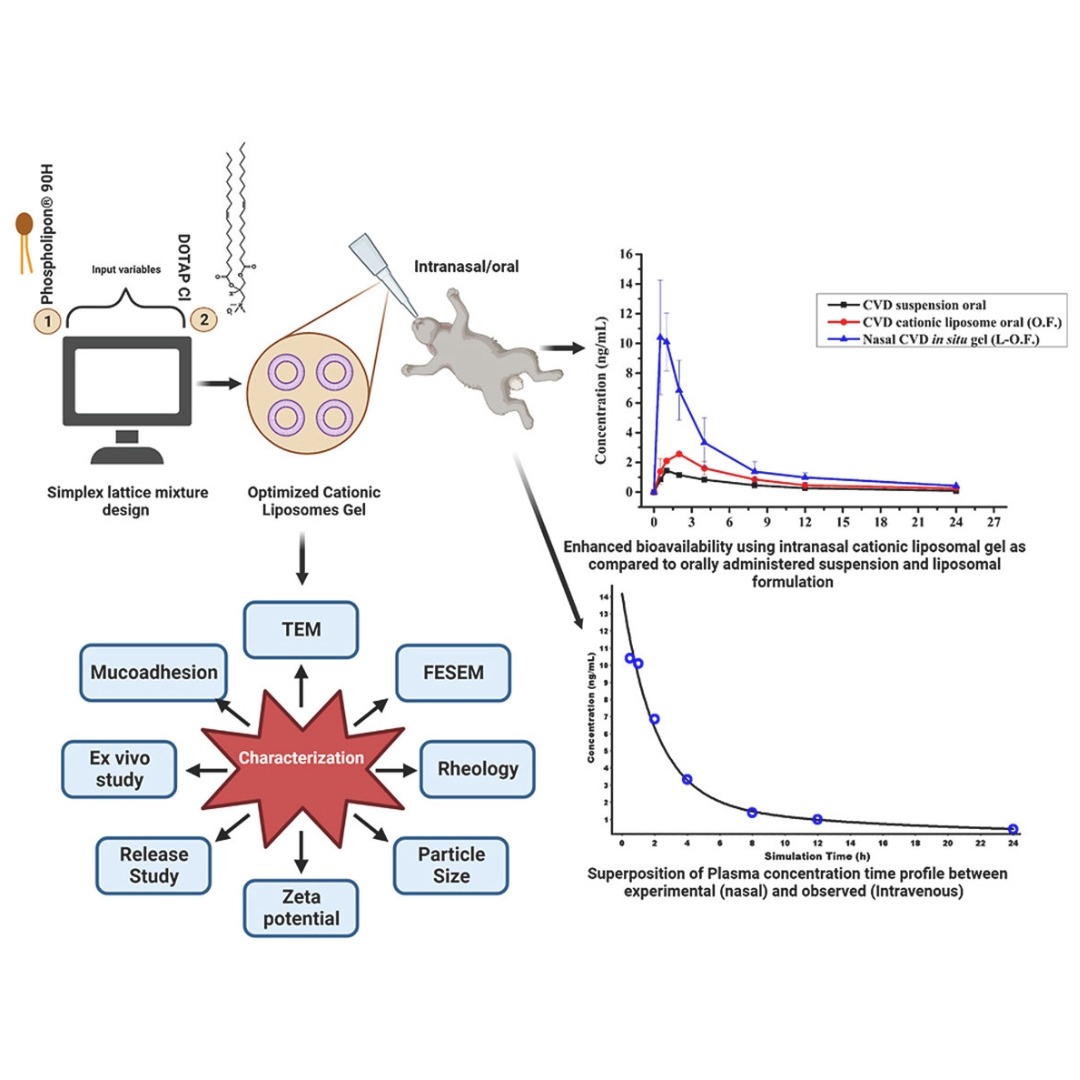
Cationic nanoliposomes of carvedilol for intranasal application: In vitro, in vivo and in silico studies
Carvedilol (CVD) is a non-selective β and α adrenoreceptor blocker, useful in treating hypertension, angina pectoris, congestive heart failure (CHF), and coronary artery...

Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Nebulized Hydroxychloroquine: A Pilot Study in Healthy Volunteers
Background: Early in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) drew substantial attention as a potential COVID-19 treatment...
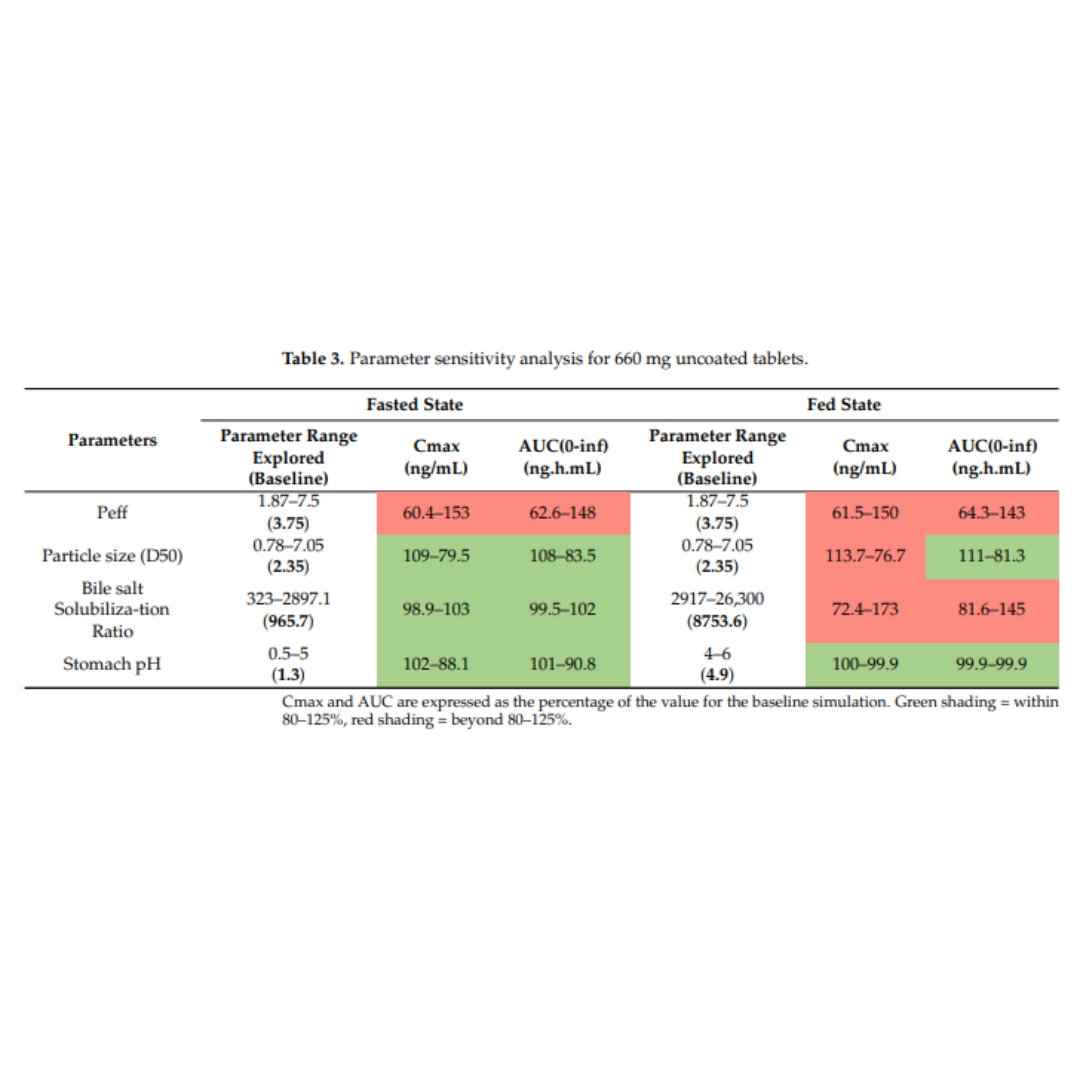
Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling of Food Effect for Basmisanil: A Retrospective Case Study of the Utility for Formulation Bridging
Basmisanil, is a lipophilic drug substance, exhibiting poor solubility and good permeability (BCS class 2). A validated physiologically based biopharmaceutics model (PBBM)...

Review and Chemoinformatic Analysis of Ferroptosis Modulators with a Focus on Natural Plant Products
Ferroptosis is a regular cell death pathway that has been proposed as a suitable therapeutic target in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.

Oral administration of VDAC1-derived small molecule peptides increases circulating testosterone levels in male rats
Cholesterol is the precursor of all steroid hormones, and the entry of cholesterol into the mitochondria is the rate-limiting step of steroidogenesis.

Regulatory utility of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling for assessing food impact in bioequivalence studies: A workshop summary report
This workshop report summarizes the presentations and panel discussion related to the use of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling approaches for food...

Structure-activity relationship read-across and transcriptomics for branched carboxylic acids
The purpose of this study was to use chemical similarity evaluations, transcriptional profiling, in vitro toxicokinetic data, and physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK)...

In-Depth Analysis of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling Utilization in Different Application Fields Using Text Mining Tools
In the past decade, only a small number of papers have elaborated on the application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling across different areas.

Pharmacokinetic Basis for Using Saliva Matrine Concentrations as a Clinical Compliance Monitoring in Antitumor B Chemoprevention Trials in Humans
This study reports the first clinical evidence of significantly high secretion of matrine in a multi-component botanical (Antitumor B, ATB) into human saliva from the systemic...

Androgens and androgen receptor signaling in prostate tumorigenesis
Androgens and androgen receptor (AR) signaling are necessary for prostate development and homeostasis. AR signaling also drives the growth of nearly all prostate cancer...

Prediction of Drug Synergism between Peptides and Antineoplastic Drugs Paclitaxel, 5-Fluorouracil, and Doxorubicin Using In Silico Approaches
Chemotherapy is the main treatment for most early-stage cancers; nevertheless, its efficacy is usually limited by drug resistance, toxicity, and tumor heterogeneity.

Non-specific binding of compounds in in vitro metabolism assays: a comparison of microsomal and hepatocyte binding in different species and an assessment of the accuracy of prediction models
Non-specific binding in in vitro metabolism systems leads to an underestimation of the true intrinsic metabolic clearance of compounds being studied.

Effect of starch, cellulose and povidone based superdisintegrants in a QbD-based approach for the development and optimization of Nitazoxanide orodispersible tablets: Physicochemical characterization, compaction behavior and in-silico PBPK modeling of its active metabolite Tizoxanide
The objective of the study was to develop a QbD based orodispersible Nitazoxanide 200 mg tablets its in-silico PBPK modeling. The central composite design was applied...

Model-Informed drug development of gastroretentive release systems for sildenafil citrate
Gastroretentive drug delivery systems (GRDDS) are modified-release dosage forms designed to prolong their residence time in the upper gastrointestinal tract...

Using mechanistic models to support development of complex generic drug products: European Medicines Agency perspective
Model‐informed drug development (MIDD) approaches receive wide regulatory acceptance in the European Medicines Agency (EMA) to support new drug development.

Impact of chemical structure on the in vitro hydrolysis of fatty esters of 2-ethylhexanoic acid or 2-ethylhexanol and extrapolation to the in vivo situation
Fatty esters of 2-ethylhexanoic acid (EHA) and 2-ethylhexanol (EH) are commonly used in cosmetics. Human liver and skin S9 and human plasma were used to determine the...

Formulation development and optimization of taste-masked azithromycin oral suspension with ion exchange resins: Bioanalytical method development and validation, in vivo bioequivalence study, and in-silico PBPK modeling for the paediatric population
The study is based on preparing taste-masked oral suspension of azithromycin using ion exchange resins Kyron T135 and Doshion-P542 AB. The complexation...