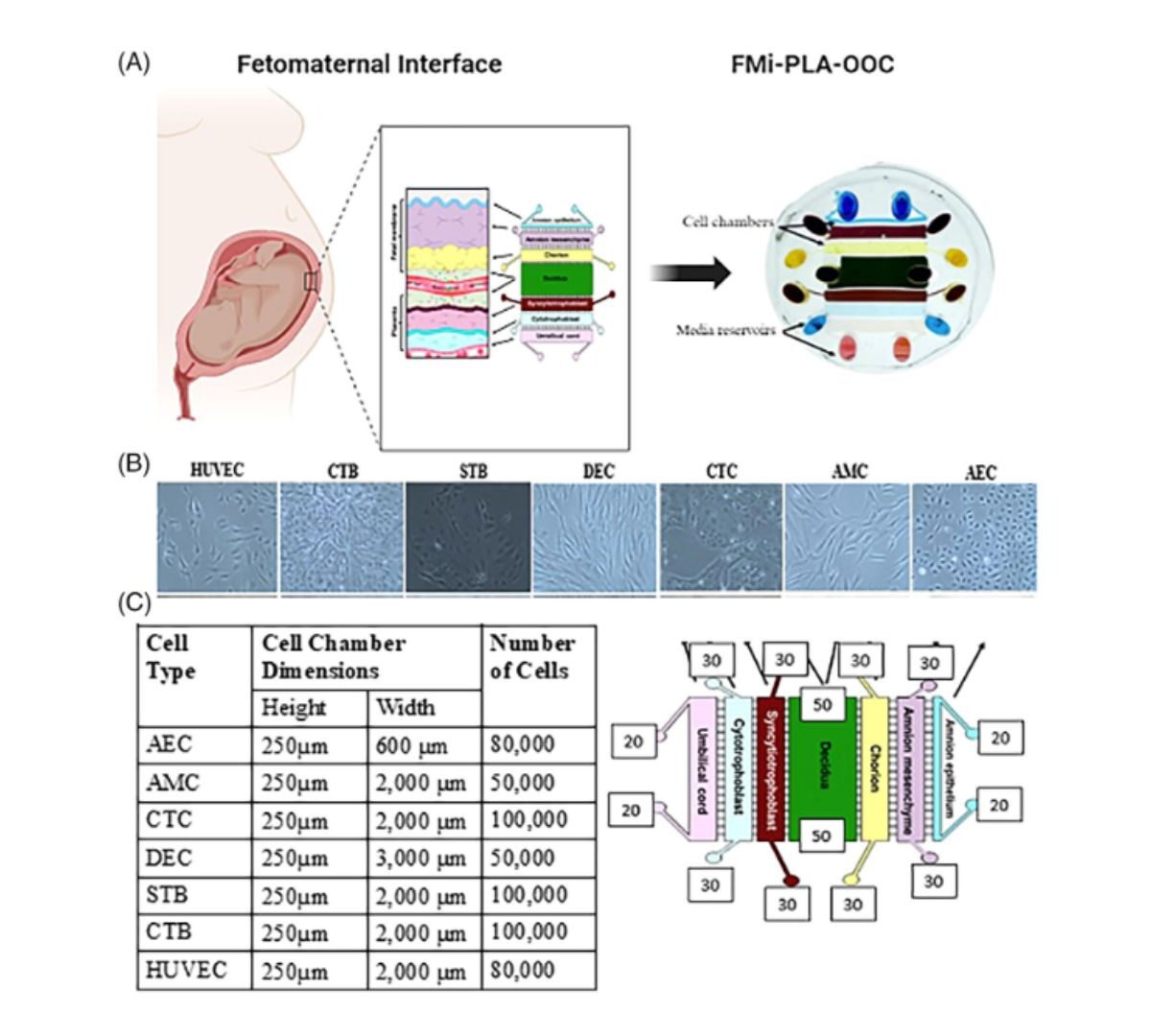
Pregnant and lactating people remain therapeutic orphans as they are often excluded from clinical trials, remaining one of the most therapeutically vulnerable.
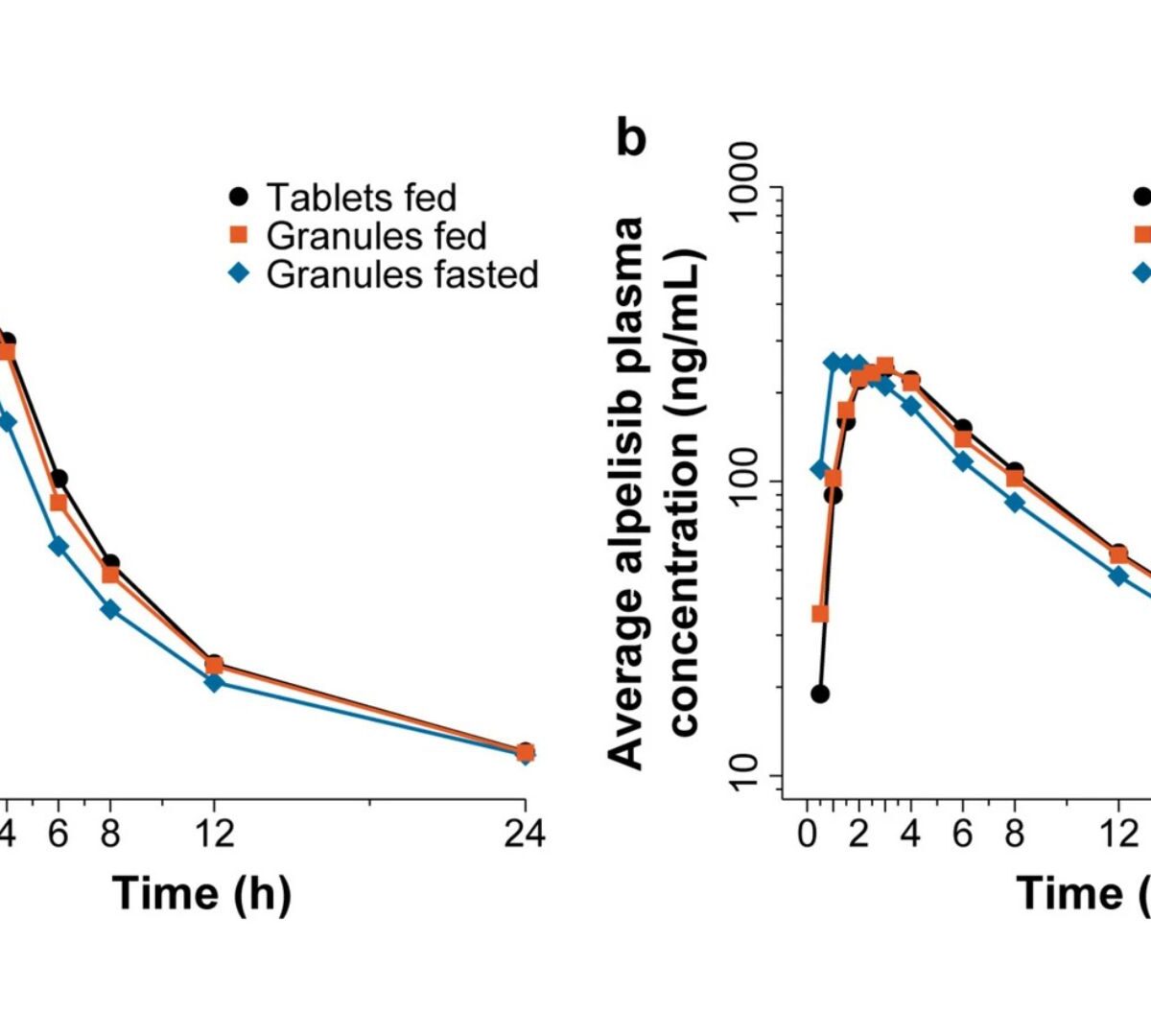
Predicting and Confirming Bioequivalence of Alpelisib Oral Granules and Tablets for Patients With PIK3CA-Related Disorders
Alpelisib, an oral α-specific phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, has been shown to be safe and effective for some patients with gain-of-function mutation in the PIK3CA oncogene
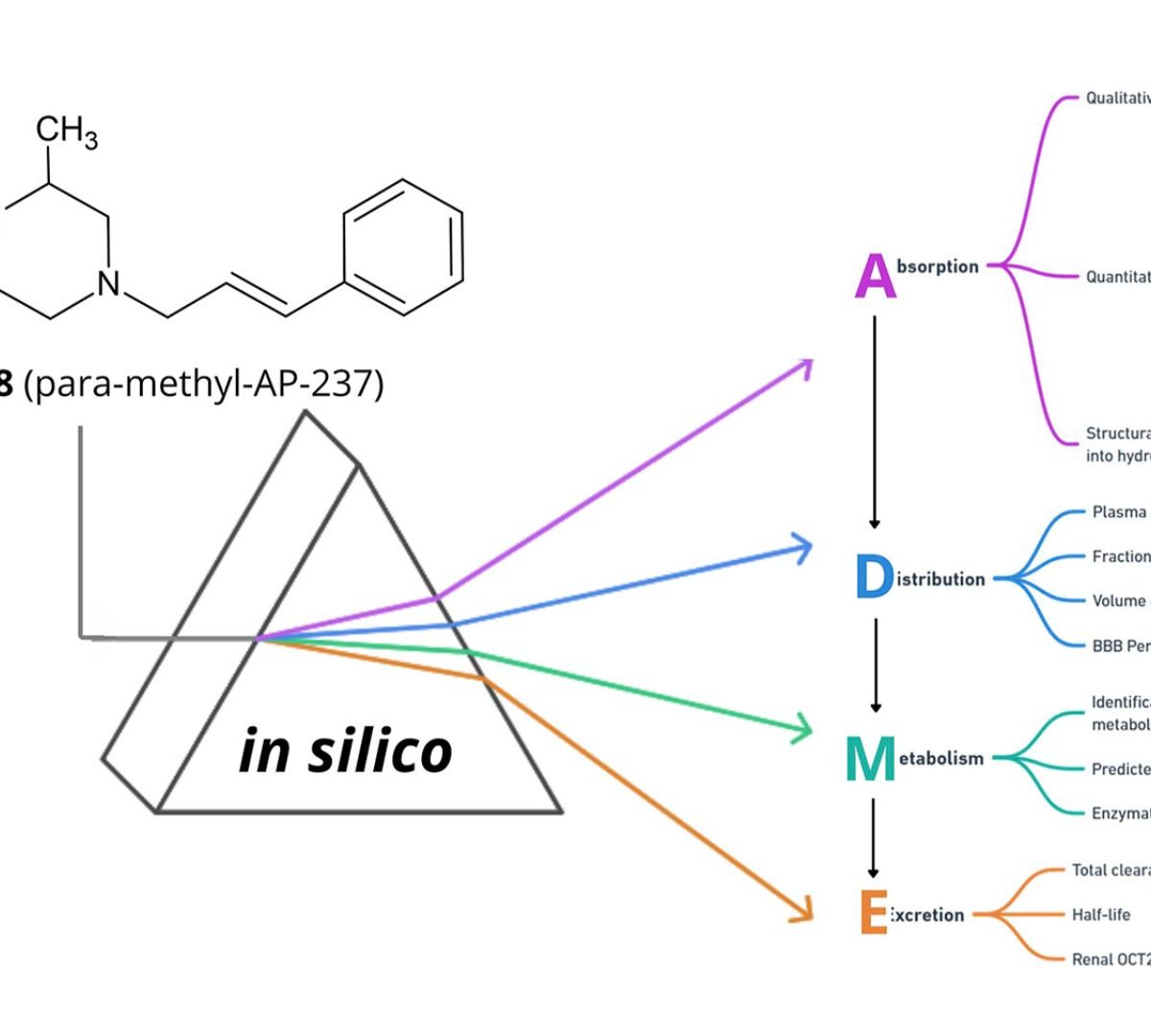
ADME profile of AP-238 – opioid designer drug (CAS: 140924-11-4): first application of multi-in silico approach methodology for comprehensive prediction of ADME profile (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion) important for clinical toxicology and forensic purposes
AP-238 is a recently emerged opioid designer drug from the cinnamylpiperazine class, raising increasing concern in forensic and clinical toxicology due to its potential for abuse and limited ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) profile.

Population Pharmacokinetics and Clinical Evaluation of Intravenous Acetaminophen and Its Metabolites in Andalusian Horses
To date, no intravenous pharmacokinetics (PK) studies have assessed acetaminophen or its major metabolites (acetaminophen-glucuronide and acetaminophen-sulphate) in horses.
Extrapolation of Midazolam Disposition in Neonates Using Physiological-Based Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modeling
There is a shortage of data in clinical studies of neonatal populations, which often utilize extrapolation strategies and model simulation techniques to support drug development and clinical applications.

Utilizing Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models to Support Rational Medication in Chinese Elderly Population
China is undergoing a pronounced shift towards an aging society, wherein the elderly constitute a prominent demographic relying significantly on medications.

Design and Development of Sulfenylated 5-Aminopyrazoles as Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase: Exploring the Implication for Aβ1–42 Aggregation Inhibition in Alzheimer’s Disease
Current therapeutic regimens approved to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD) provide symptomatic relief by replenishing the acetylcholine levels in the brain by inhibiting AChE.

Formulation Strategy of BCS-II Drugs by Coupling Mechanistic In-Vitro and Nonclinical In-Vivo Data with PBPK: Fundamentals of Absorption-Dissolution to Parameterization of Modelling and Simulation
BCS class II candidates pose challenges in drug development due to their low solubility and permeability.

Rat-to-Human PBPK Model of U-47700: Unveiling Pharmacokinetic Risks of a Synthetic Opioid Through Interspecies Extrapolation
U-47700, a synthetic μ-opioid receptor agonist and emerging new psychoactive substance, poses critical public health risks due to its high abuse liability and fatal overdose potential.

From In Vivo Predictive Dissolution to Virtual Bioequivalence: A GastroPlus®-Driven Framework for Generic Candesartan Cilexetil Tablets
Candesartan cilexetil, a Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) II prodrug, demonstrates compromised bioavailability attributable to its limited aqueous solubility coupled with P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated efflux and hepatic first-pass metabolism, thereby introducing complexities in generic drug bioequivalence assessments.

Mode of Action Approach Supports a Lack of Carcinogenic Potential of Six Organic UV Filters
Ultraviolet (UV) filters, the active ingredients in sunscreens, have been used for several decades to reduce the risk of acute and chronic damage to the skin from solar UV radiation, which can lead to skin cancer.

Mode of Action Approach Supports a Lack of Carcinogenic Potential of Six Organic UV Filters
Ultraviolet (UV) filters, the active ingredients in sunscreens, have been used for several decades to reduce the risk of acute and chronic damage to the skin from solar UV radiation, which can lead to skin cancer.

Development of a Biorelevant Dissolution Method for Inhalation Products: Proof of Concept Using Drugs with Diverse Solubilities
Due to their unique application and action, inhalation products require specific quality tests, such as Uniformity of Delivered Dose and Aerodynamic Assessment of Fine Particles.

Thermodynamics-Informed Neural Networks and Extensive Data Sets: Key Factors to Accurate Blind Predictions of Apparent pKa Values in the EuroSAMPL Challenge
Microscopic and macroscopic pKa values for 35 compounds selected by the organizers of euroSAMPL 1 challenge were blindly predicted with our thermodynamics-informed empirical S + pKa model (ranked submission 0x4cb7101f).

Anxiety Disorders, PTSD and OCD: Systematic Review of Approved Psychiatric Medications (2008–2024) and Pipeline Phase III Medications
This systematic review examines psychiatric medications approved by the FDA for anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) from 2008 to 2024 and describes the mechanism of action, indications for both labelled and off-label uses, evidence for efficacy, dosing and adverse effects for each medication.

Advances in Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling and its Regulatory Utility to Support Oral Drug Product Development and Harmonization
This report summarizes the proceedings of Session 1 of the one-day public workshop titled “Advances in PBPK Modeling and its Regulatory Utility for Oral Drug Product Development” hosted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Center for Research on Complex Generics (CRCG) on October 12, 2023.

High vs. Low Vancomycin Therapeutic Concentrations in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis
Current guidelines recommend vancomycin concentrations of 10–20 μg/mL for most infections, with higher levels (15–20 μg/mL) suggested for severe cases.

PBPK Modeling to Support Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Assessment in Pediatric Populations
This report summarizes the proceedings for Session 3 of the one-day public workshop entitled “Advances in PBPK Modeling and its Regulatory Utility for Oral Drug Product Development” a jointly sponsored workshop by U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Center for Research on Complex Generics (CRCG) on October 12, 2023.

In Vitro and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Characterization of 7-Hydroxymitragynine, an Active Metabolite of Mitragynine, in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Kratom, a Southeast Asian tree, has been researched for its potential as a therapeutic for substance use disorders.

Antiviral Activity of Halogenated Compounds Derived from L-Tyrosine Against SARS-CoV-2
Currently, there are no effective medications for treating all the clinical conditions of patients with COVID-19.