SHEN211 is a selective 3-chymotrypsin-like protease inhibitor that can protect against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
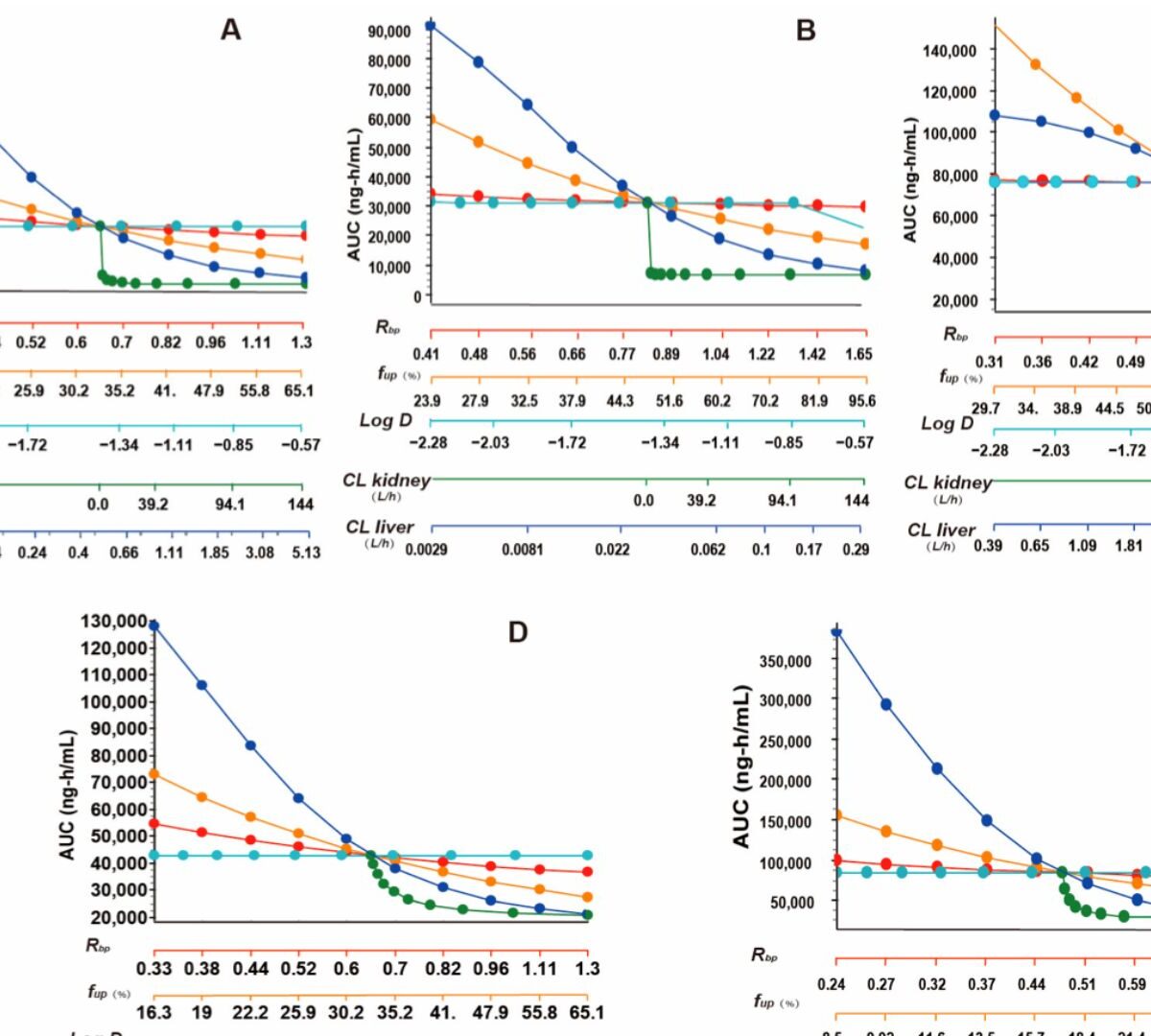
Tissue Distribution and Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Aztreonam Based on Multi-Species PBPK Model
As a monocyclic β-lactam antibiotic, aztreonam has regained attention recently because combining it with β-lactamase inhibitors helps fight drug-resistant bacteria.
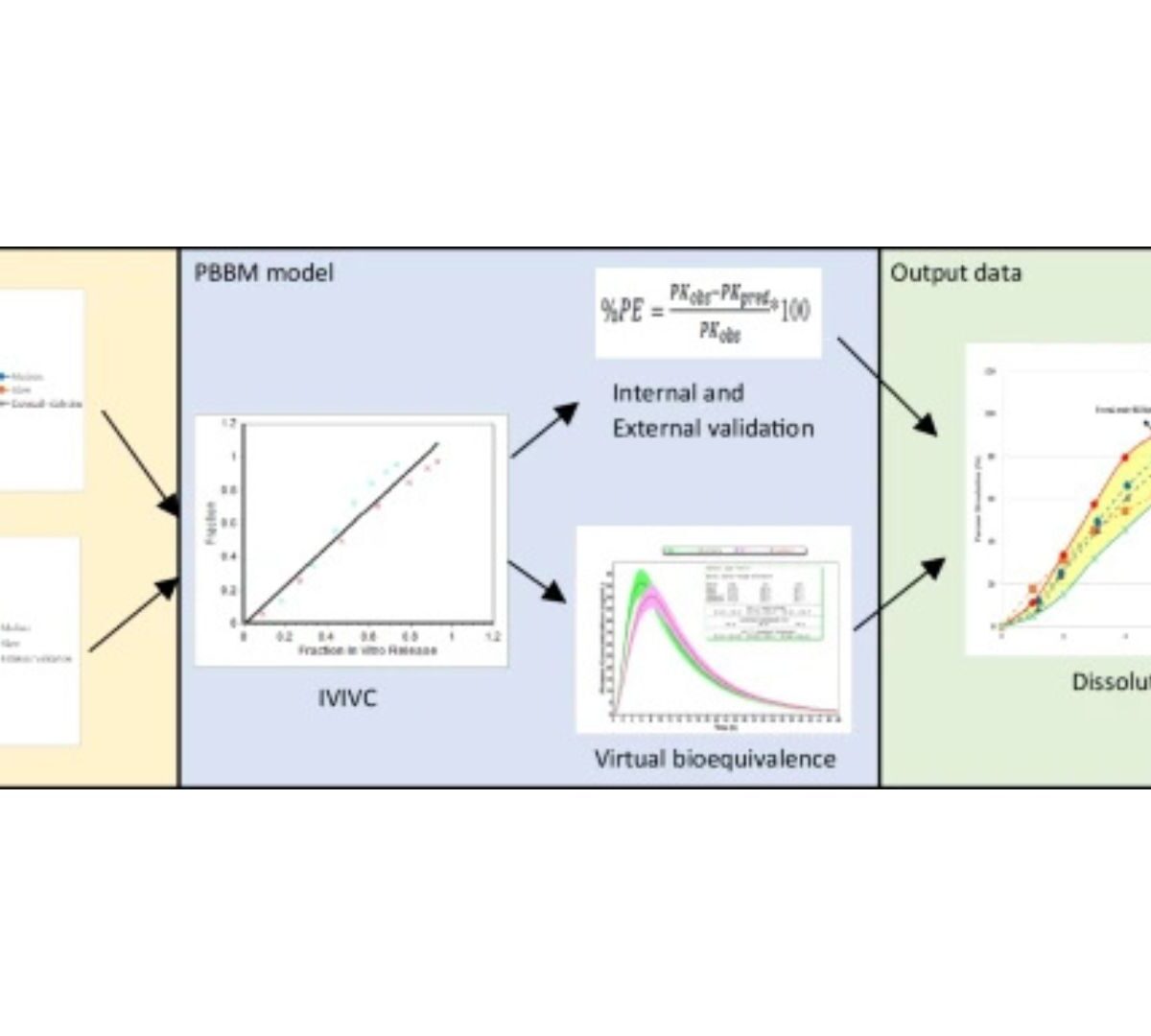
Application of Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) to Establish Clinically Relevant Dissolution Specifications for a Prolonged Release Tablet Formulation of Verapamil, a BCS Class I Drug
Our work aimed at setting clinically relevant dissolution specifications for a prolonged release formulation of verapamil, a BCS Class I drug.
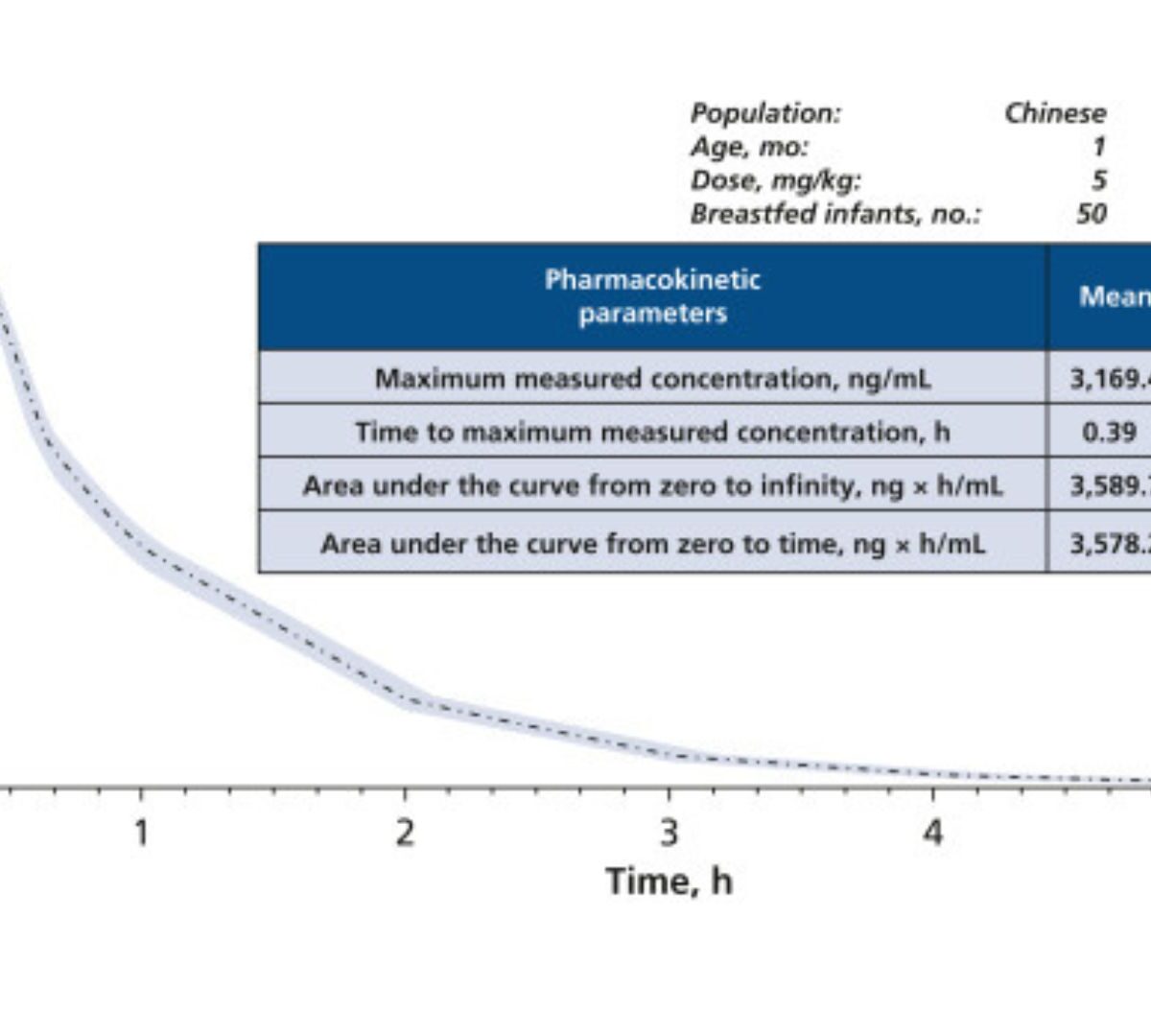
Assessing Whether Breastfeeding is Safe After an Intraoral Injection of 68 mg of Articaine
Limited information is available about the transfer of articaine into breast milk and the associated risks to breastfed infants.

Using Model Master Files to Support Oral Drug Product Development and Regulatory Submissions
This report summarizes the proceedings of Session 2 of the two-day public workshop titled “Considerations and Potential Regulatory Applications for a Model Master File” hosted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Center for Research on Complex Generics (CRCG) on May 2–3, 2024.
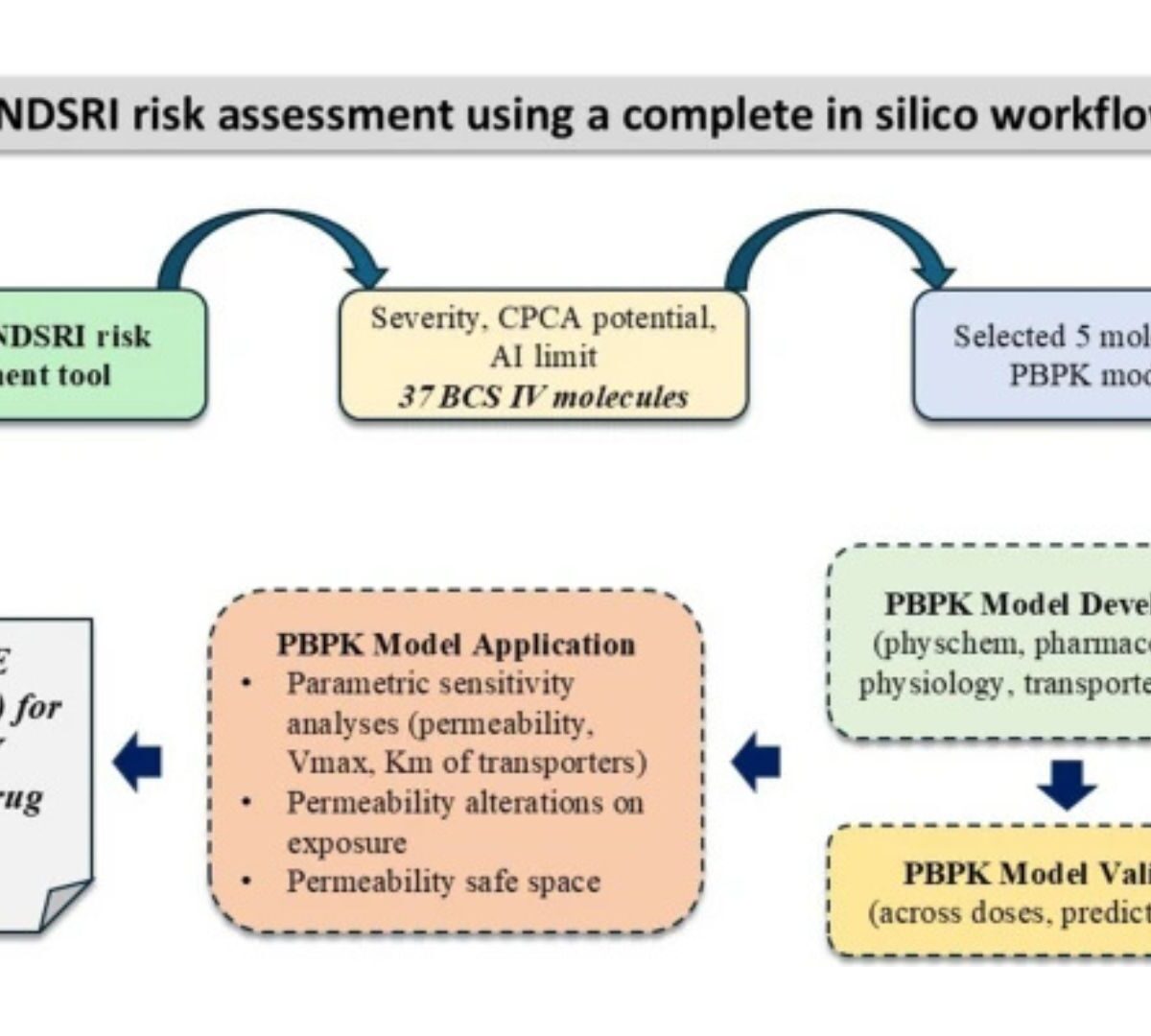
Nitrosamines Risk Assessment for Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class IV Molecule Containing Immediate Release Products: Use of In-Silico Prediction Tools and Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling
Nitrosamines drug substance related impurities (NDSRI) are organic impurities, highly potent mutagenic substances that are classified as human carcinogens.
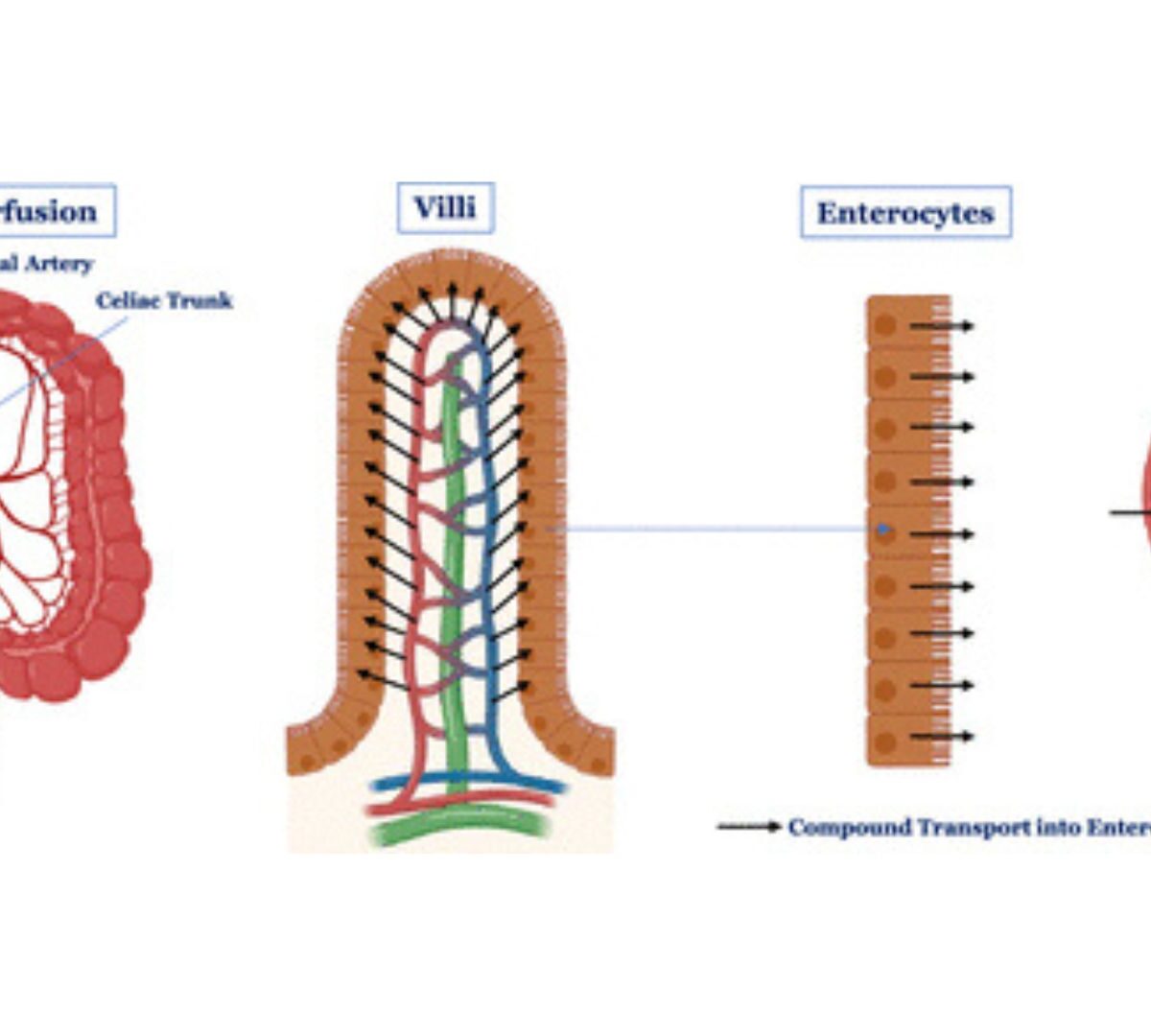
Intestinal Secretion Is a Potentially Important Clearance Mechanism for Low Metabolic Clearance Compounds
Intestinal excretion/secretion (IE) from the systemic circulation via the enterocytes into the intestinal lumen has traditionally been considered a minor clearance (CL) pathway.
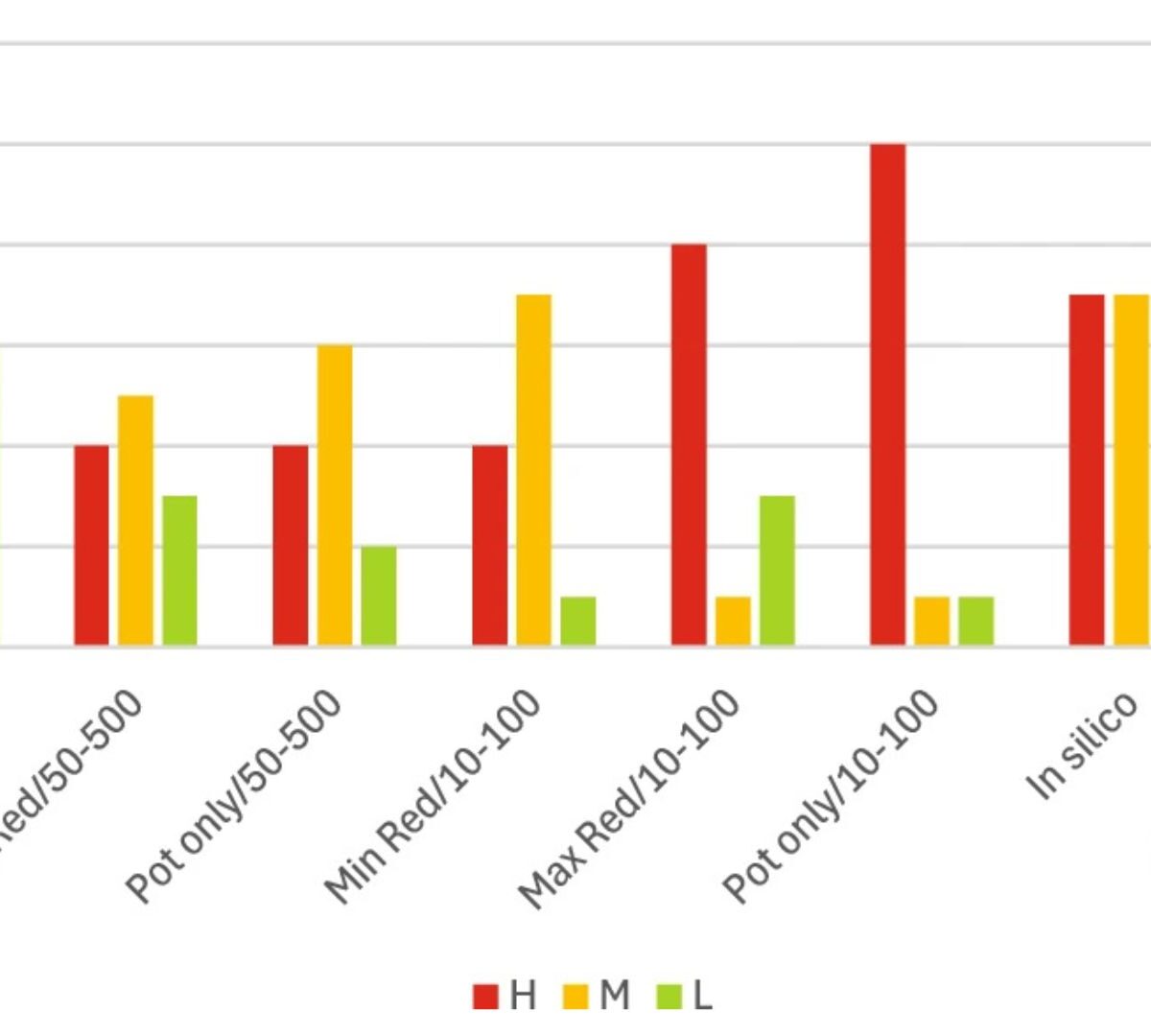
Framework for Classifying Chemicals for Repeat Dose Toxicity Using NAMs
EPAA’s ‘NAM Designathon 2023’ challenge for human toxicity sought to identify a classification system capable of categorising chemicals based on their bioactivity and bioavailability properties determined using non-animal methodologies (Worth et al. 2025).

Multi-target Property Prediction and Optimization Using Latent Spaces of Generative Model
Multi-target property prediction has the potential to improve generalization by exploiting the positive transfer between targets.
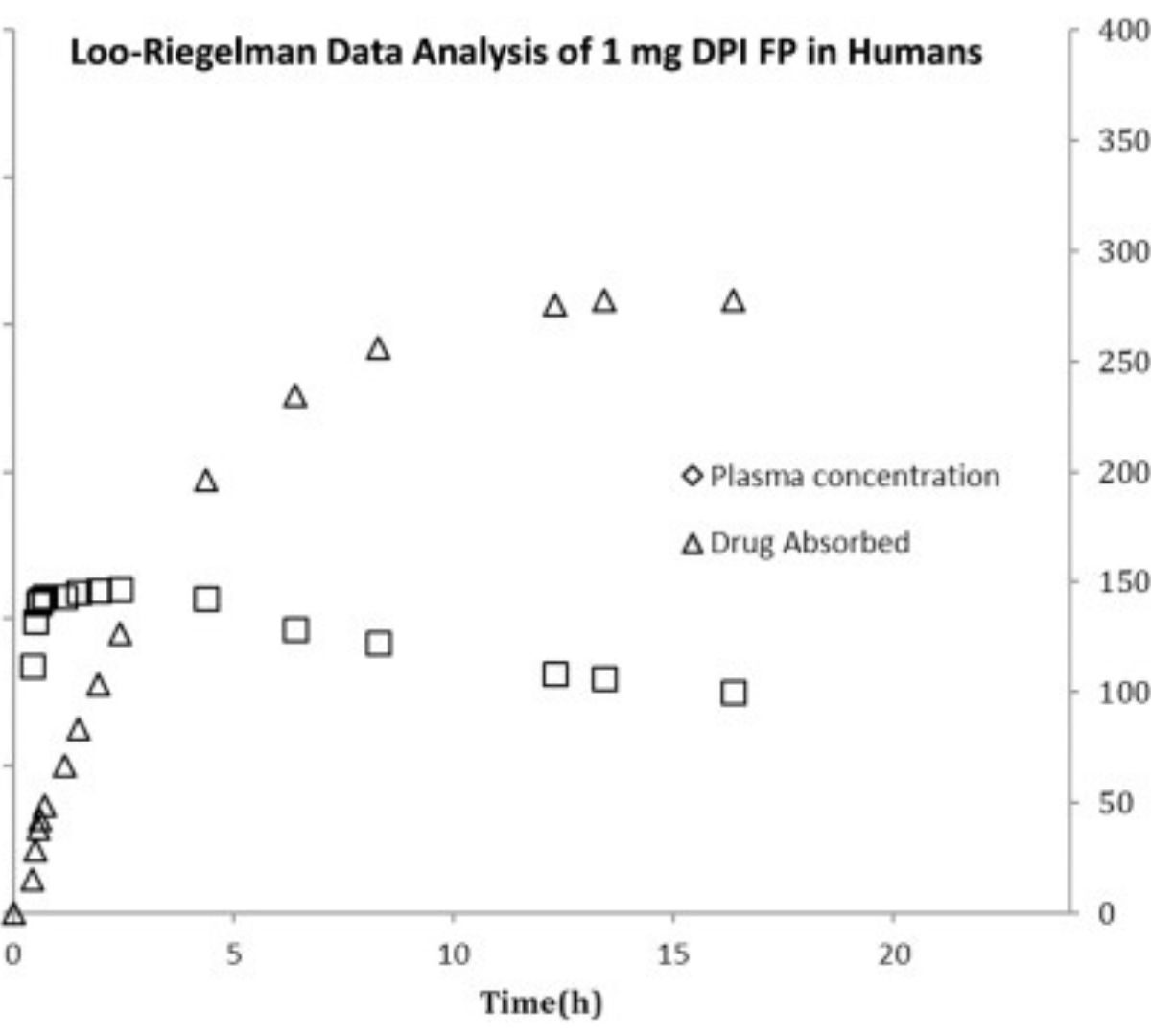
Investigation of the Suitability of Utilizing Plasma Concentration as a Surrogate to Understand Lung Exposure of Inhaled Drug in Rats: Different Delivery Methods of Fluticasone Propionate
Pulmonary diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are complex human airway diseases that affect millions of people worldwide.

From Lab-to-Clinic with Model Informed Formulation Development: a Case Study of Hydroxyzine SR Tablets
Model Informed Formulation Development (MIFD) uses physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling and other in silico tools to facilitate new product development.
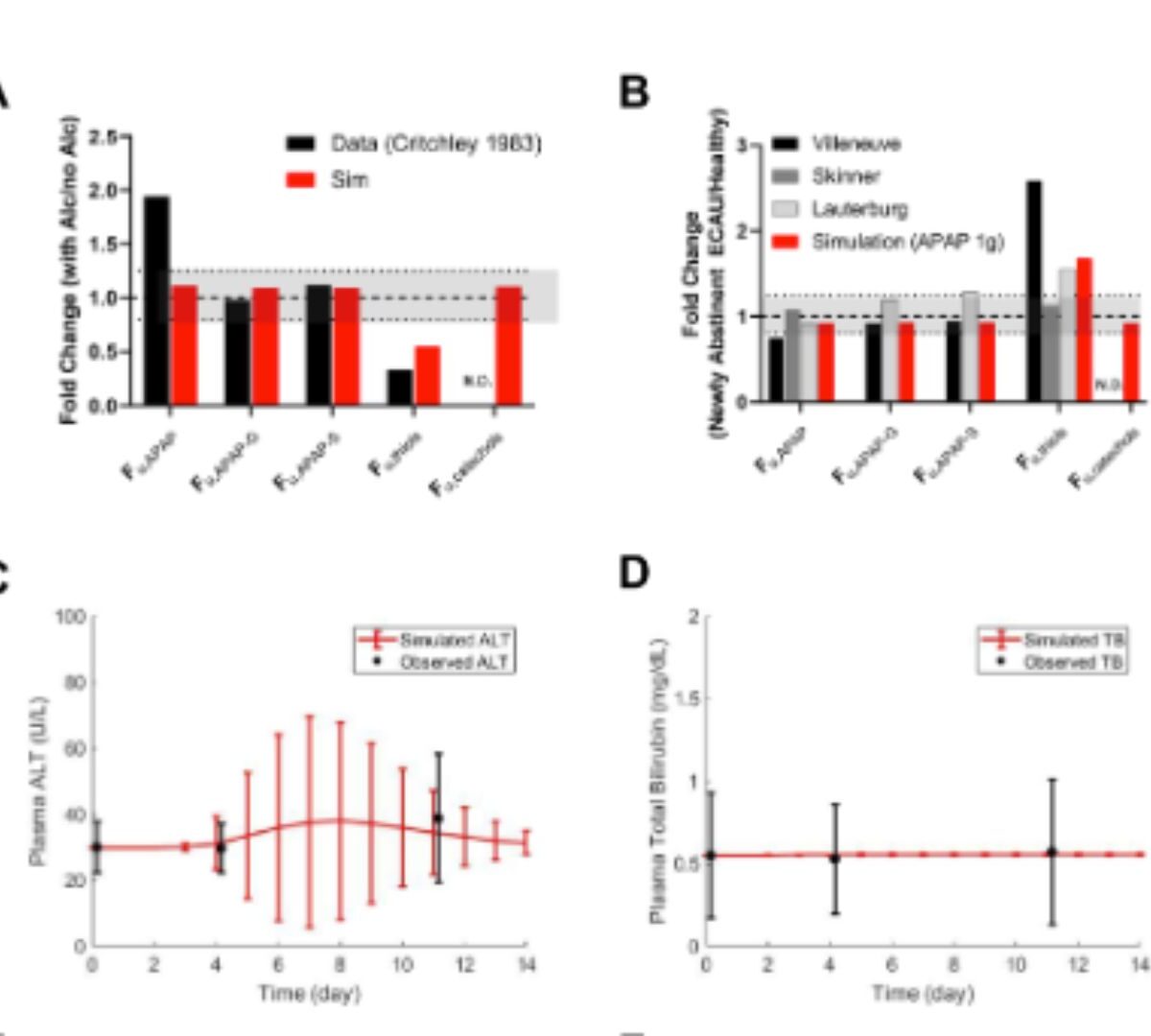
Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling of Acetaminophen Pharmacokinetics and Hepatic Biomarkers After Overdoses of Extended-Release and Immediate-Release Formulations in Adults With Chronic Alcohol Use or Low Glutathione
Acetaminophen (APAP), an over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic, can cause hepatotoxicity when ingested in large overdoses.
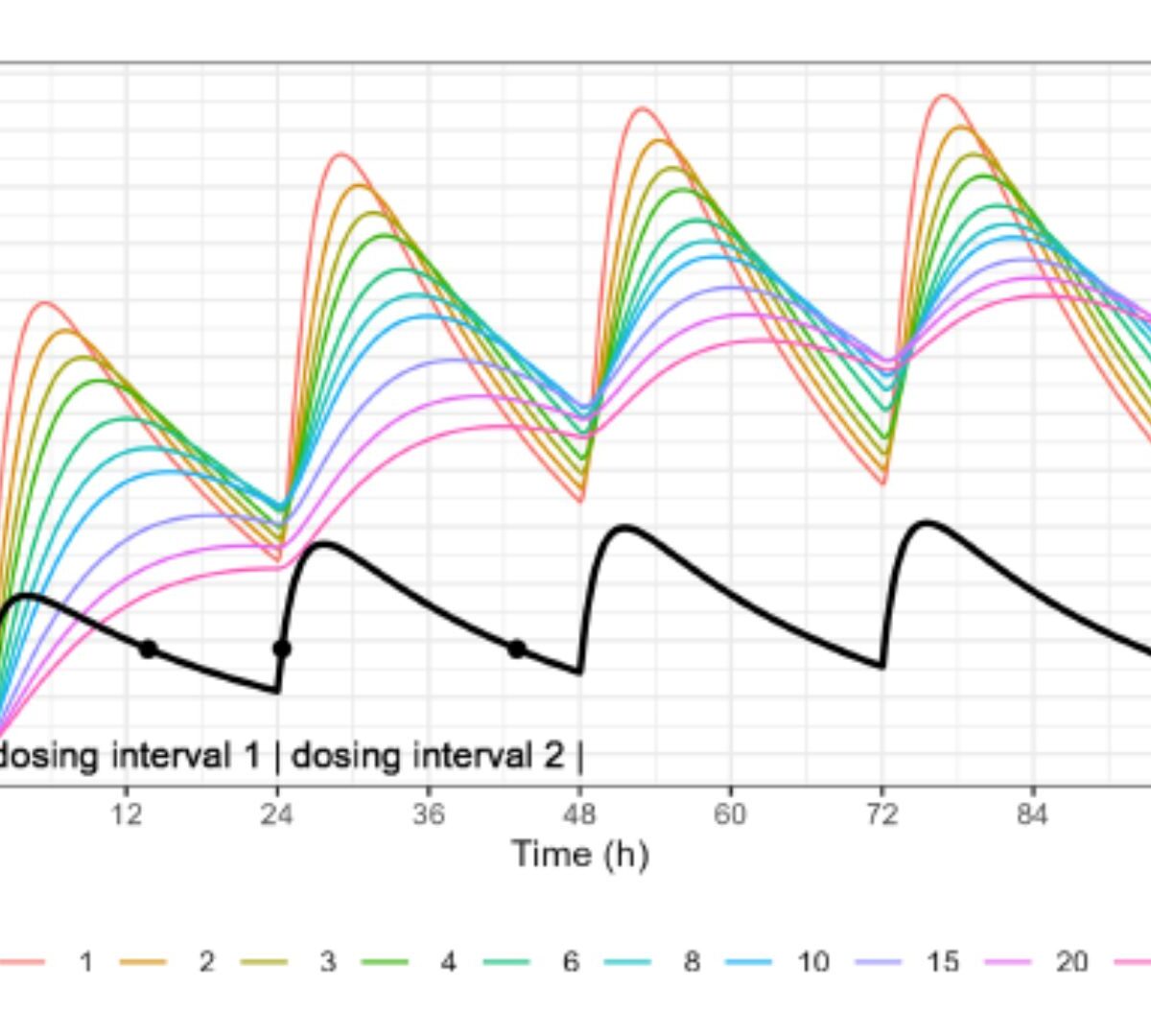
Beyond the Linear Model in Concentration-QT Analysis
This work introduces several extensions for concentration-QT modeling in a pharmacometric context.
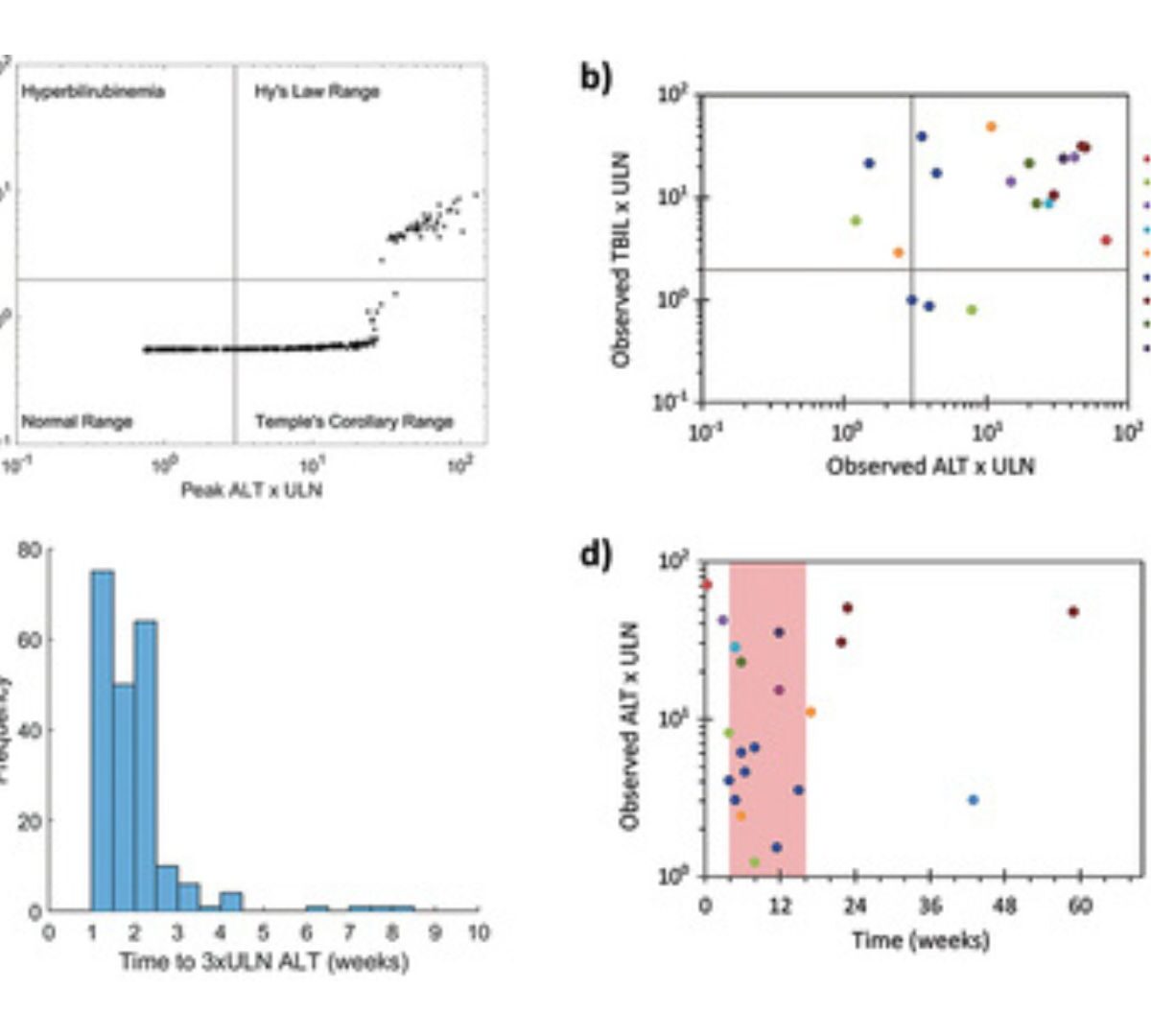
A Well-Characterized Mechanistic Model for Exploring Known or Hypothesized T cell Mediated Drug Induced Liver Injury: Current Capabilities and Challenges for Future Predictivity
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is an adverse event whose emergence can slow or halt drug development programs.
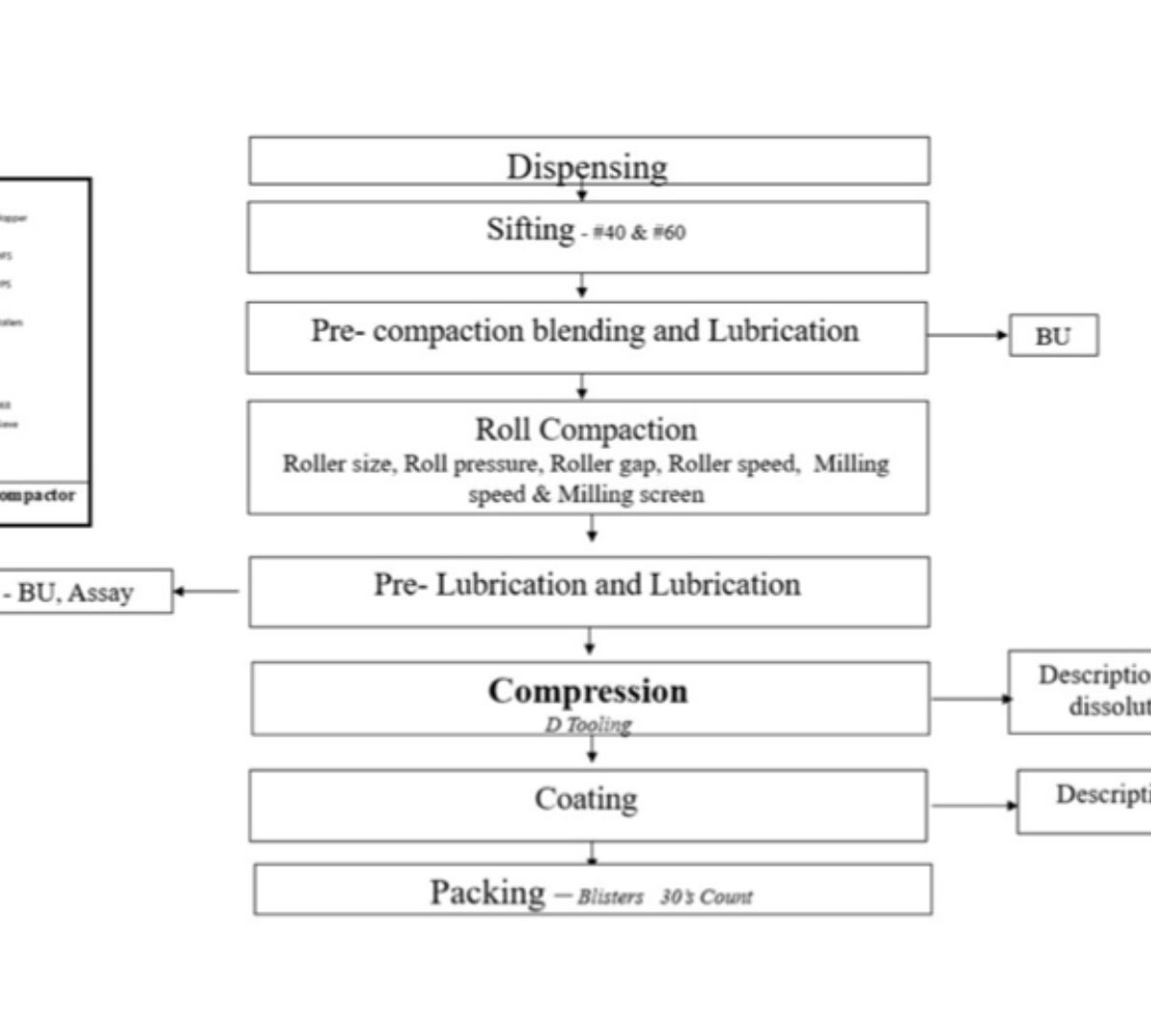
Model Integrated Evidence Approach for Rational and Safe Formulation Development: case of alfuzosin prolonged-release tablets
The model integrated evidence (MIE) approach aims to utilize simulation tools like physiologically based biopharmaceutic model (PBBM) or physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for the development of new drugs and generic formulations.
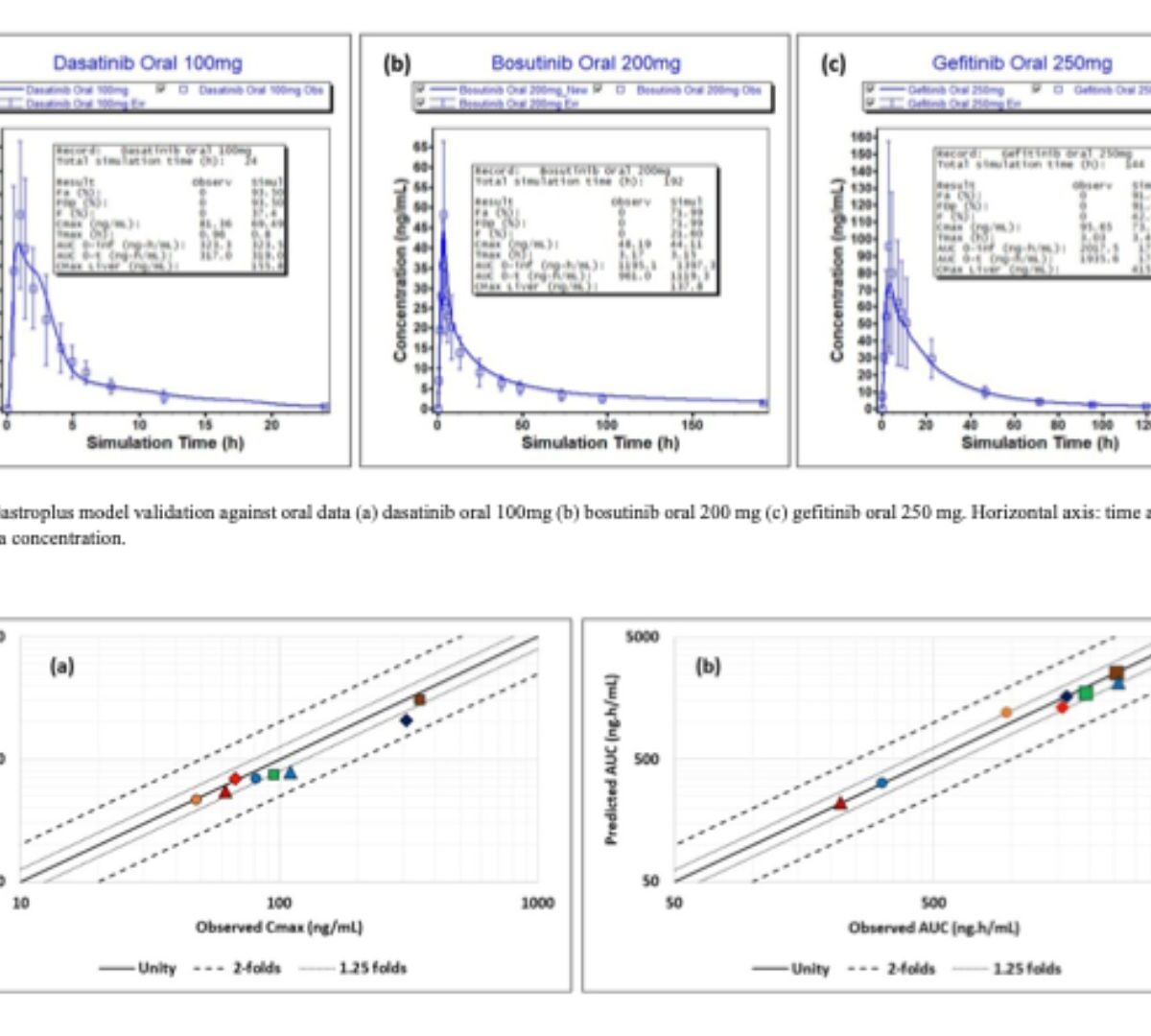
Role of Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling in Predicting and Circumventing the Drug-Drug Interactions of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with Acid-Reducing Agents
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are molecular targeting agents used to treat various types of cancer. During the treatment with TKIs, acid-reducing agents (ARAs) are prescribed to prevent gastric mucosal damage.
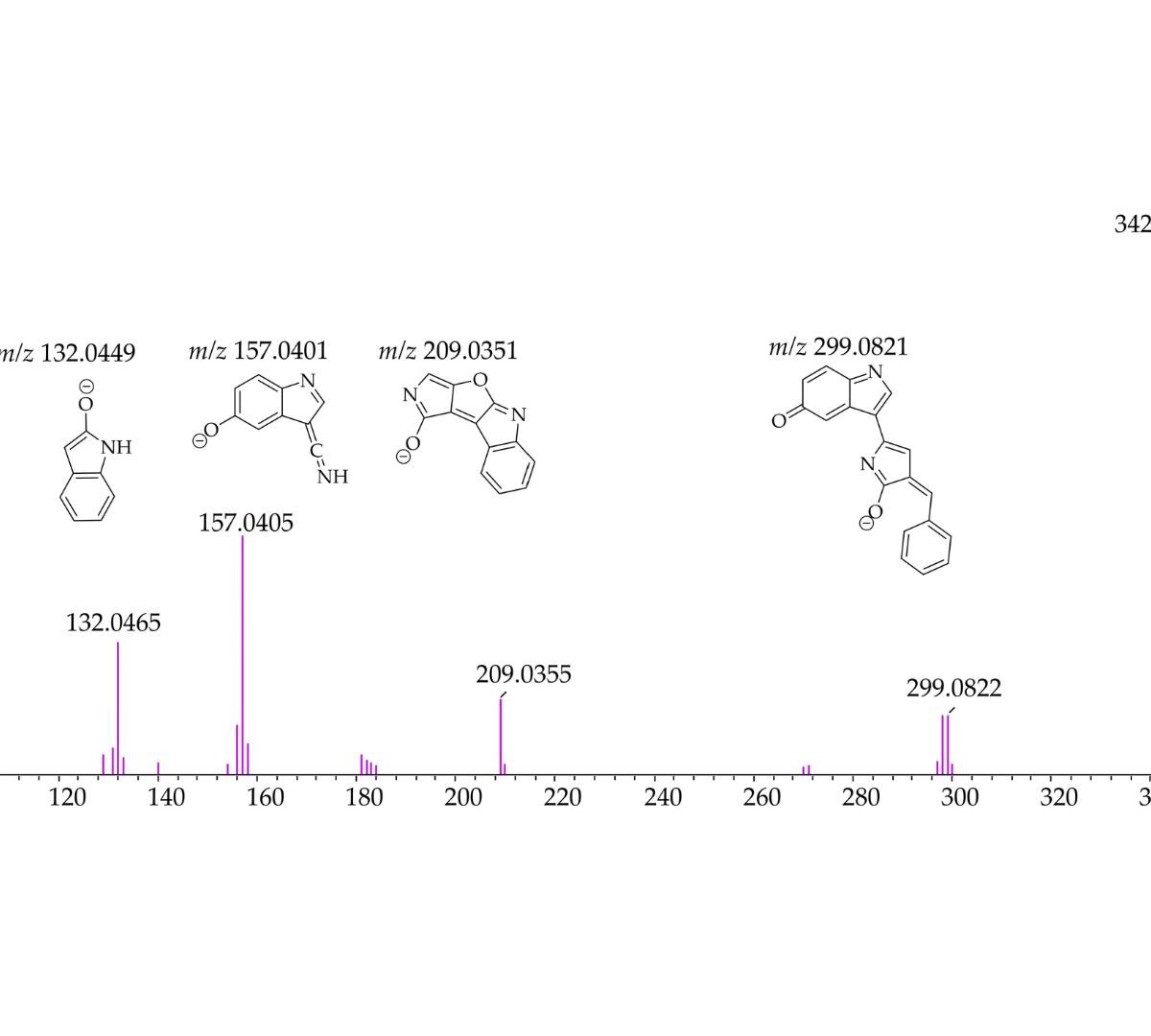
Evaluation of Violacein Metabolic Stability and Metabolite Identification in Human, Mouse, and Rat Liver Microsomes
Malaria significantly impacts the health of populations living in poverty and vulnerable conditions. Resistance to current antimalarial drugs remains a major challenge and highlights the urgent need for novel, effective, and safer therapies.
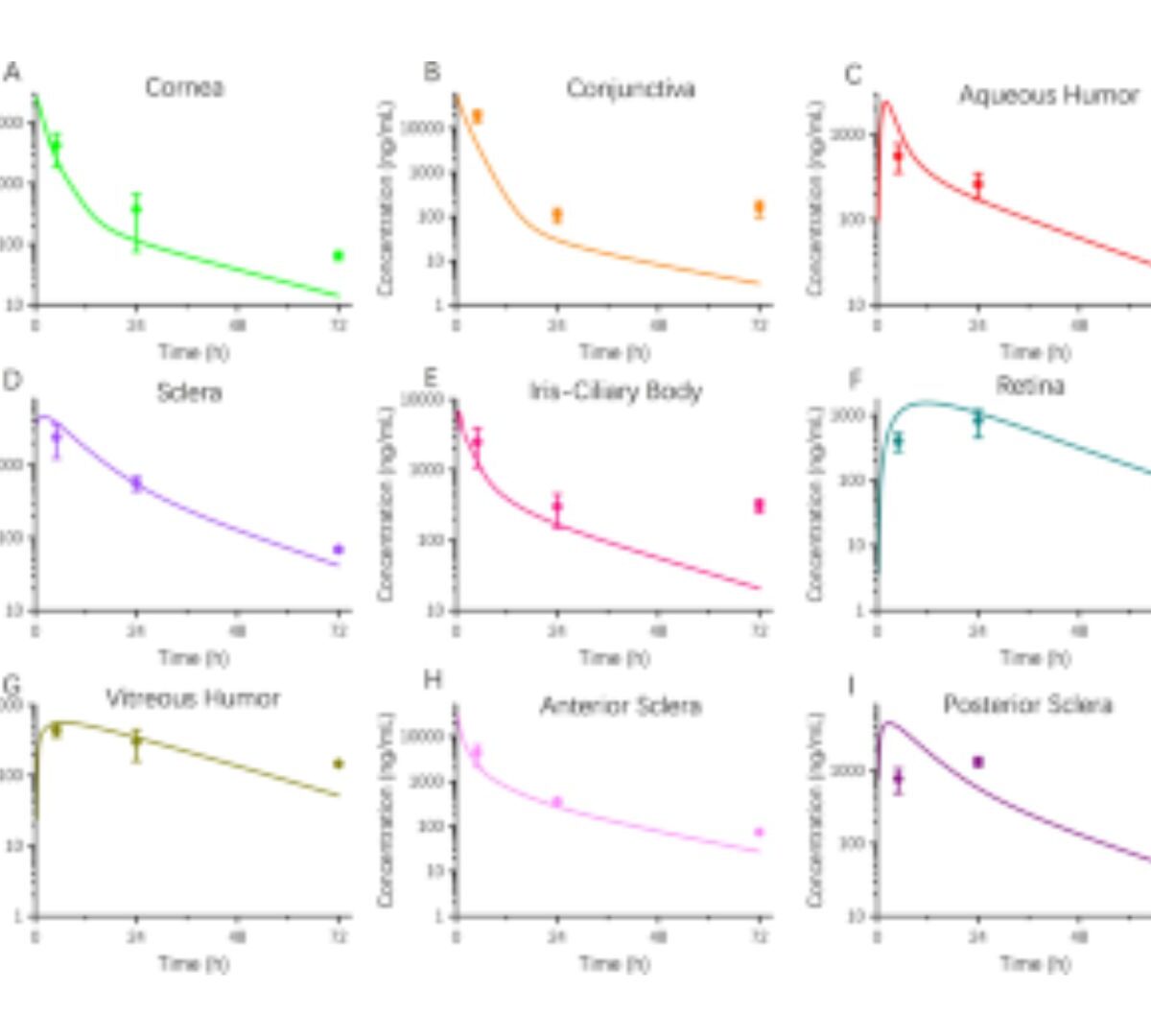
An Ocular Exposure Prediction for Topical Atropine in Human Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling
Developing a mathematical model to predict the distribution and bioavailability of atropine in human eyes is an insight approach for clinical practice.
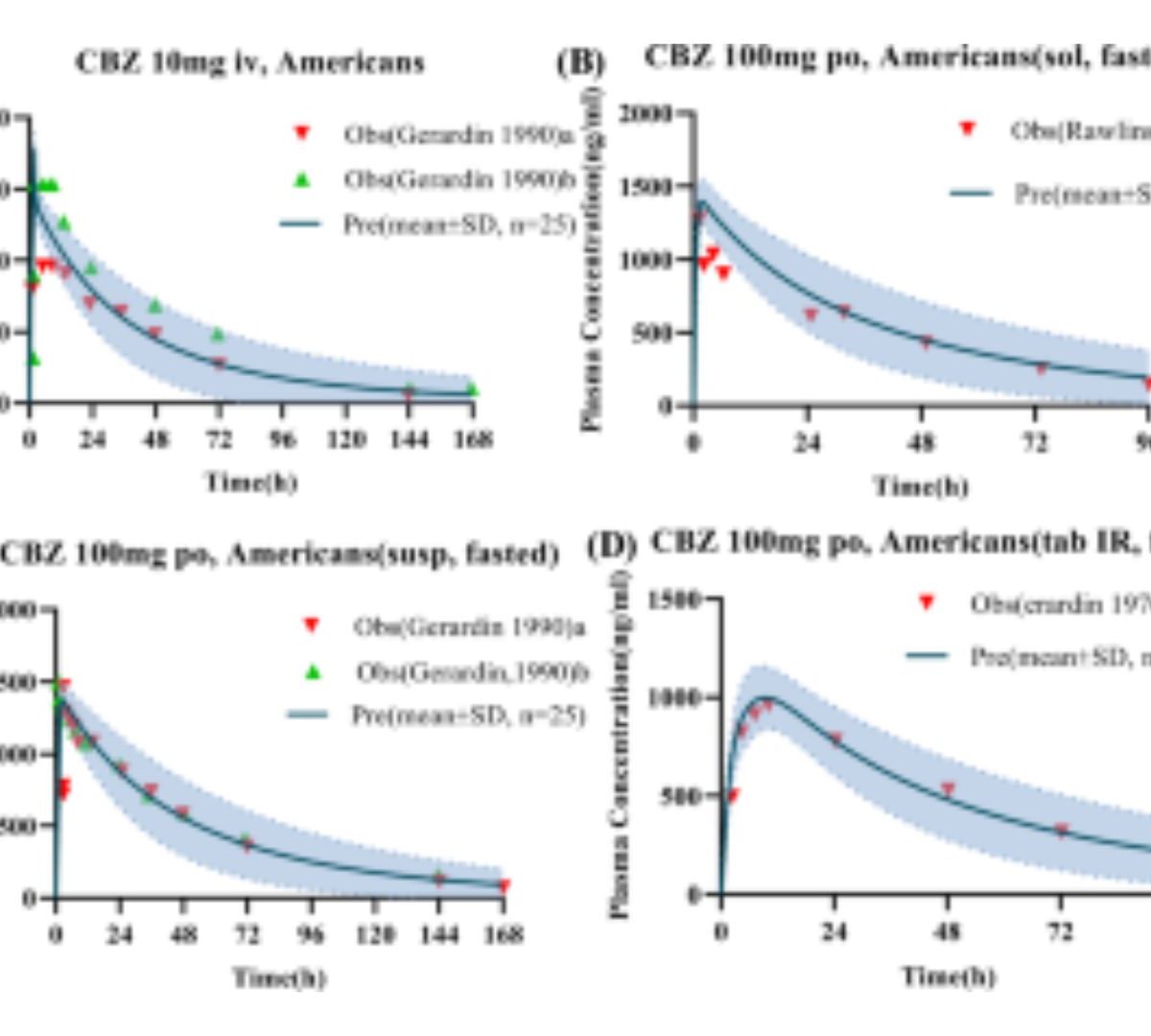
Establishing Clinically Relevant Specifications for Carbamazepine Tablets Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling
The purpose of this study was to establish a clinically relevant specification for carbamazepine (CBZ) tablets, a classic narrow therapeutic index drug (NTID), within the Chinese population.
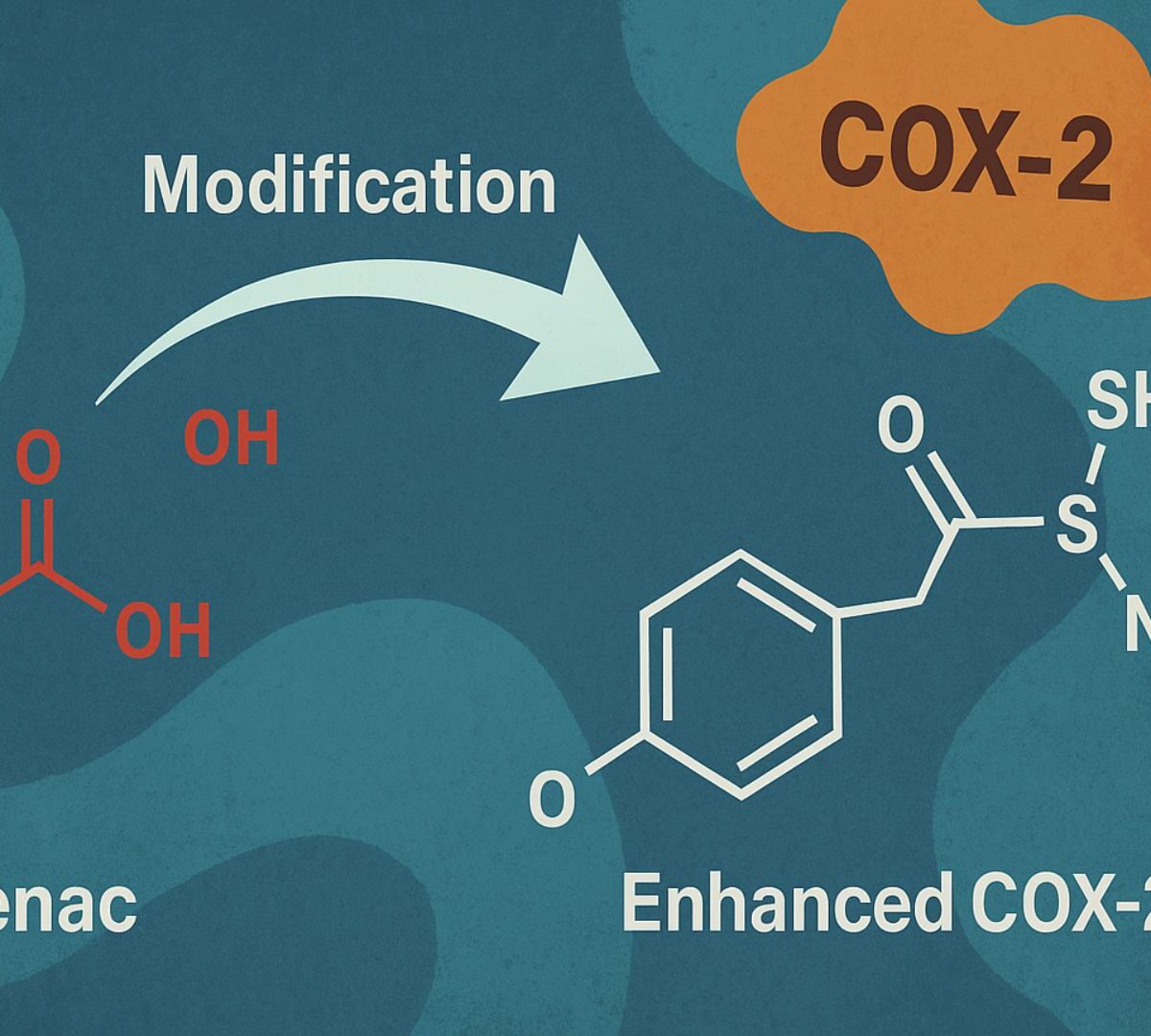
Structural Modification of Aceclofenac to Design Enhanced COX-2 Inhibitors: A Medicinal and Toxicological Study
Aceclofenac (ACF) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), prescribed for treating pain and inflammation.

![Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion of [14C]SHEN211, a Nonpeptidic Small-Molecule 3CLpro Inhibitor, in Rats](https://www.simulations-plus.com/wp-content/uploads/ChatGPT-Image-Jul-15-2025-at-03_34_17-PM-1200x1024.jpg)