In vivo pharmacokinetic simulations and virtual bioequivalence (BE) evaluation of cilostazol have not yet been described for humans.

Exploring the Role of Drug Repurposing in Bridging the Hypoxia–Depression Connection
High levels of oxidative stress are implicated in hypoxia, a physiological response to low levels of oxygen.

Comprehensive evaluation of the pharmacological and toxicological effects of γ-valerolactone as compared to γ-hydroxybutyric acid: Insights from in vivo and in silico models
Γ-valerolactone (GVL), marketed online as “Tranquilli-G” and “excellent Valium”, is used as a legal substitute for γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB); however, until now, GVL has only been connected to one Drug-Facilitated Sexual Assault (DFSA) case.
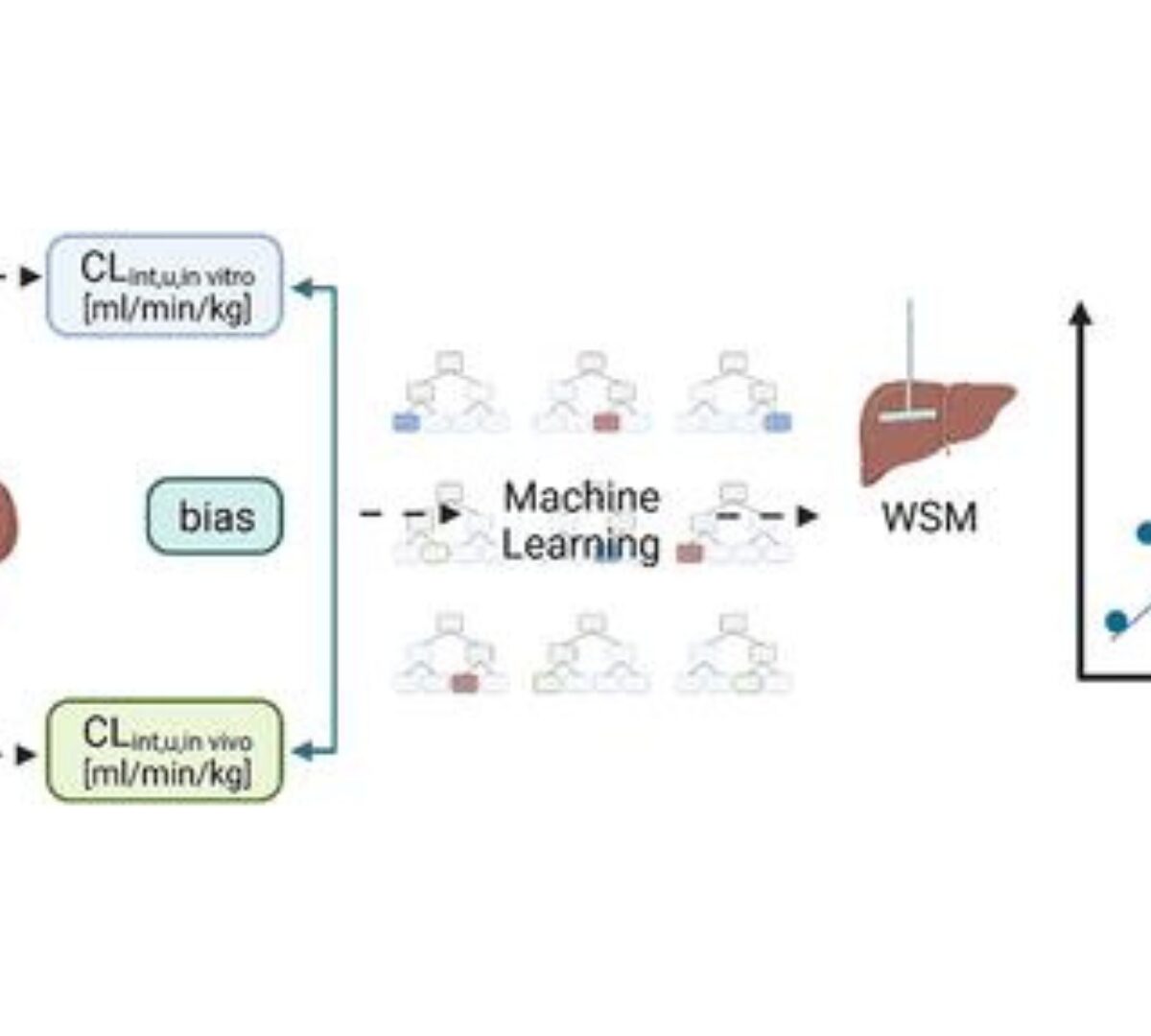
A Machine Learning Framework to Improve Rat Clearance Predictions and Inform Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling
During drug discovery and development, achieving appropriate pharmacokinetics is key to establishment of the efficacy and safety of new drugs.

Ligand Based Pharmacophore Modeling, Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamic simulation and In-silico ADMET Studies for the Discovery of Potential BACE-1 Inhibitors
Pharmacophore modeling is an innovative technology to explore and extract potential interactions between ligand-protein complexes.
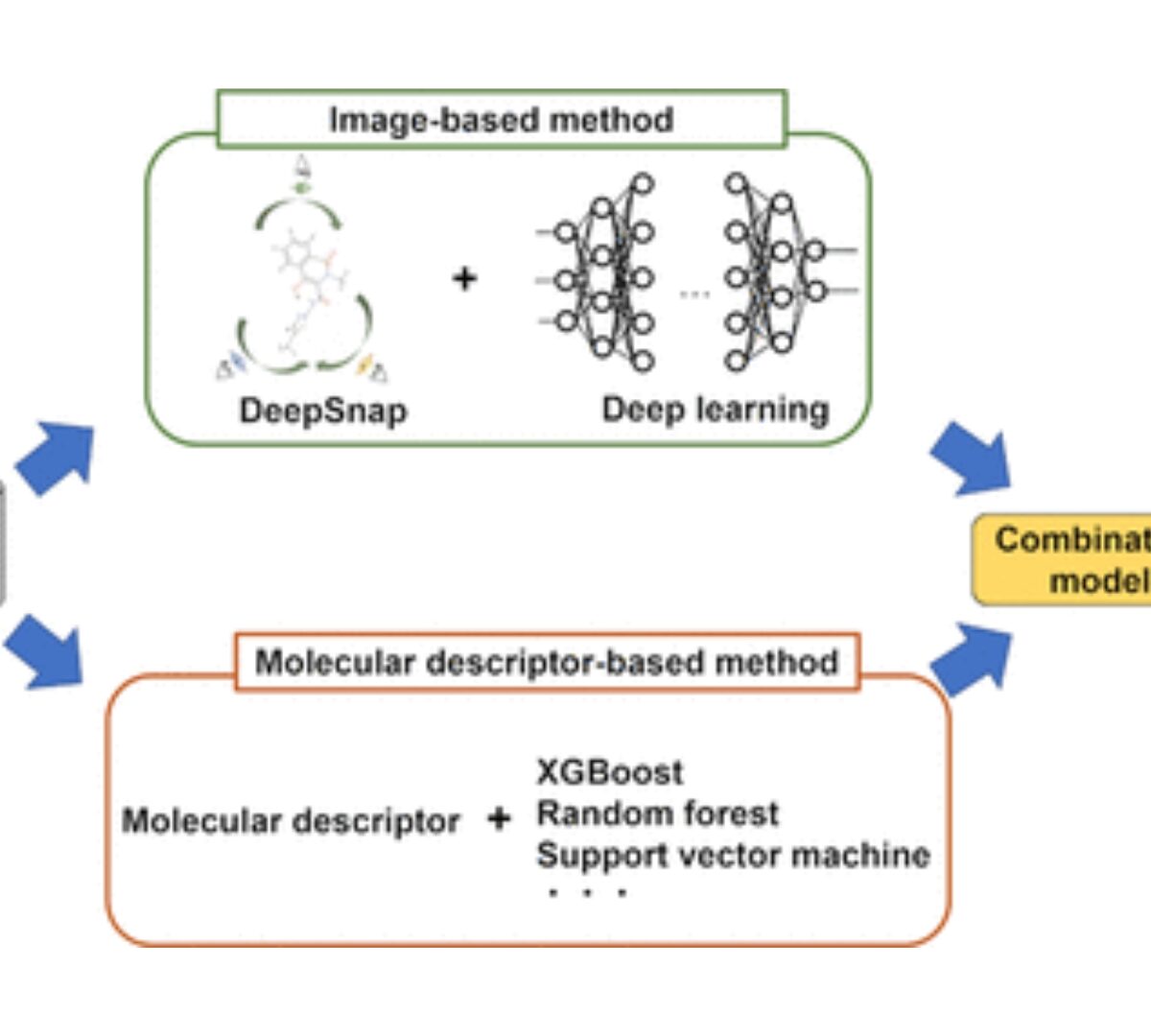
Predictive Models Based on Molecular Images and Molecular Descriptors for Drug Screening
Various toxicity and pharmacokinetic evaluations as screening experiments are needed at the drug discovery stage.
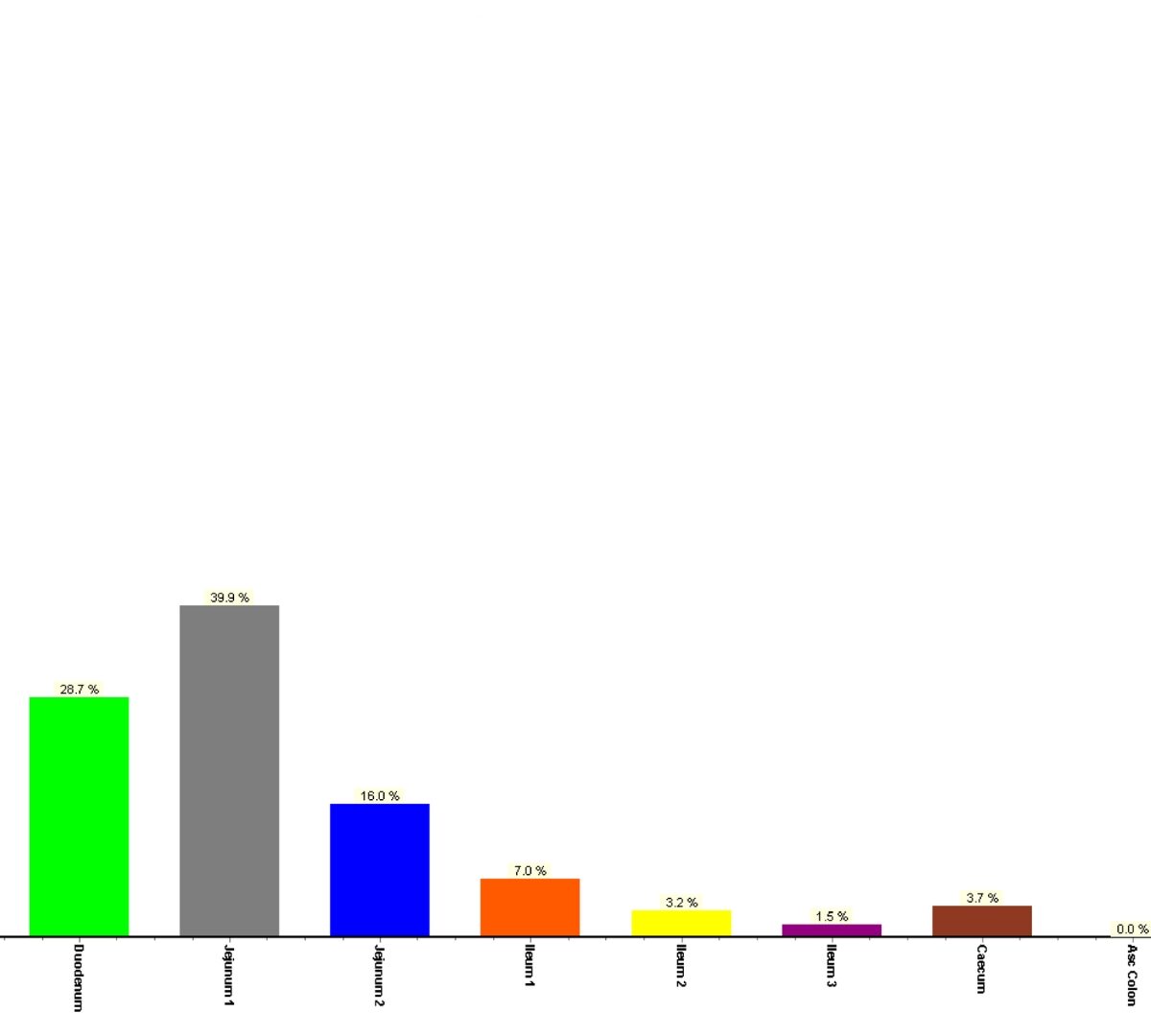
The First Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for an Oral Vaccine Using Alpha-Tocopherol as an Adjuvant
Oral vaccines represent many advantages compared to standard vaccines. They hold a simple method of administration and manufacturing process.
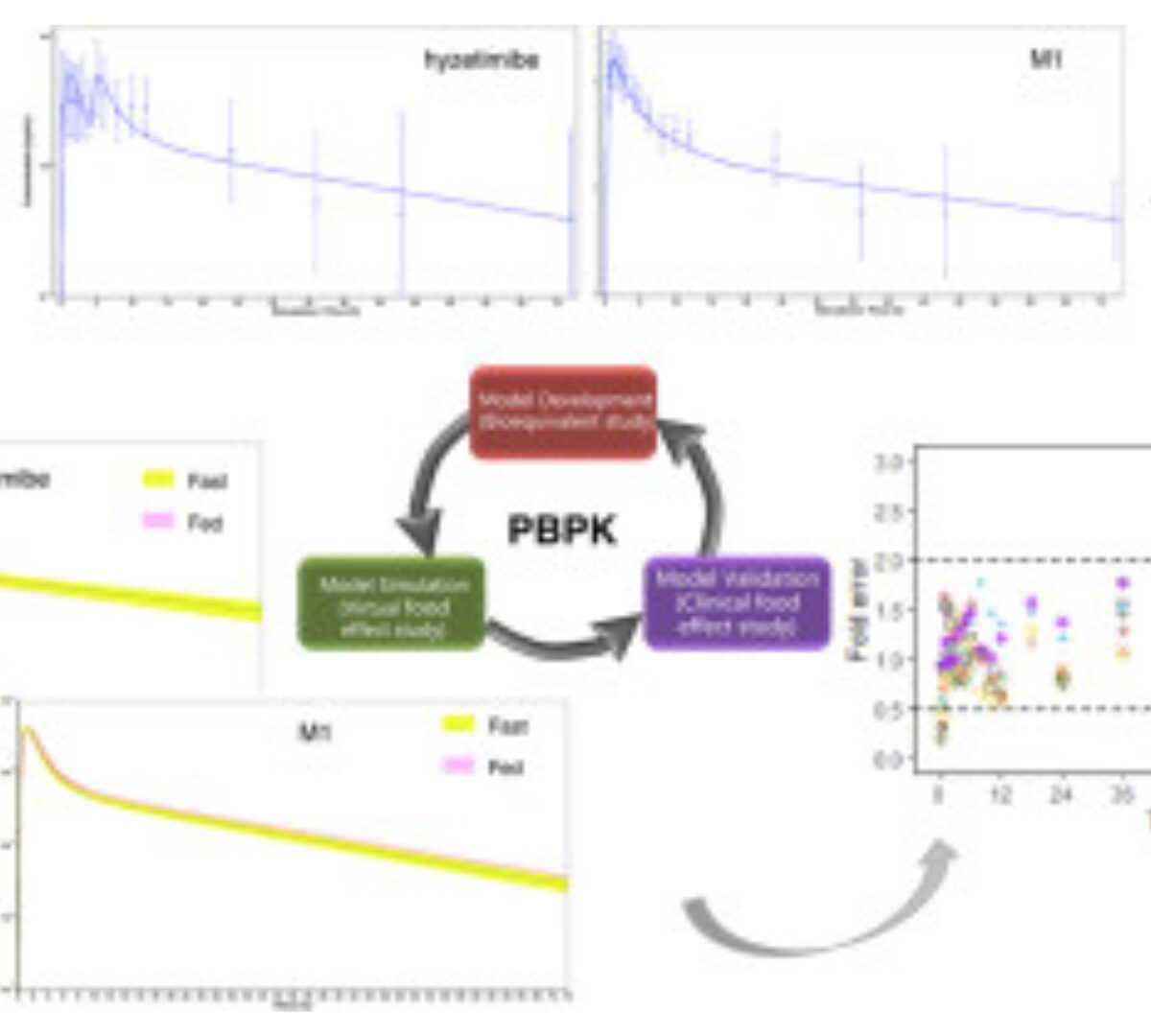
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to characterize enterohepatic recirculation and predict food effect on the pharmacokinetics of hyzetimibe
Hyzetimibe is a cholesterol absorption inhibitor indicated for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
![The anti-infective crotalicidin peptide analog RhoB-Ctn[1–9] is harmless to bovine oocytes and able to induce parthenogenesis in vitro](https://www.simulations-plus.com/wp-content/themes/simulations-plus/library/dist/img/default_square-large.jpg)
The anti-infective crotalicidin peptide analog RhoB-Ctn[1–9] is harmless to bovine oocytes and able to induce parthenogenesis in vitro
Crotalicidin is a cathelicidin-related anti-infective (antimicrobial) peptide expressed in the venom glands of the South American rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus.
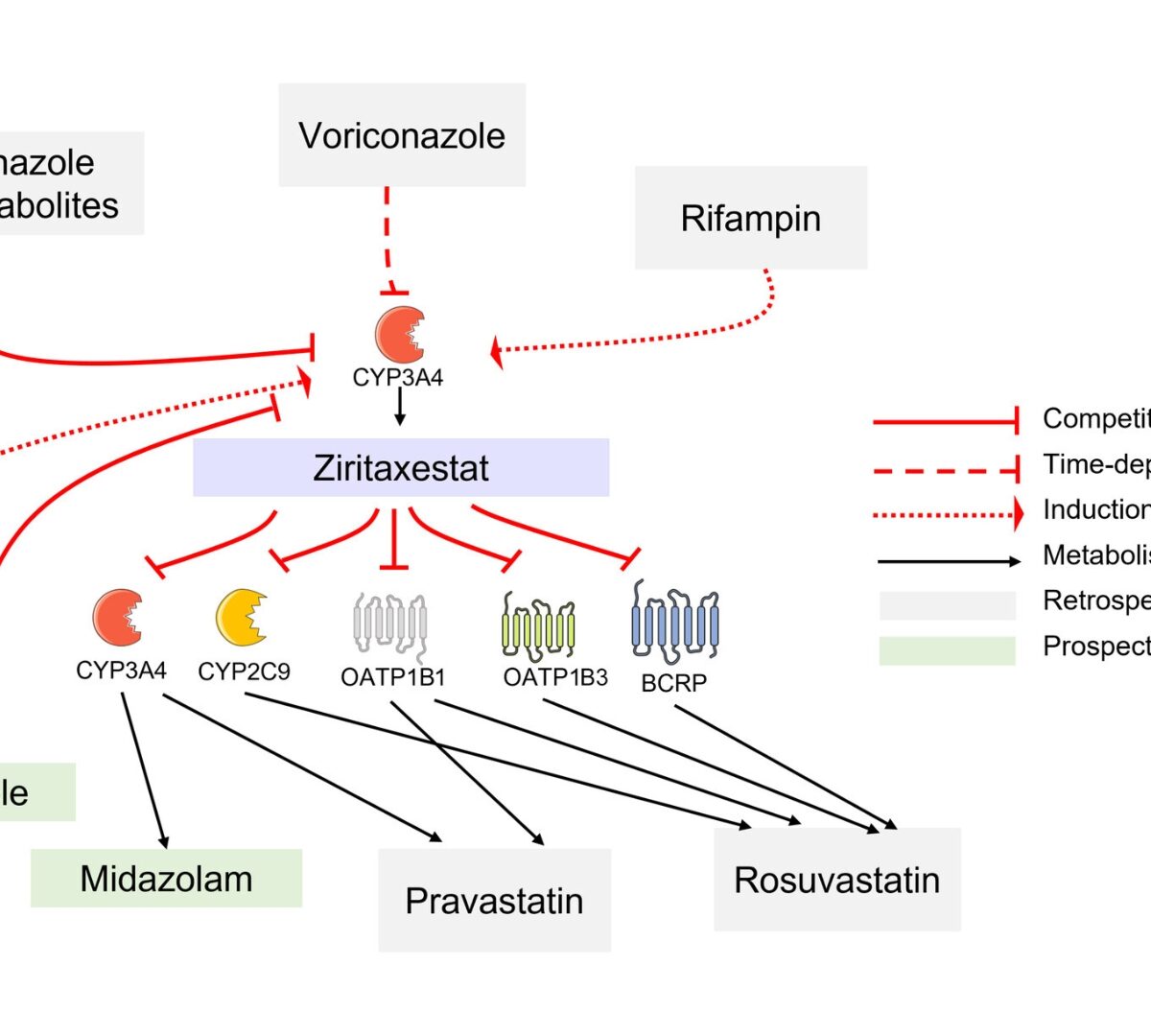
Drug–drug interaction prediction of ziritaxestat using a physiologically based enzyme and transporter pharmacokinetic network interaction model
Ziritaxestat, an autotaxin inhibitor, was under development for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.

Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling to predict drug–drug interactions for encorafenib. Part I. Model building, validation, and prospective predictions with enzyme inhibitors, inducers, and transporter inhibitors
Encorafenib, a potent BRAF kinase inhibitor undergoes significant metabolism by CYP3A4 (83%) and CYP2C19 (16%) and also a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp).

Mind the Gap: Model-Based Switching from Selatogrel to Maintenance Therapy with Oral P2Y12 Receptor Antagonists
The P2Y12 receptor antagonist selatogrel is being developed for subcutaneous self-administration with a ready-to-use autoinjector at the onset of acute myocardial infarction (AMI)symptoms.
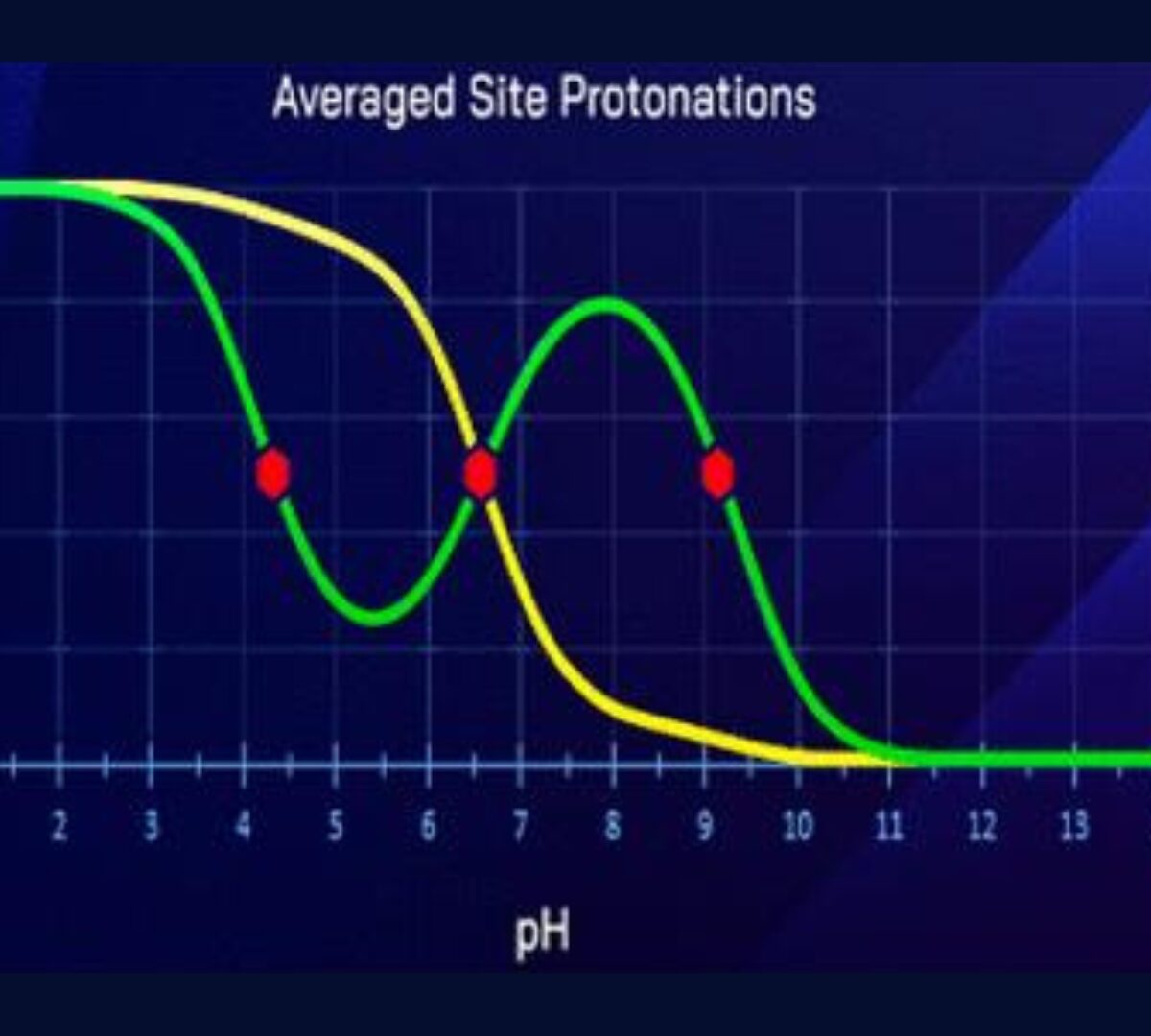
Can an Amine Be a Weaker and a Stronger Base at the Same Time? Curious Cases of Chameleonic Ionization
We discovered an anomalous basic dissociation in certain multiprotic compounds.
Dabigatran Dosing Proposal for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation: Stress-Testing Renal Function Range in Real World Patients
Dabigatran is the first of four direct-acting oral anticoagulants approved to prevent stroke in adult patients with atrial fibrillation using a fixed two-dose scheme compared with warfarin dosing adjusted to...
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling (PBPK) to predict drug-drug interactions for encorafenib. Part II. Prospective predictions in hepatic and renal impaired populations with clinical inhibitors and inducers
Encorafenib, a potent BRAF kinase inhibitor gets significantly metabolised by CYP3A4 (83%) and CYP2C19 (16%) and is a substrate for P-glycoprotein...

Pyronaridine: a review of its clinical pharmacology in the treatment of malaria
Pyronaridine-artesunate was recently strongly recommended in the 2022 update of the WHO Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria, becoming the...
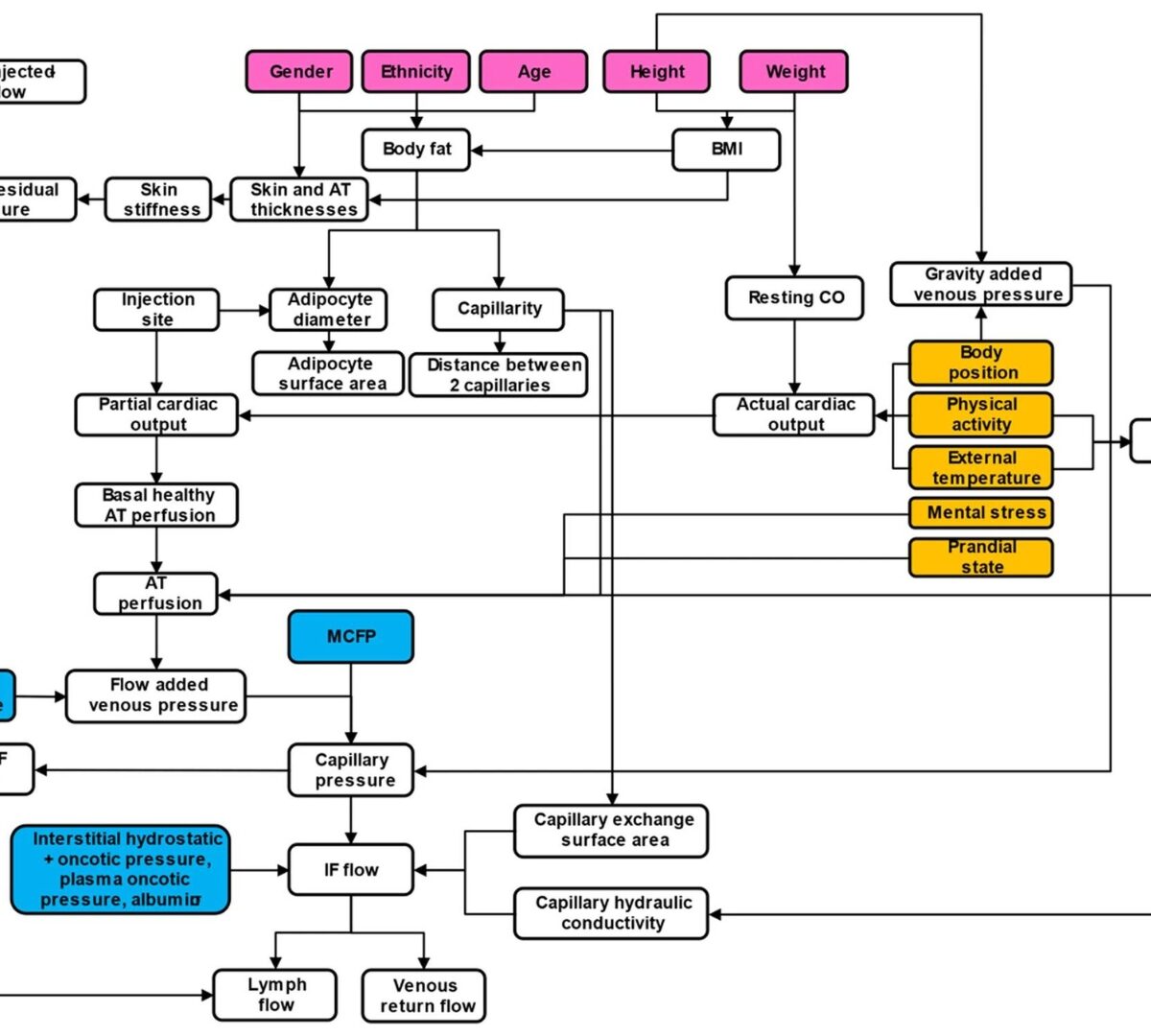
SubQ-Sim: A Subcutaneous Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model. Part 1: The Injection and System Parameters
To construct a detailed mechanistic and physiologically based biopharmaceutics model capable of predicting 1) device-formulation-tissue interaction during the injection process and 2) binding, degradation, local distribution, diffusion, and drug absorption, following subcutaneous injection.
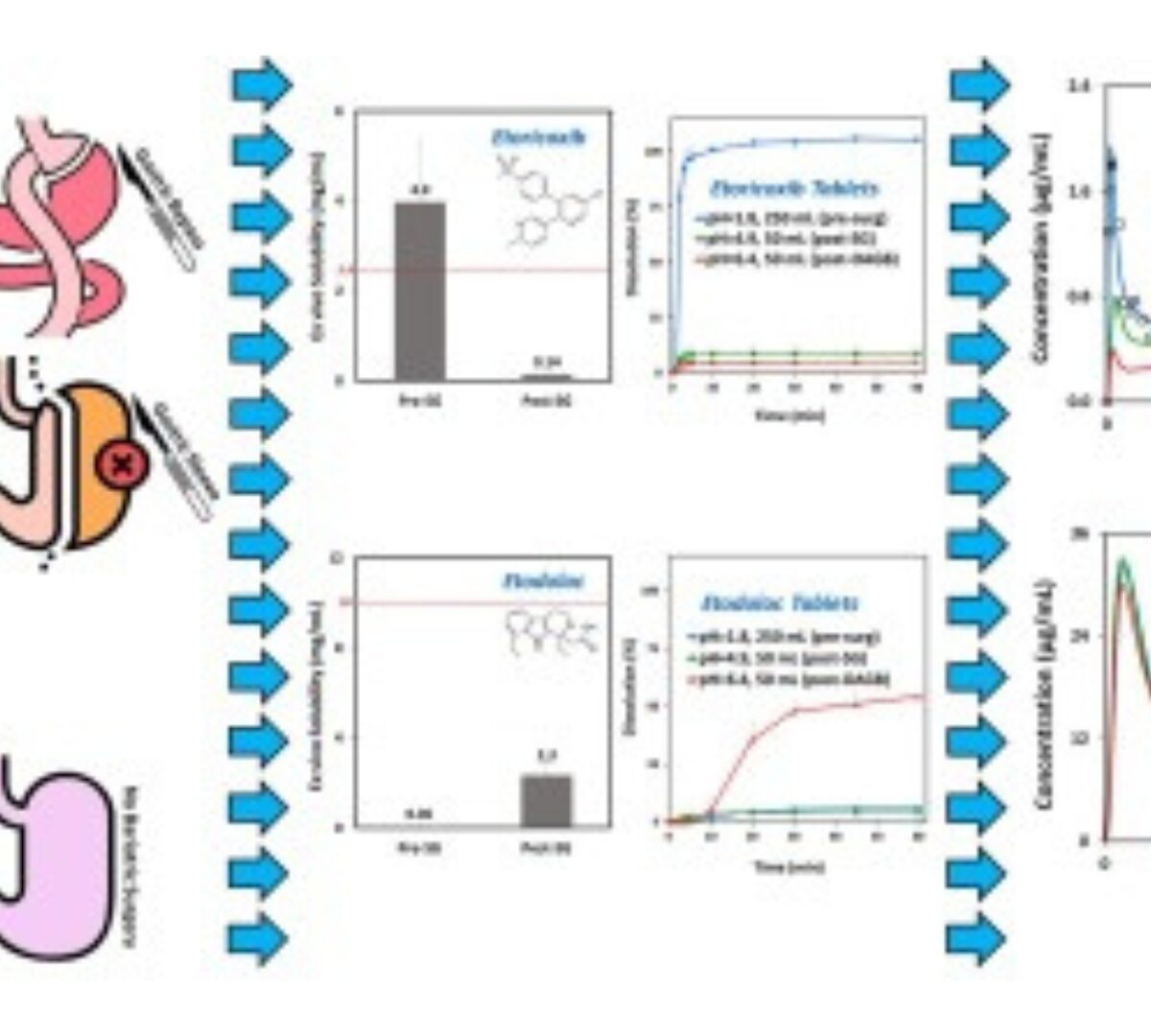
Selective COX-2 inhibitors after bariatric surgery: Celecoxib, etoricoxib and etodolac post-bariatric solubility/dissolution and pharmacokinetics
Anatomical/physiological gastrointestinal changes after bariatric surgery may influence the fate of orally administered drugs.

A robust, viable, and resource sparing HPLC-based logP method applied to common drugs
Reliable, experimentally determined partition coefficient P (logP) for most drugs are often unavailable in the literature. Many values are from in silico predictions and may not accurately reflect drug lipophilicity.

Halloysite nanotubes-cellulose ether based biocomposite matrix, a potential sustained release system for BCS class I drug verapamil hydrochloride: Compression characterization, in-vitro release kinetics, and in-vivo mechanistic physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling studies
This study investigated the ability of natural nanotubular clay mineral (Halloysite) and cellulose ether based biocomposite matrix as a controlled release...
