Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a major source of acute liver failure and is one of the leading causes of drug development failures. As such, there remains an important unmet need for earlier...

Pharmacokinetic Profile of an Ascending-Dose, Estrogen/Progestin Combination Oral Contraceptive
The estrogen component of oral contraceptives provides stability to the endometrium so that irregular shedding and unwanted breakthrough bleeding are minimized. An ascending-dose, extended-regimen…

The PK/PD Relationship of Ethinyl Estradiol and Unscheduled Bleeding or Spotting for an Ascending-dose, Estrogen/Progestin Combination Oral Contraceptive (OC)
The estrogen component of OCs provides stability to the endometrium so that irregular shedding and unwanted breakthrough bleeding are minimized. An ascending-dose, extended-regimen ethinyl estradiol…

Mechanistic Modeling Reveals the Most Important Unknowns in Bile Acid-Mediated DILI
BSEP inhibition and consequent bile acid (BA) buildup has been proposed to be an important mechanism in druginduced liver injury (DILI). There are many gaps in the knowledge of BA homeostasis and its…

DILIsym™, a Mechanistic Model of Drug-Induced Liver Injury, Supports the Interpretation of Elevated Liver Transaminase Levels in a Healthy Volunteer Pooled Safety Population for an Orphan Drug Designed for a Life-Threatening Situation
Compound A is in development for a life-threatening situation. The “Animal Rule” applies to efficacy, but not to safety assessment, which must be determined in humans. In a pooled safety population…
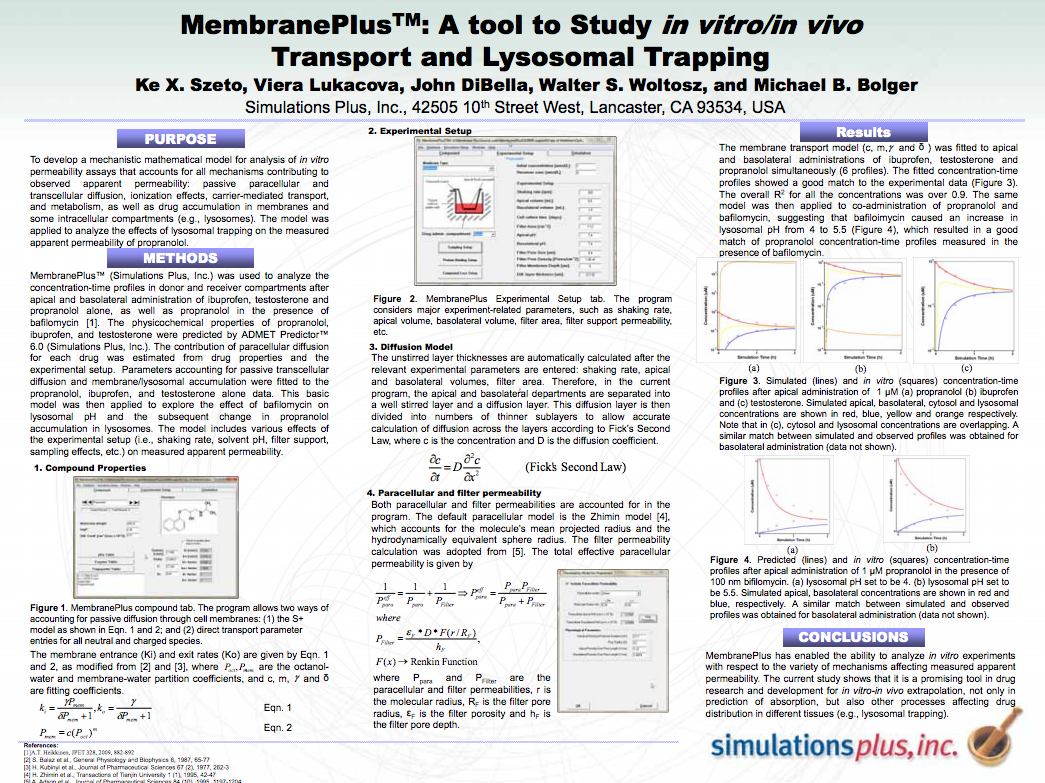
MembranePlus™: A Tool to Study in vitro/in vivo Transport and Lysosomal Trapping
To develop a mechanistic mathematical model for analysis of in vitro permeability assays that accounts for all mechanisms contributing to observed apparent permeability: passive paracellular and…
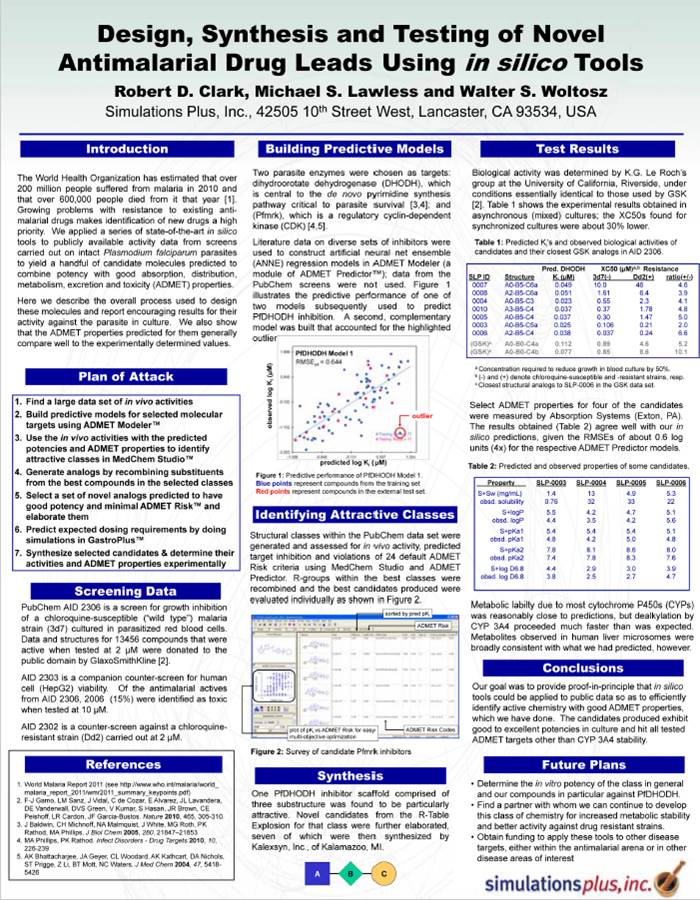
Design, Synthesis and Testing of Novel Antimalarial Drug Leads Using in silico Tools
The World Health Organization has estimated that over 200 million people suffered from malaria in 2010 and that over 600,000 people died from it that year [1]. Growing problems with resistance to existing anti…

PBPK Model Simulation of CYP3A4 and Transporter Mediated Drug-drug Interactions Involving Erythromycin
Erythromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, is cleared primarily by cytochrome P450-3A4 metabolism to the N-demethylated metabolite and C-formaldehyde. Its uptake into hepatocytes is mediated by organic…

Novel Antimalarial Drug Candidates Generated in silico by Analysis of Public HTS Data
Carry out a prospective experiment to demonstrate the ability of in silico drug design tools to design new lead drug candidates from phenotypic screening data.

Prediction of Amoxicillin Pharmacokinetics in Populations with Altered Renal Function
Purpose of the study was to predict amoxicillin pharmacokinetics in populations with altered renal function to further validate an absorption/PBPK model for amoxicillin.

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Amoxicillin Absorption and Pharmacokinetics
Purpose of the study was to develop a PBPK model for amoxicillin incorporating saturable transport processes affecting the drug’s absorption and distribution.

PBPK Modeling of Erythromycin Absorption and Disposition Mediated by Transporters in Humans
Erythromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, is cleared primarily by cytochrome P450-3A4 metabolism. Its uptake into enterocytes and hepatocytes is mediated by organic anion transporter (OAT) and organic anion…

In Silico Metabolite Prediction Using Artificial Neural Network Ensembles
Drug metabolism plays a crucial role in understanding bioavailability and drug-drug interactions, as well as in the design of prodrugs and in avoiding undesirable toxic metabolites.

Modeling of Furosemide in DILIsym™ Model Reveals Testable Hypotheses about Hepatotoxicity Mechanisms
A predictive, quantitative, mathematical model (DILIsym™) is under development as a public-private initiative based on the physiological processes involved in drug-induced liver injury. The model includes…
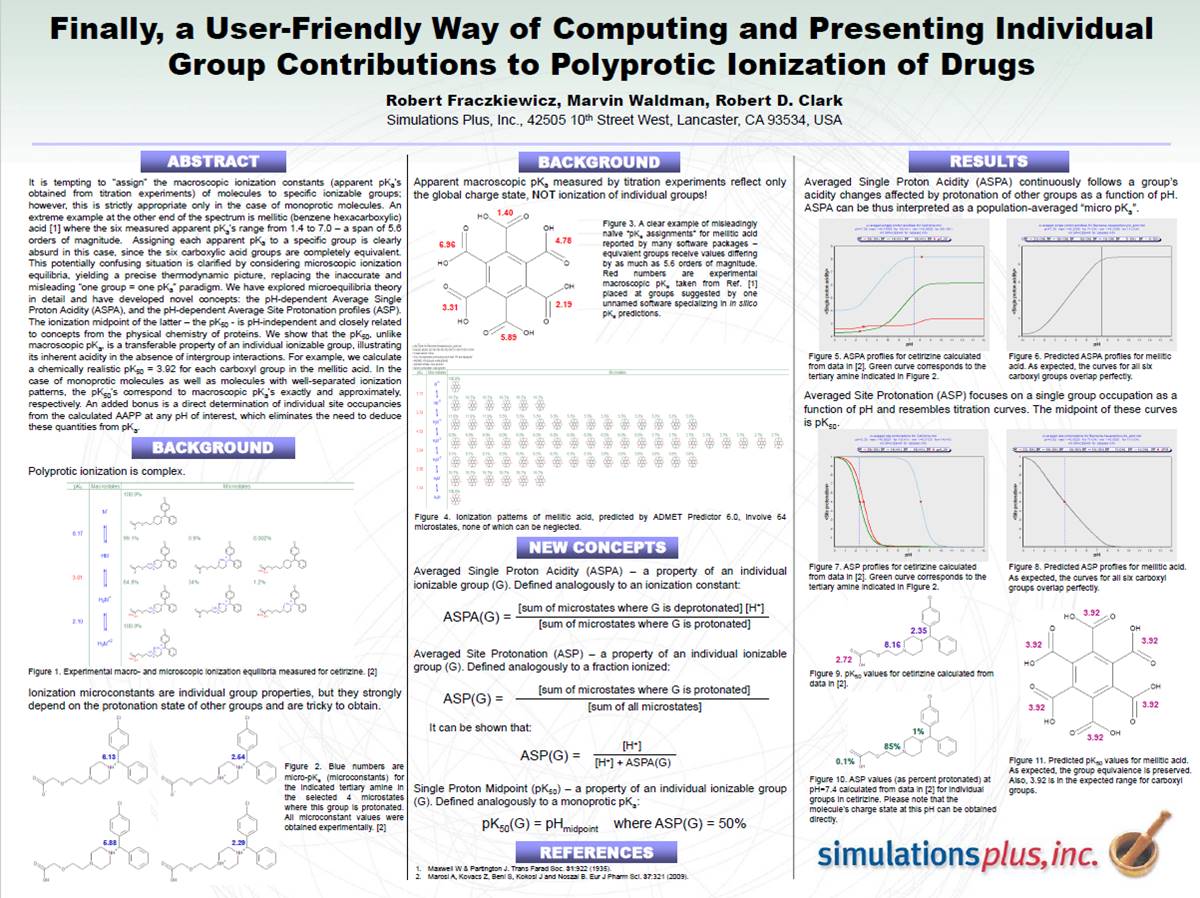
Finally, a User-Friendly Way of Computing and Presenting Individual Group Contributions to Polyprotic Ionization of Drugs
It is tempting to “assign” the macroscopic ionization constants (apparent pKa ‘s obtained from titration experiments) of molecules to specific ionizable groups; however, this is strictly appropriate only…

Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for Prediction of Midazolam Pharmacokinetics After Intranasal Administration in Children
To predict midazolam absorption and pharmacokinetics (PK) after intranasal (i.n.) administration in young children. The absorption and PK of midazolam were simulated using GastroPlus™. The program’s…

Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Models for Prediction of Saquinavir Effect on Midazolam Pharmacokinetics
Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models for prediction of saquinavir effect on midazolam pharmacokinetics
Viera Lukacova, Walter S. Woltosz, Michael B. Bolger

Translating Disposition of Sotalol from Healthy Adults to Predict Its Behavior in Pediatric and Adult Subjects with Enhanced and Diminished Renal Clearance
To extend a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model of sotalol developed in healthy adults to predict its behavior in pediatric subjects and adults with varying degrees of renal clearance…

A Pharmacokinetic and Safety Evaluation of Single Oral Doses of Eszopiclone in Pediatric Subjects from 6 to 17 Years of Age with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Insomnia
Eszopiclone is a single-isomer, nonbenzodiazepine, cyclopyrrolone agent that has demonstrated efficacy with both polysomnography (PSG) and patient-reported measures in non-elderly adults with chronic primary…

Grouping Pharmacokinetic Profiles Using Kohonen Self-Organizing Maps
The shapes of plasma concentration versus time (Cp-time) profiles from large clinical trials are often highly variable, even in well-controlled trials involving homogeneous cohorts.
