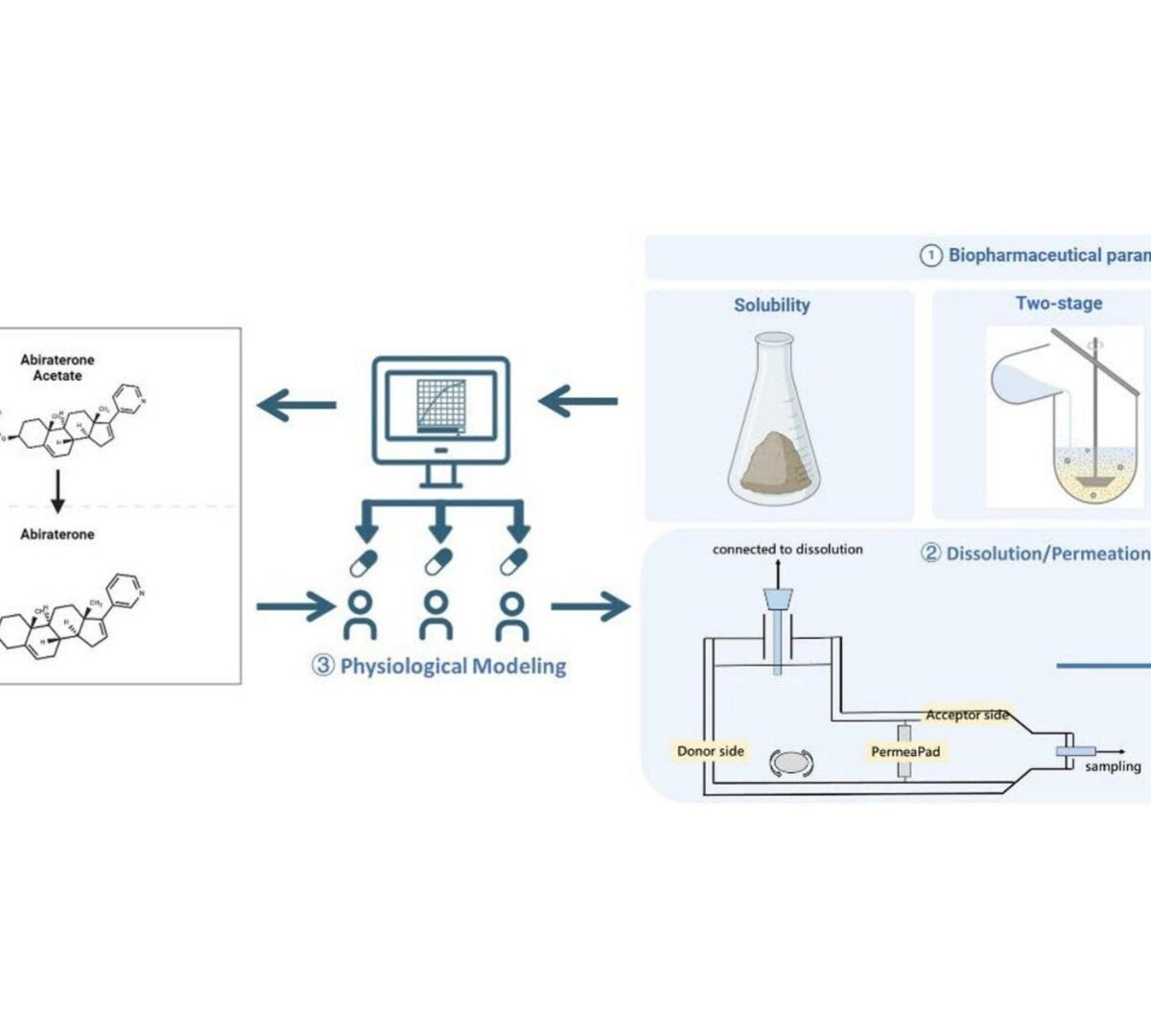
Prodrugs with enzymatic activation requirements, such as the weakly basic biopharmaceutical classification system (BCS) class IV compound...
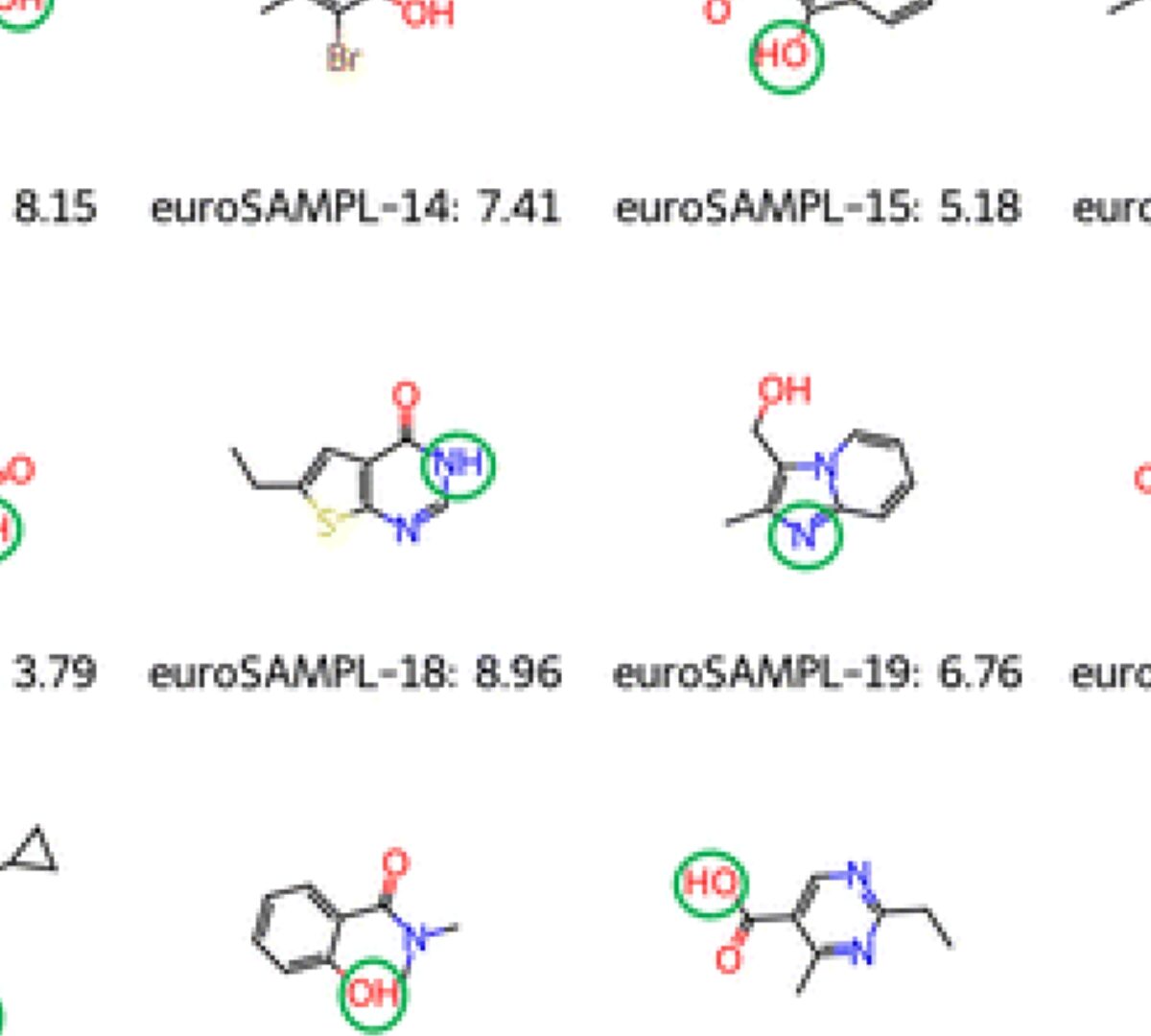
The EuroSAMPL1 pKa Blind Prediction and Reproducible Research Data Management Challenge
The development and testing of methods in computational chemistry for the prediction of physicochemical properties is by now a mature form of scientific research, with a number of different methods ranging from molecular mechanics simulations, over quantum calculations, to empirical and machine learning models.
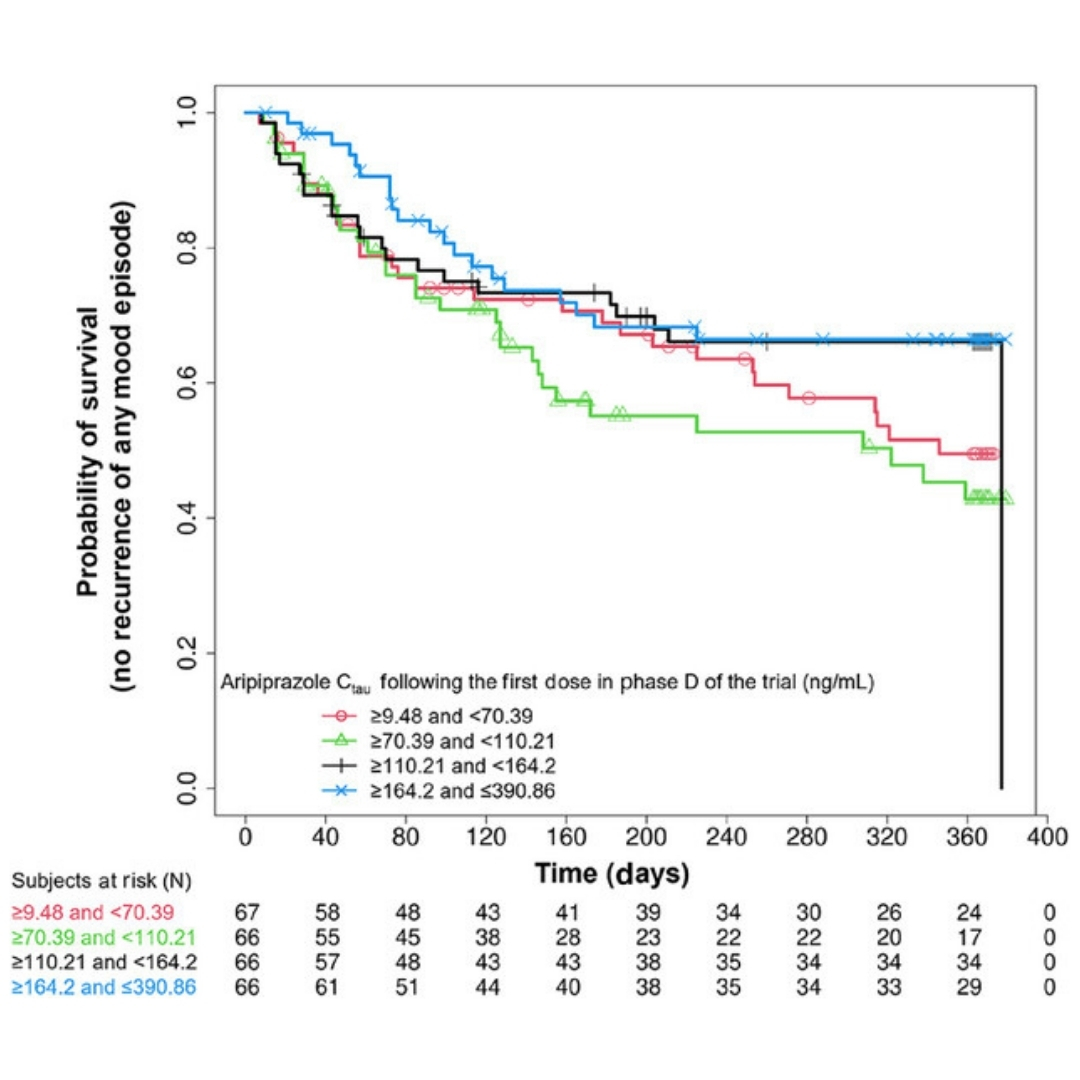
Exposure–Response Analysis for Aripiprazole Once-Monthly in Patients Diagnosed With Bipolar I Disorder
Aripiprazole once-monthly (AOM) is approved for the maintenance monotherapy treatment of bipolar I disorder (BP-I) in adults.
Dissolving Microneedle Patches for Transdermal Delivery of Paroxetine: in-vitro, ex-vivo Studies and its PBPK Modeling
Paroxetine HCl (PRX-HCl), an antidepressant, has poor water solubility and low oral bioavailability with 50% being metabolized in the liver.
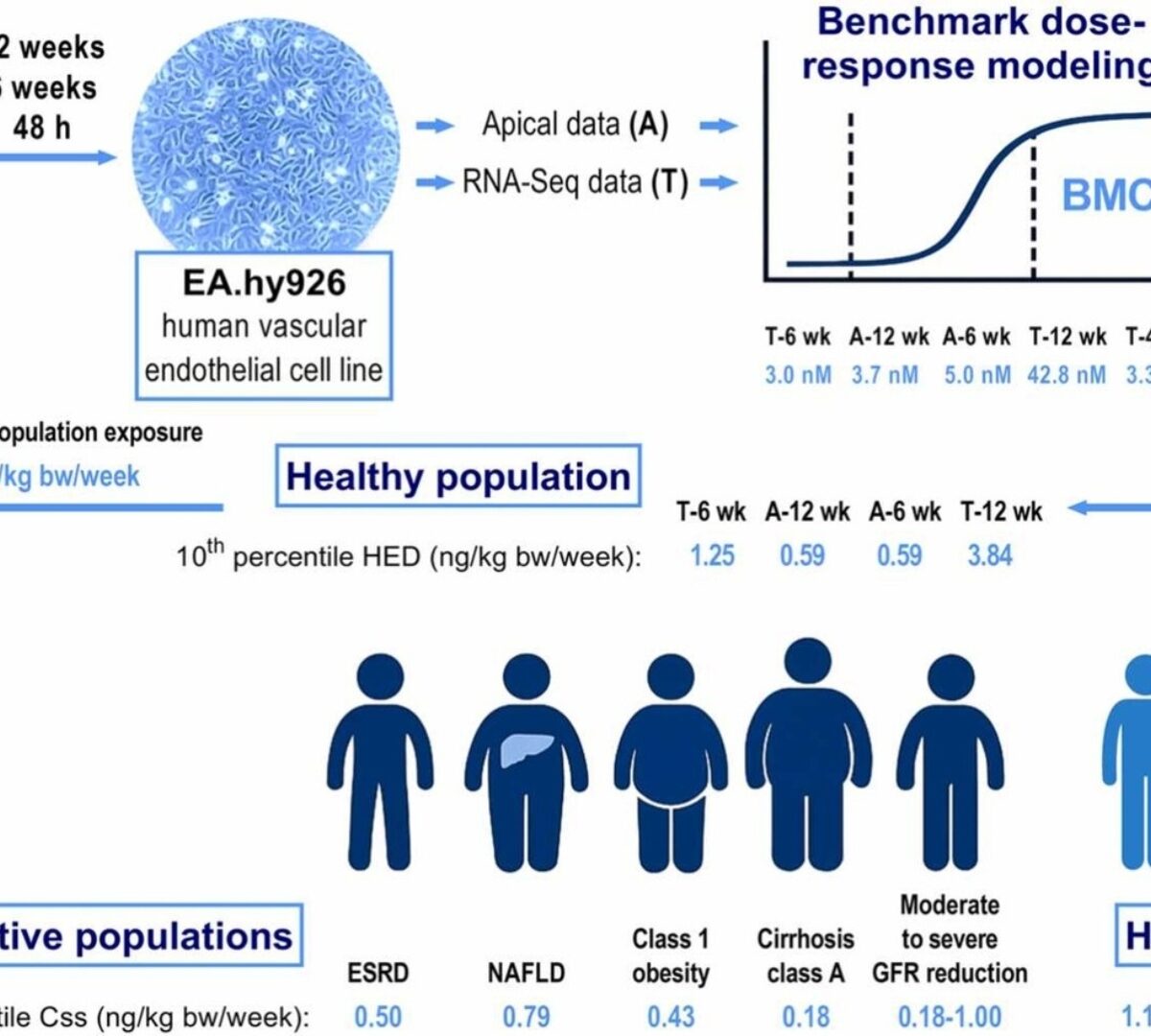
Advancing Probabilistic Risk Assessment of Perfluorooctanoic Acid Through Integration of in vitro Data and Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic Modeling Coupled with Population-Specific Analysis
Current human health risk assessment for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) has proven inadequate due to a lack of innovative approaches.

New Era in Bioequivalence Global Harmonization Through ICH M13 Initiative: Critical Review on Mew Concepts, Alternative Approaches for High-Risk Products
Bioequivalence (BE) studies have made significant advancements, particularly with the introduction of the ICH M13 guidances.
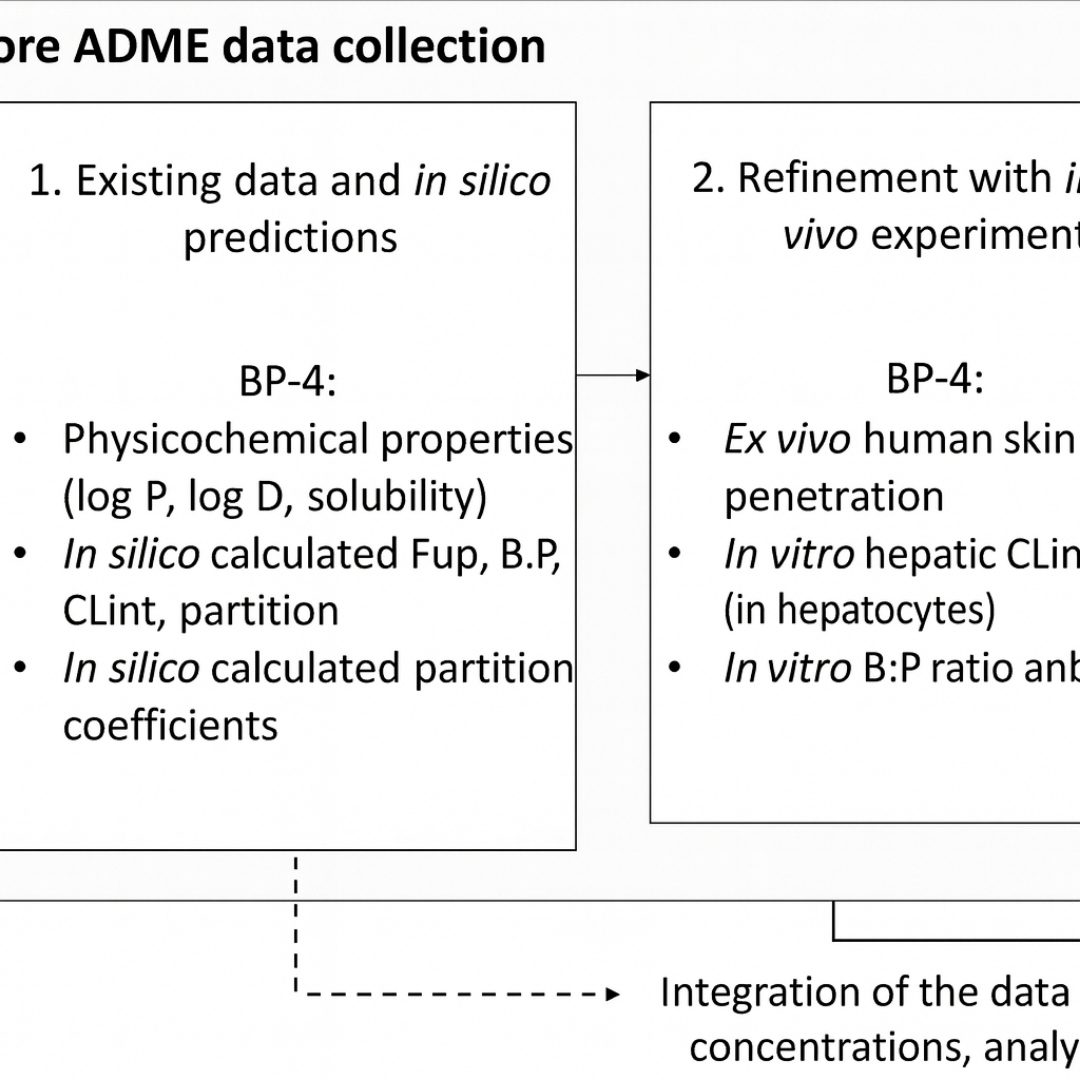
Building Confidence in PBK Model Predictions in the Absence of Human Kinetic Data: Benzophenone-4 Case Study
This study aimed to develop a physiologically based kinetic (PBK) model for benzophenone-4 (BP-4) in humans based on in vitro and in silico input data and to achieve scientific confidence in predicted internal...
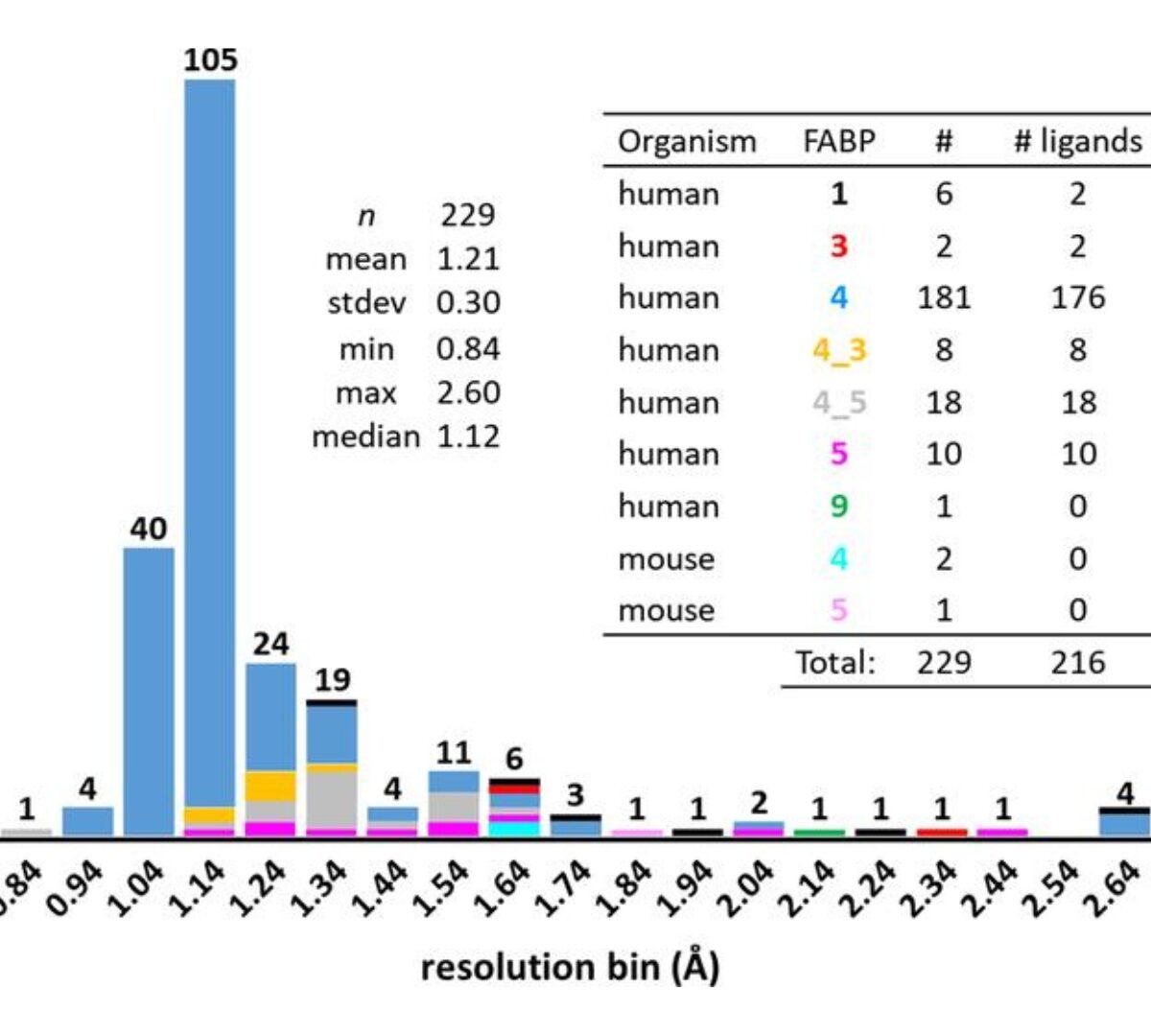
A High-Resolution Data Set of Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Structures. II. Crystallographic Overview, Ligand Classes and Binding Pose
Fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) belong to the calycin superfamily of proteins, sharing a similar overall structure with a ten-stranded β-barrel that encloses a large interior cavity for fatty-acid binding.
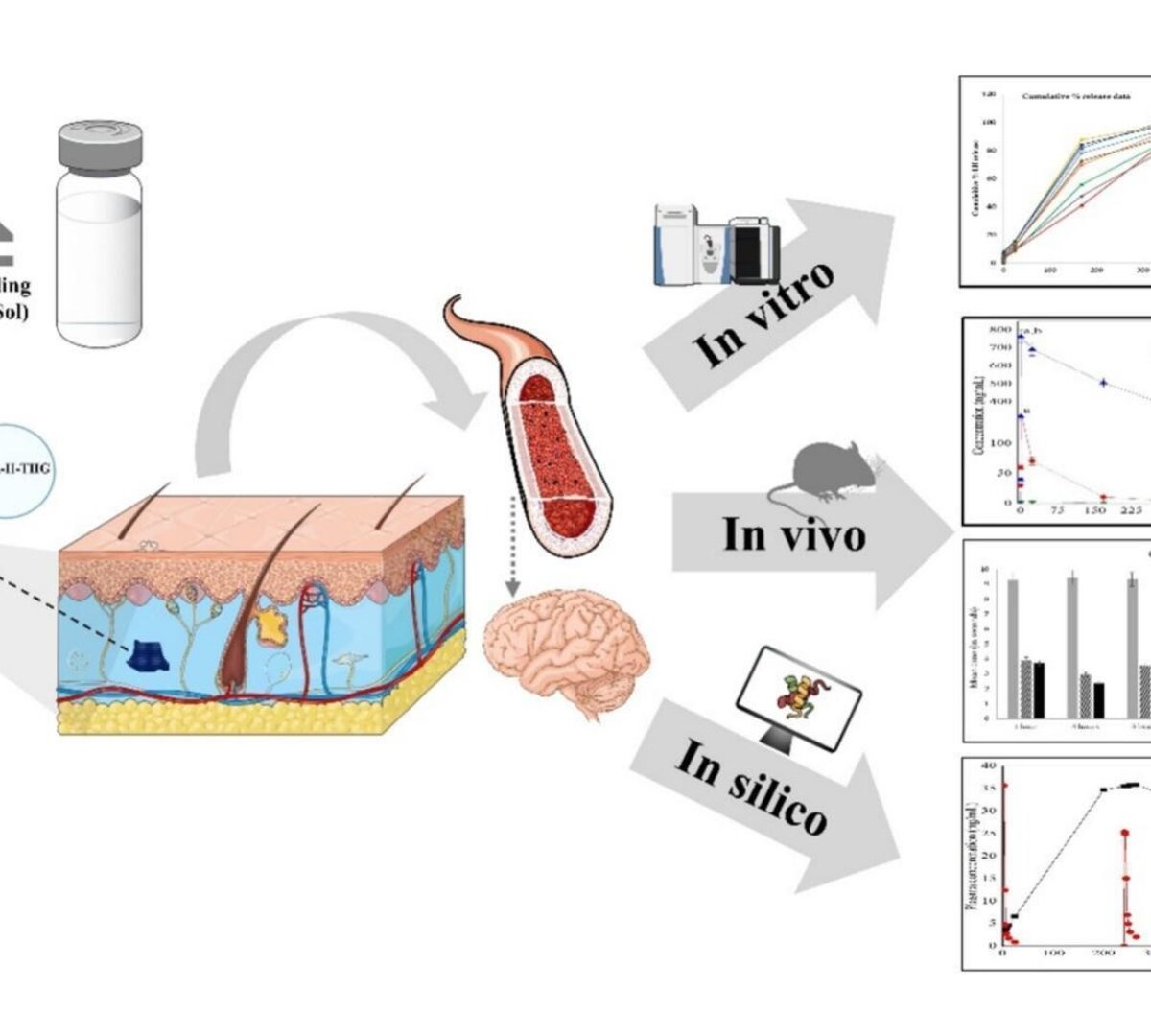
In vitro, in vivo and in silico Assessment of Bioresorbable PLGA-PEG-PLGA Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel Mediated 30-days Delivery of Lurasidone HCl for Schizophrenia
A novel once-monthly sustained-release injectable dosage form of Lurasidone hydrochloride thermosensitive hydrogel (LURA-H-THG) developed using PLGA-PEG-PLGA, for the treatment of schizophrenia.
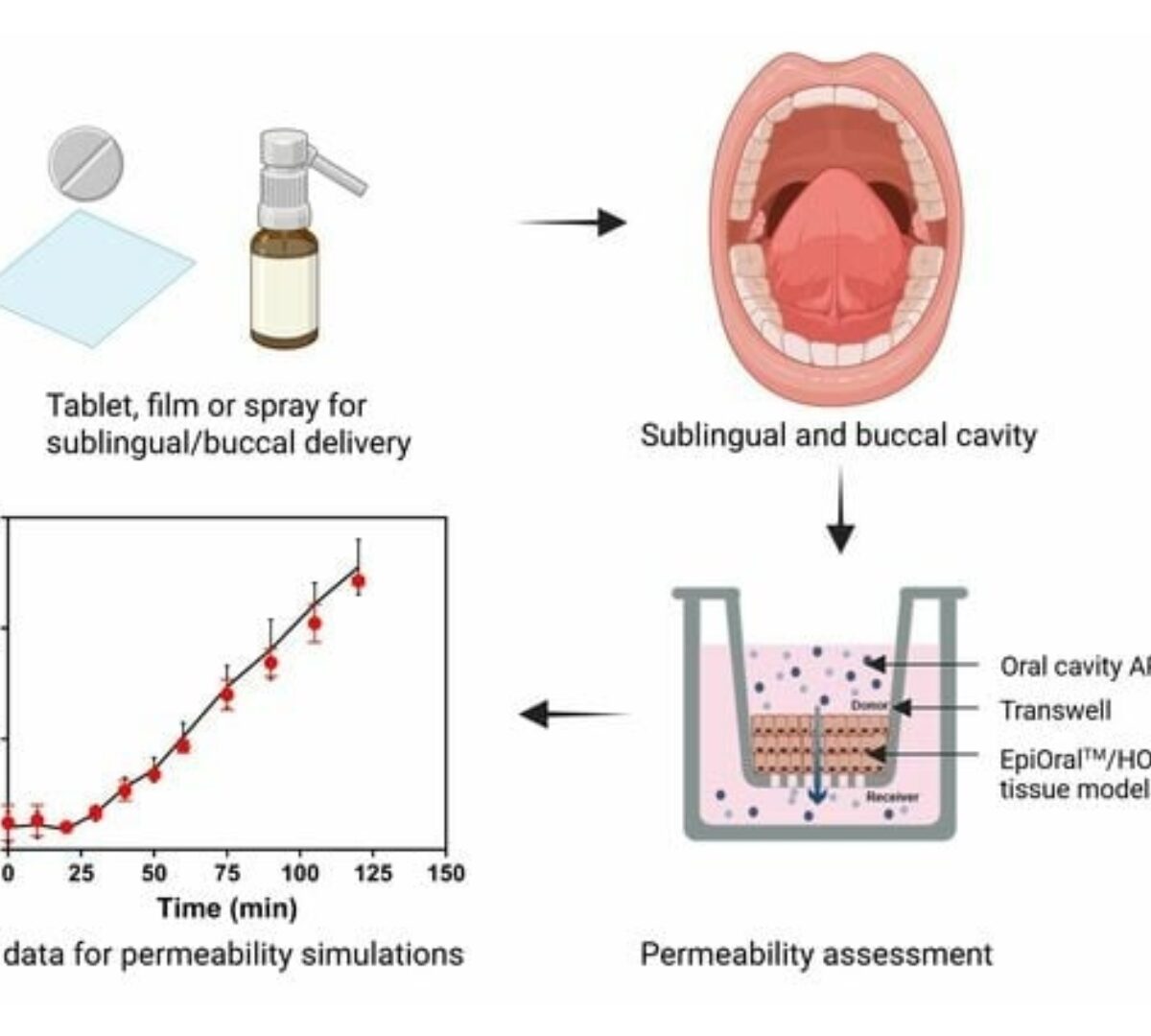
In Vitro Oral Cavity Permeability Assessment to Enable Simulation of Drug Absorption
The oral cavity represents a convenient route of administration for drugs that exhibit significant hepatic first-pass extraction.
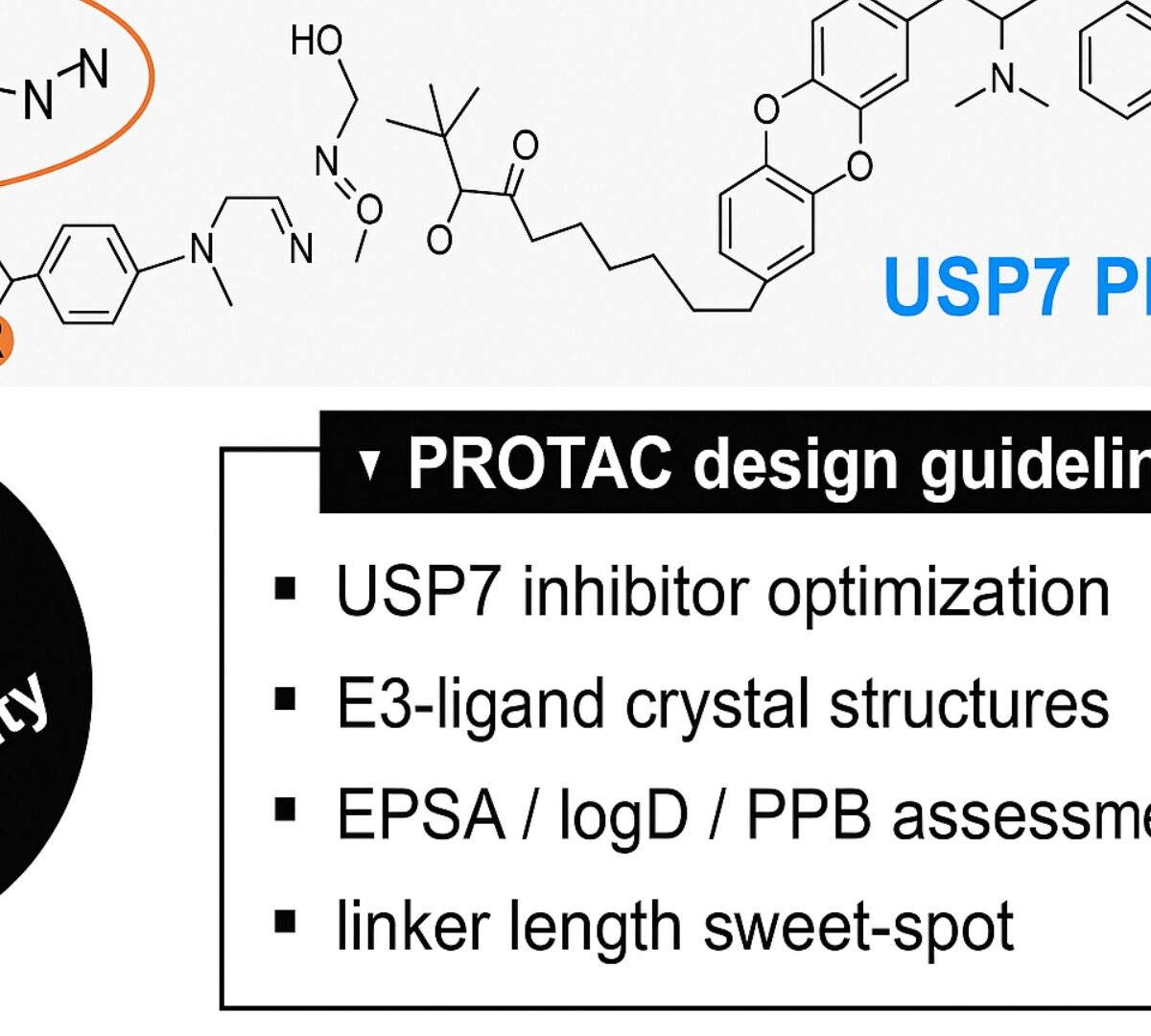
Enhancing Solubility in VHL-Based PROTACs: Optimized USP7 Degraders for Improved Developability
Limited aqueous solubility, high total polar surface area (TPSA), and high hydrogen-bond donor (HBD) counts have hampered the clinical development of VHL-based proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs).
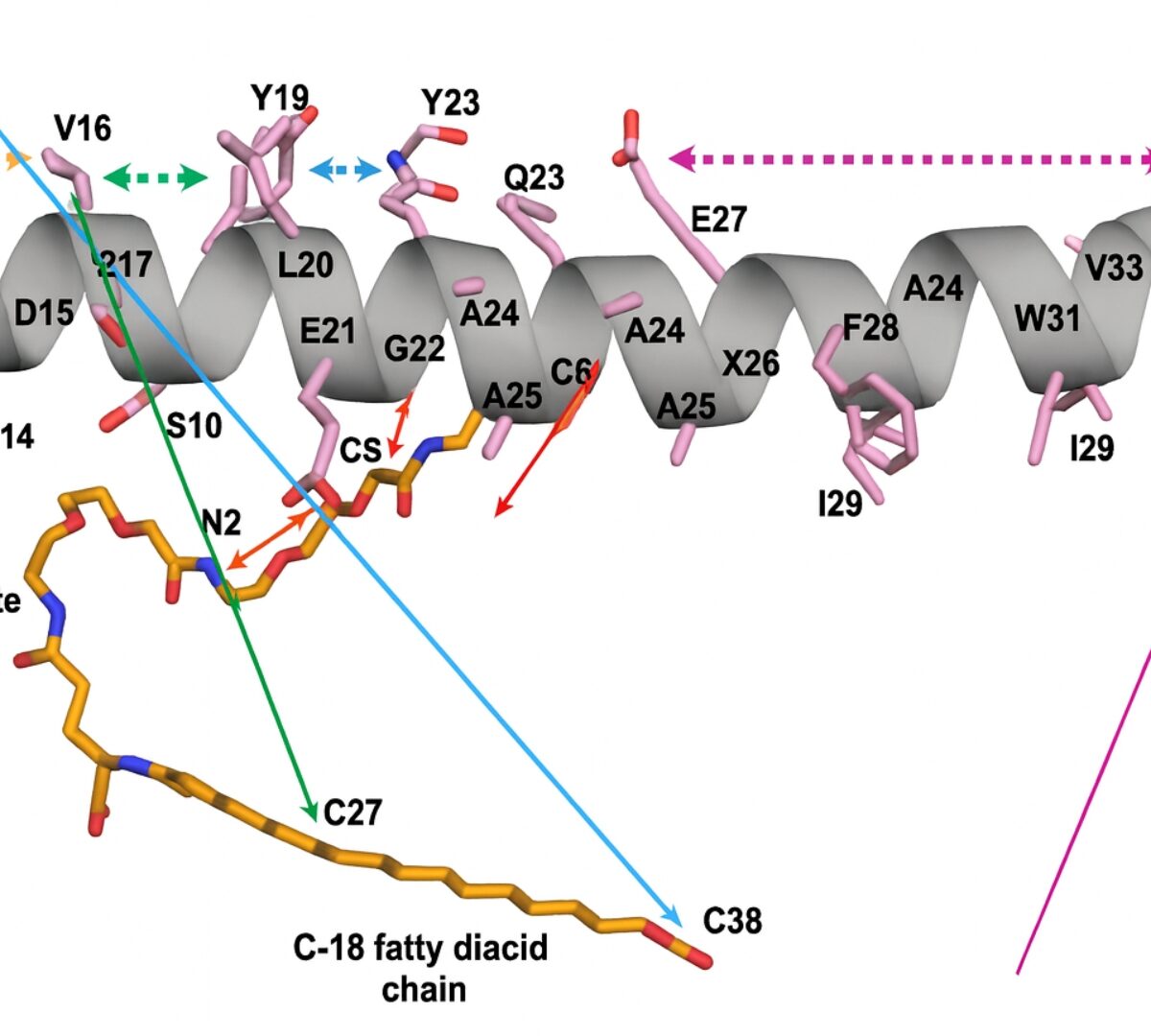
Oral Absorption of Semaglutide: Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist that is formulated for oral administration as Rybelsus®.
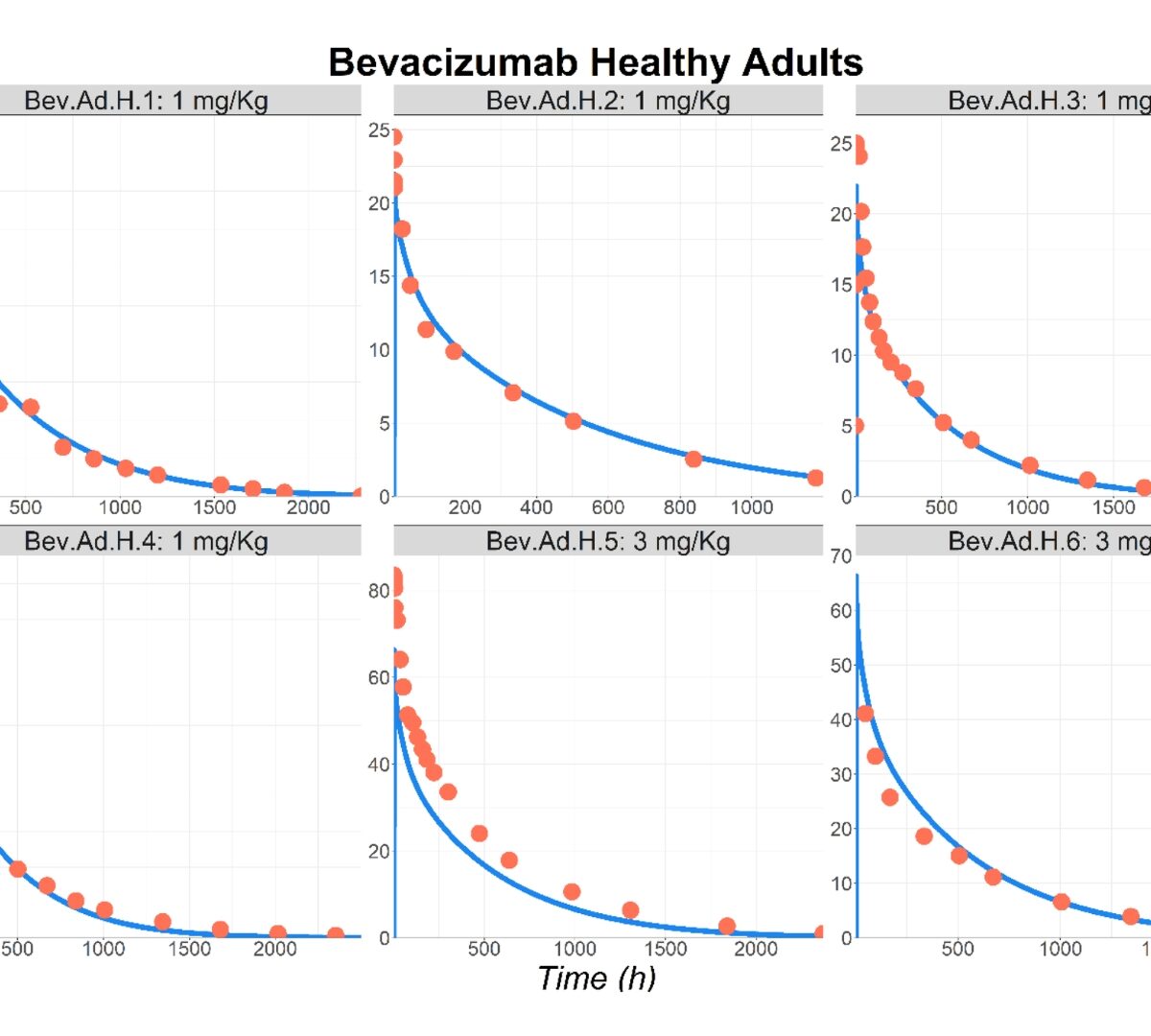
Prediction of Monoclonal Antibody Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Populations Using PBPK Modeling and Simulation
Accurately determining pediatric dosing is essential prior to initiating clinical trials or administering medications in routine clinical settings.
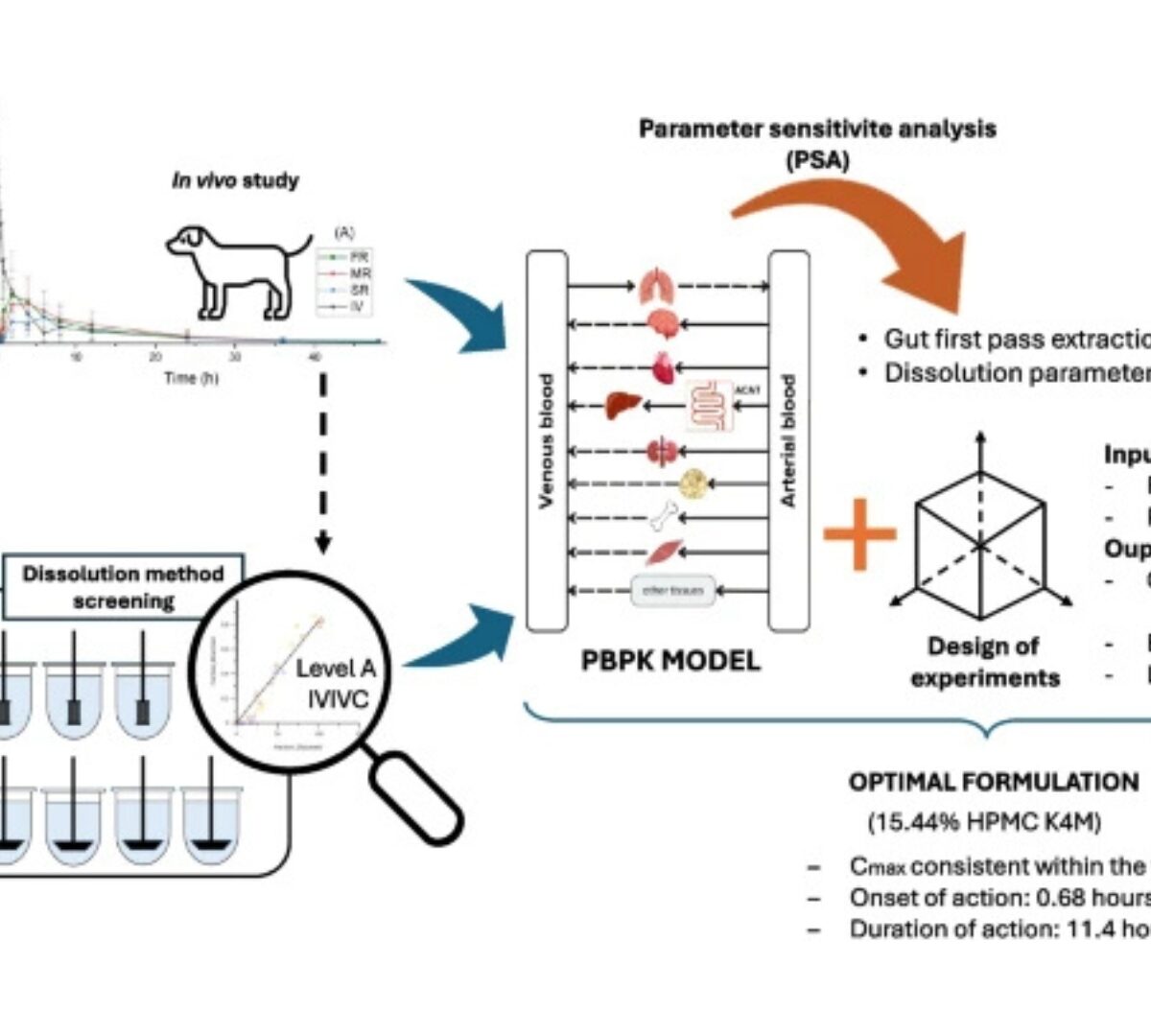
Optimizing Extended-release Formulation of l-tetrahydropalmatine Based on In Vivo Outcomes Using Integrated Modeling Approaches
l-Tetrahydropalmatine (l-THP) is a promising drug candidate for addiction treatment and needs to be delivered in extended-release dosage forms for safety and efficiency.
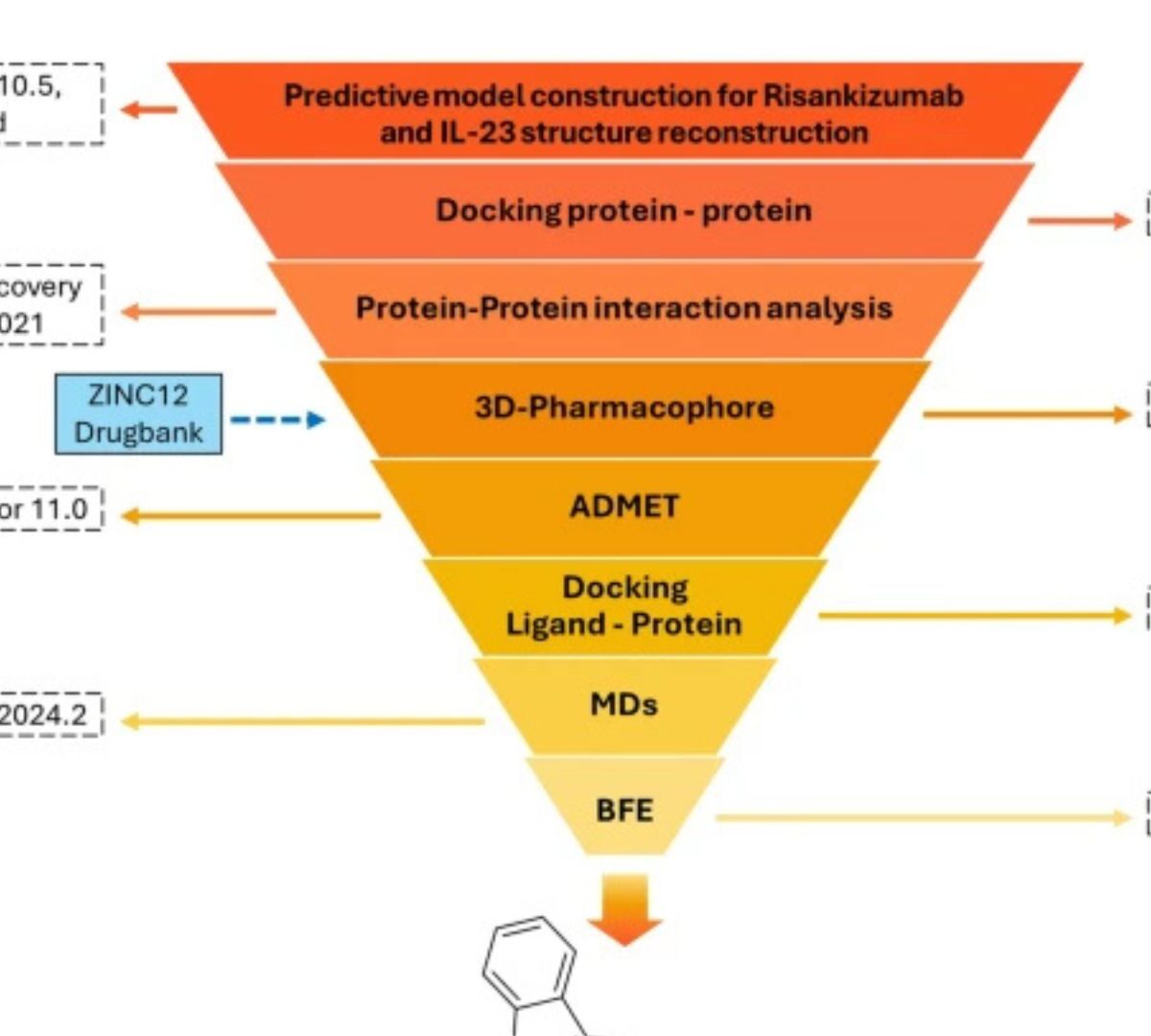
Structure-Based Screening of Small-Molecule Interleukin-23 Inhibitors Inspired by Monoclonal Antibody Interactions
Interleukin-23 (IL-23) is a key driver of chronic inflammatory diseases, yet current therapies rely on costly monoclonal antibodies.
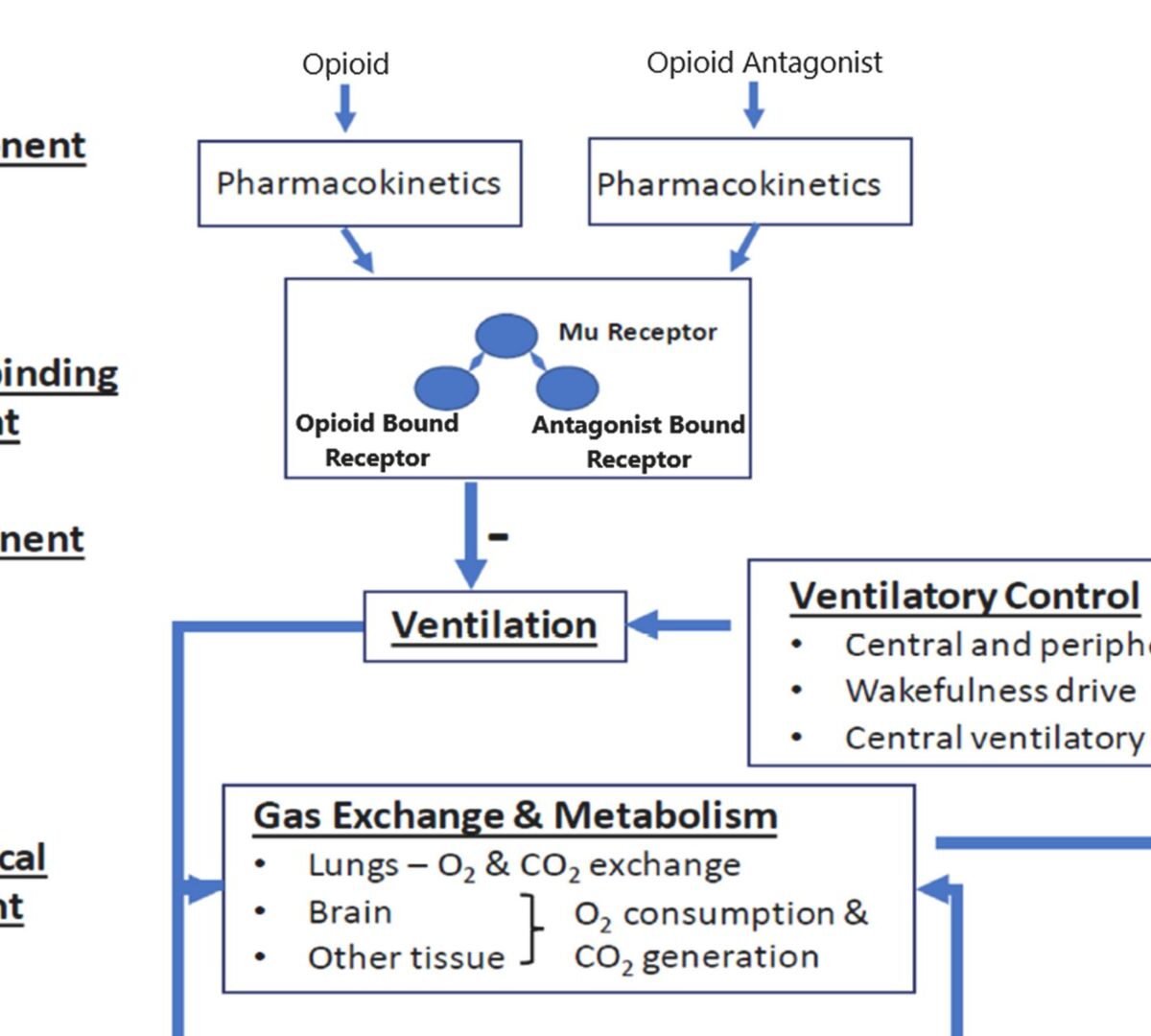
Reversal of a Synthetic Opioid Overdose: Insights From a Validated Translational Model
Synthetic opioids are linked to >90 % of opioid overdose deaths in the United States.
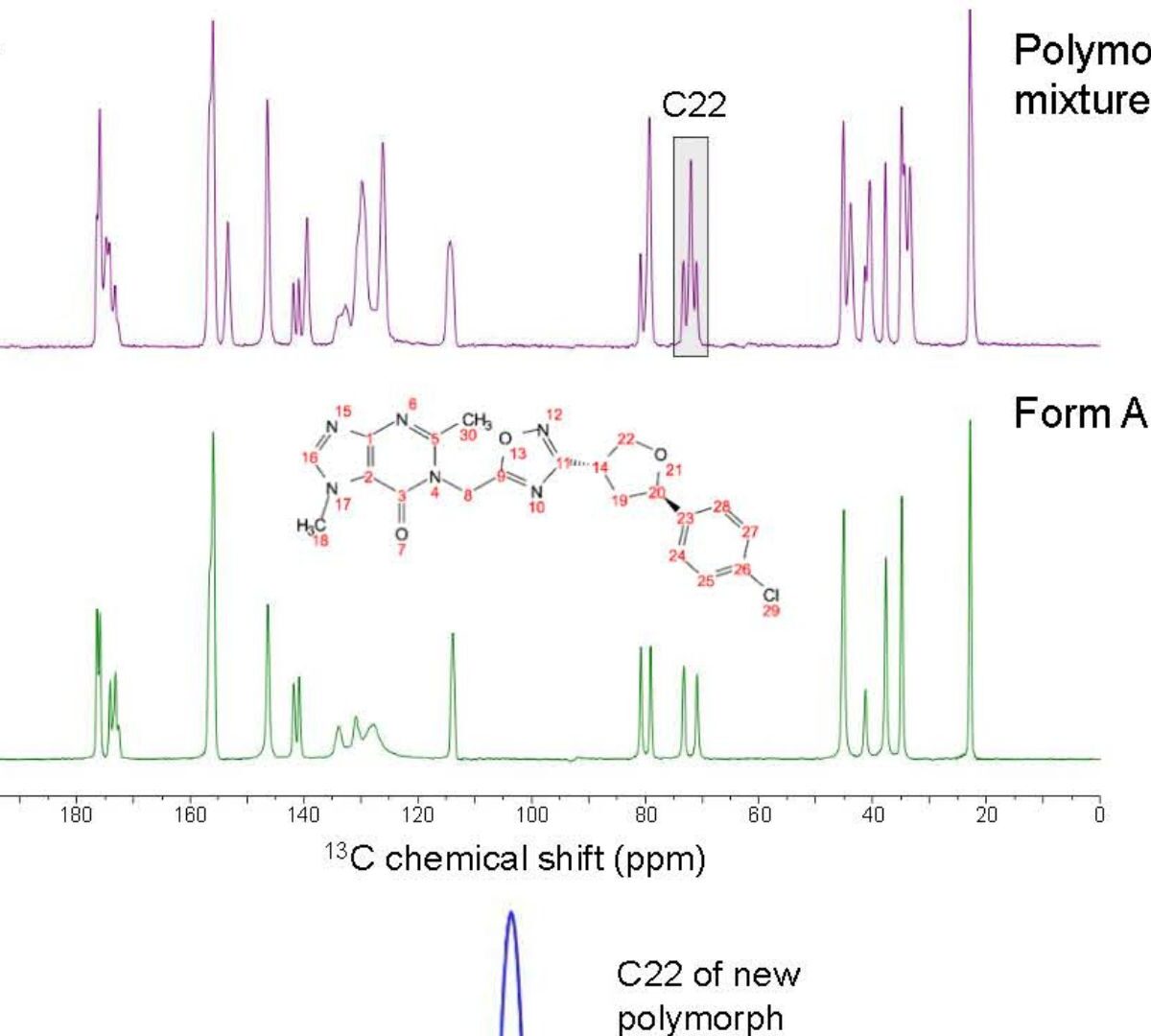
Solid-State Evaluation of a Newly Emerged Polymorph for Early-Stage Pharmaceutical Development
This work presents the solid-state evaluation of a new polymorph (Form M) discovered during the early-stage pharmaceutical development of a new chemical entity GDC-6599.

Identification of a Novel Indolizine RORγT Inverse Agonist Using the AI-Driven Drug Design Platform
Automated multiparameter optimization (MPO) at the point of initial drug design is a powerful emerging approach to improve and expedite drug development.
Establishing Virtual Bioequivalence and Bio-related Dissolution Specifications for Naproxen Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and in vitro Biorelevant Dissolution Testing
The aim of the present study was to assess the accuracy of the PBPK model in predicting the pharmacokinetic behavior of weakly acidic BCS class II drugs in humans through a multipronged approach of in vitro dissolution, in vivo studies, and in silico simulations.
Utilizing Metabolism-Based Structure-Activity Relationships and Biokinetic Modeling for Toxicological Evaluation: A Case Study on L-menthyl D-Lactate
Structure activity relationship (SAR) based read across uses existing toxicity data from an analog to predict the toxicity of a target chemical.