When scientifically well-founded, the mechanistic basis of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models can help reduce the uncertainty and increase confidence in extrapolations outside the studied scenarios or studied populations.

In Silico Prediction of Isoliquiritigenin and Oxyresveratrol Compounds to BCL-2 dan VEGF-2 Receptors
Isoliquiritigenin and oxyresveratrol are compounds that have been reported to have anticancer activities.

Overview of Brazilian Requirements for Therapeutic Equivalence of Orally Inhaled and Nasal Drug Products
Brazil has established a framework for provision of generic pharmaceuticals including for orally inhaled and nasal drug products (OINDP) to its populace.

Stability behaviour of antiretroviral drugs and their combinations. 10: LC-HRMS, LC-MSn, LC-NMR and NMR characterization of fosamprenavir degradation products and in silico determination of their ADMET properties
The present study focused upon the forced degradation behaviour of fosamprenavir (FPV), an antiretroviral drug. A total of six degradation products (DPs) were separated on a non-polar stationary phase by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).

Impact of Intracellular Concentrations on Metabolic Drug-Drug Interaction Studies
Accurate prediction of drug-drug interactions (DDI) is a challenging task in drug discovery and development. It requires determination of enzyme inhibition in vitro which is highly system-dependent for many compounds.

Lipid profile is associated with decreased fatigue in individuals with progressive multiple sclerosis following a diet-based intervention: results from a pilot study
To investigate associations between lipid profiles and fatigue in a cohort of progressive multiple sclerosis (MS) patients on a diet-based multimodal intervention.

A focus on riociguat in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Current treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) targets three signalling pathways: the nitric oxide (NO) pathway, the endothelin pathway and...
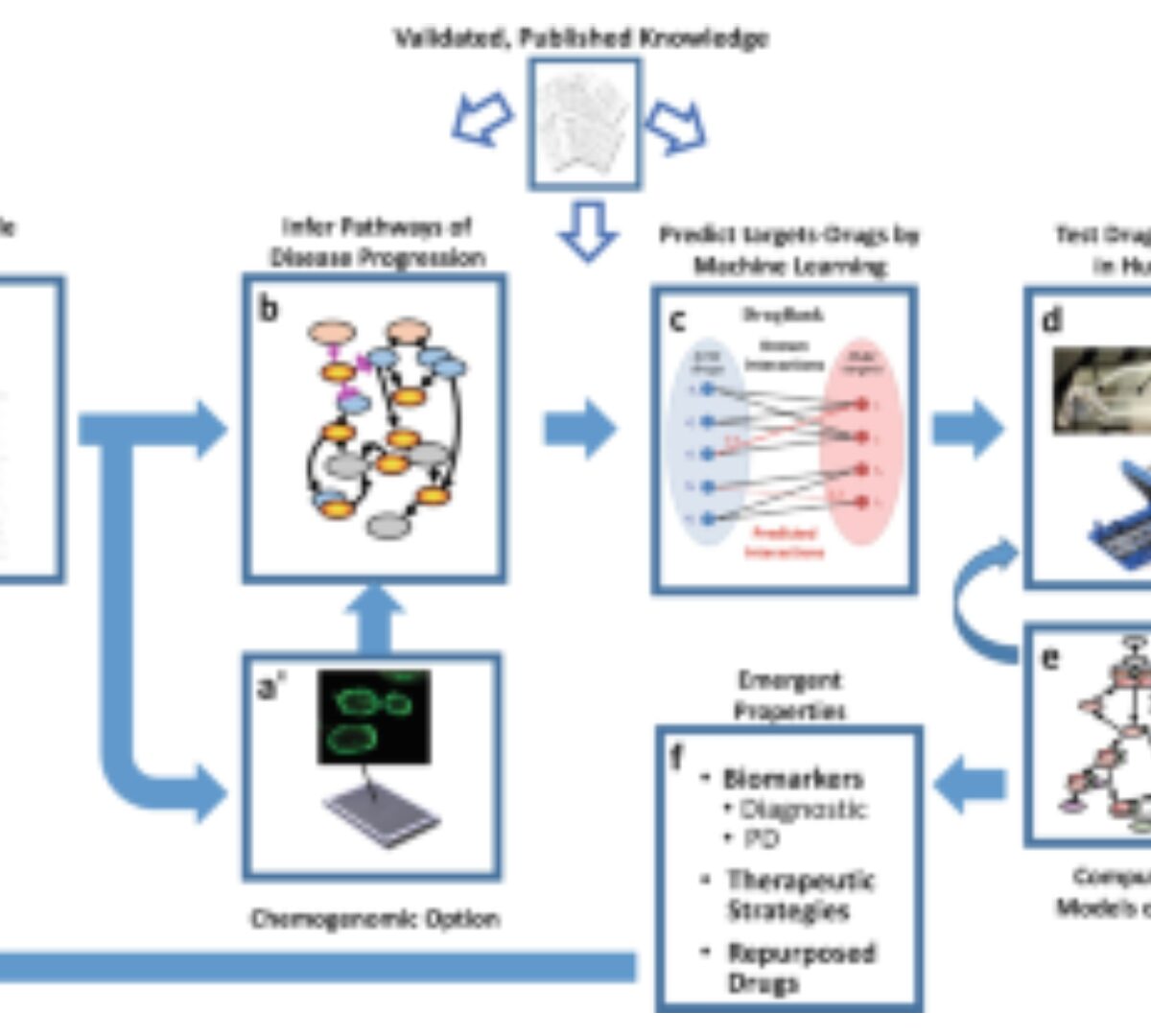
Harnessing Human Microphysiology Systems as Key Experimental Models for Quantitative Systems Pharmacology
Two technologies that have emerged in the last decade offer a new paradigm for modern pharmacology, as well as drug discovery and development.

Different roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma isoforms in prostate cancer
Due to the increasing occurrence of and high costs associated with prostate cancer (PC), there is an urgent need to develop novel PC treatment and chemoprevention...

Uncovering the pharmacological mechanism of Carthamus tinctorius L. on cardiovascular disease by a systems pharmacology approach
Carthamus tinctorius L. is widely used in traditional Chinese medicines for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.

“Development of Fixed Dose Combination Products” Workshop Report: Considerations of Gastrointestinal Physiology and Overall Development Strategy
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is one of the most popular and used routes of drug product administration due to the convenience for better patient compliance and reduced costs to the patient compared to other routes.

Metabolites of Vinca Alkaloid Vinblastine: Tubulin Binding and Activation of Nausea-Associated Receptors
Vinblastine (VLB) is an antimitotic drug that binds to the vinca site of tubulin.

Investigation of potent inhibitors of cholinesterase based on thiourea and pyrazoline derivatives: Synthesis, inhibition assay and molecular modeling studies
Owing to the desperate need of new drugs development to treat Alzheimer's ailment the synthesis of 1-aroyl-3-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazole-3-thioneaminylthioureas (2–6)...

Ceftolozane/tazobactam population pharmacokinetics and dose selection for further clinical evaluation in pediatric patients with complicated urinary tract or complicated intraabdominal infections
Ceftolozane-tazobactam, a combination of the novel antipseudomonal cephalosporin ceftolozane and the...

In Silico Design of Dapsone Analogues Effective Towards Enoyl Acyl Carrier Protein Reductase Enzyme of Mycrobacterium Leprae
A series of new antileprotic drugs targeting enoyl acyl carrier protein reductase (ENR) enzyme of Mycobacterium lepraewere designed by in silico techniques.

Insights into DPI sensitivity to humidity: An integrated in-vitro-in-silico risk-assessment
Dry powder inhalers (DPIs) are known to be sensitive to humidity. Erroneous storage of these products by patients in high humidity environments, could present a potential risk.

Toward the establishment of a standardized pre-clinical porcine model to predict food effects – Case studies on fenofibrate and paracetamol
A preclinical porcine model that reliably predicts human food effect of fenofibrate was developed. Fenofibrate was administered to pigs as model compound with a positive food effect.

Exposure-response (E-R) analysis of efficacy of pegvorhyaluronidase alfa (PEGPH20) in combination with nab-paclitaxel + gemcitabine (AG) in patients (Pts) with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
PEGPH20 depolymerizes extracellular matrix hyaluronan (HA) and is an investigational agent for the treatment of pts with HA-accumulating tumors

Solidified SNEDDS for the oral delivery of rifampicin: Evaluation, proof of concept, in vivo kinetics, and in silico GastroPlusTM simulation
The present investigation was performed to develop a rifampicin (RIF)-loaded solidified self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) (solidified RIF-OF1) for in vitro and in vivo evaluations.

Towards regulatory endorsement of drug development tools to promote the application of model-informed drug development in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Drug development for rare diseases is challenged by small populations and limited data.
