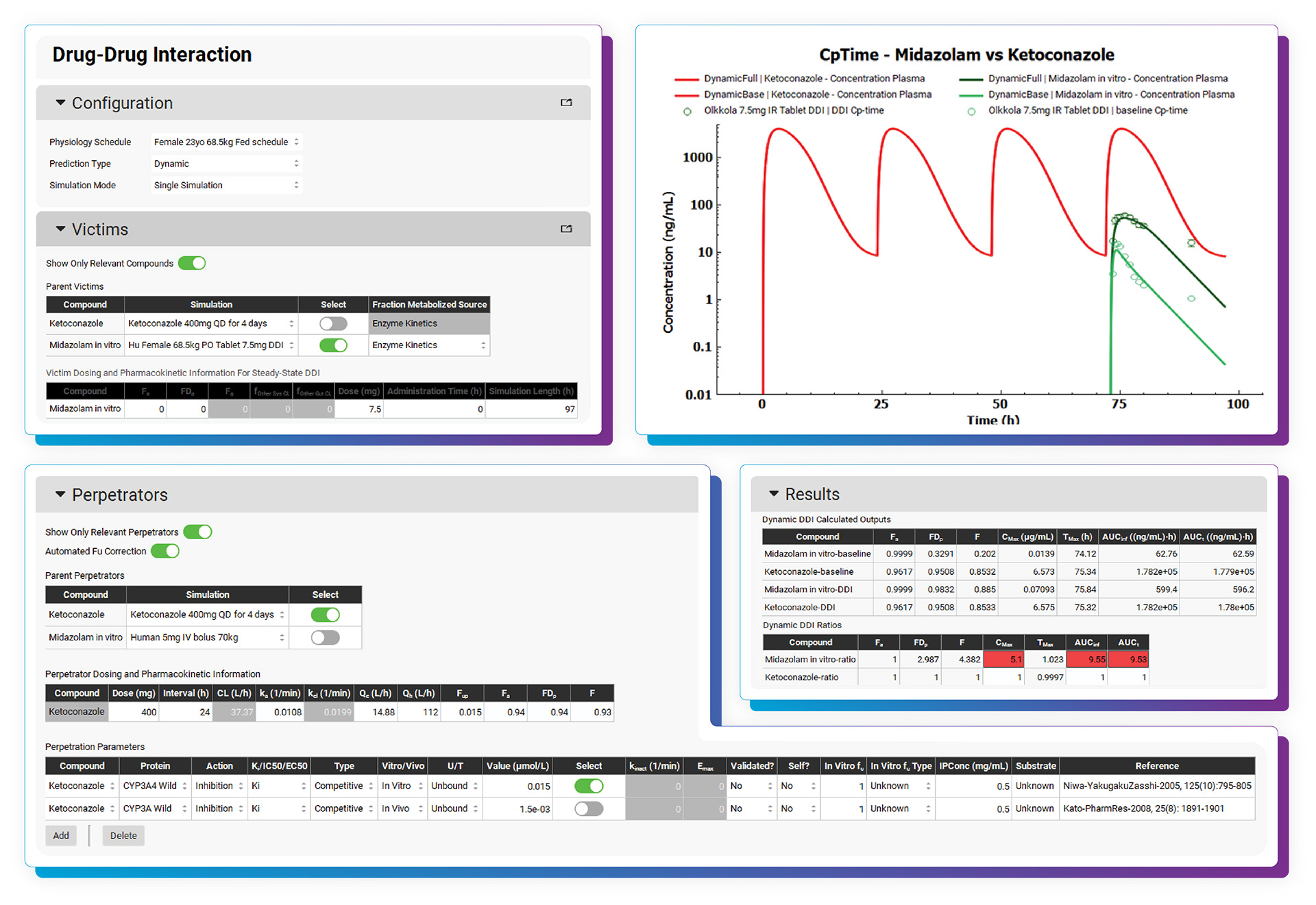
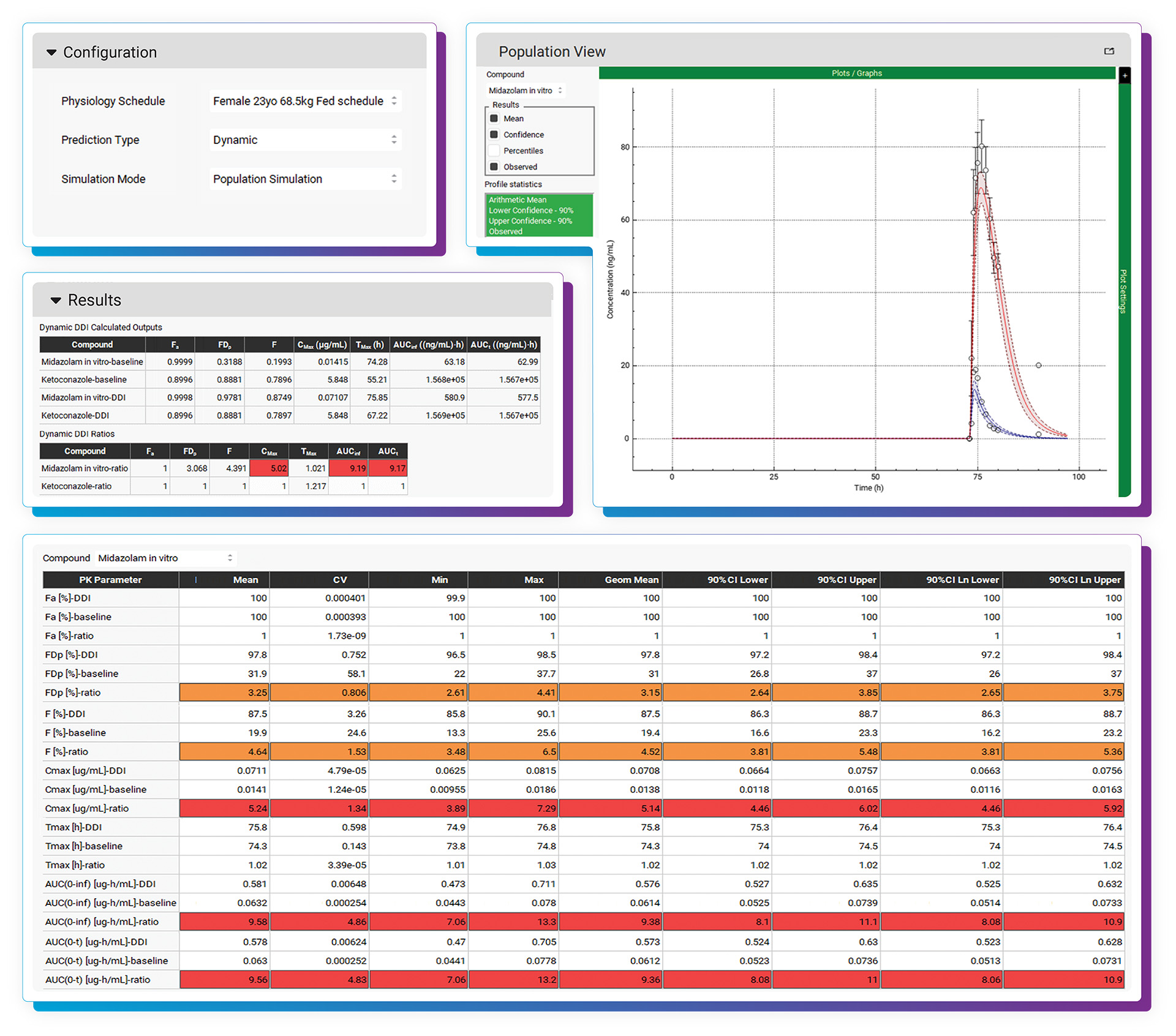
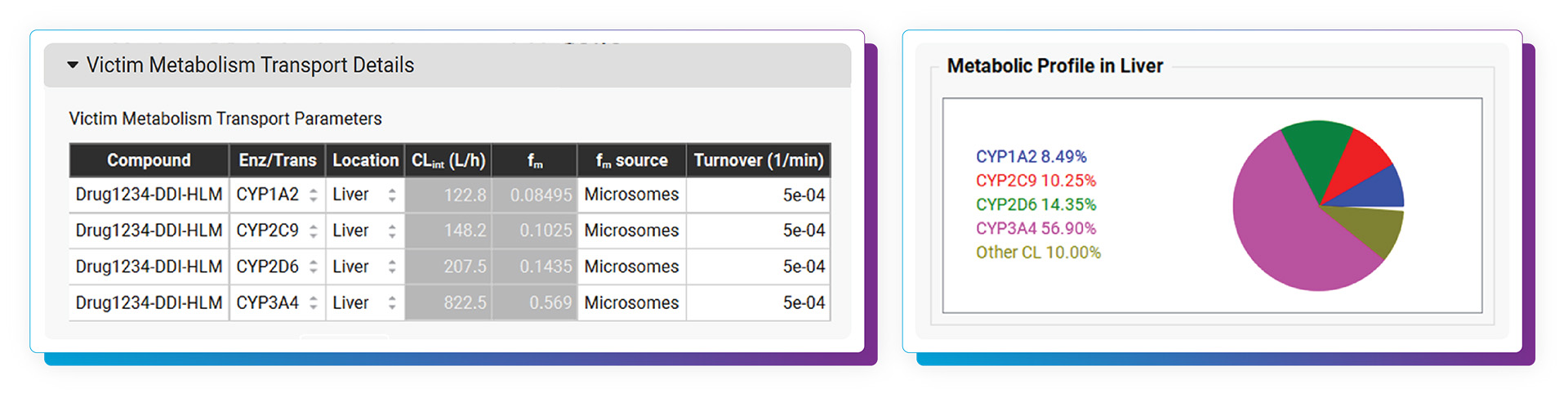
With the DDI Module, calculating either mechanistic steady-state and/or dynamic drug interactions is managed through our easy-to-use interface. We provide a database of validated compound model files (>30) for which all relevant parameters (including reported Kis and full compartmental PK & PBPK models) are defined. Of course, you may predict DDIs among any drugs by simply entering the required inputs. As with other GastroPlus modules, there is no equation or code writing required.
Explore possible effects on the pharmacology and toxicology of drugs