Tizanidine, a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant, is predominantly metabolized by CYP1A2 and undergoes extensive hepatic first-pass metabolism after oral administration.

Simulation of febuxostat pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects and patients with impaired kidney function using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling
Febuxostat is recommended by the American College of Rheumatology Gout Management Guidelines as a first-line therapy for lowering the level of urate in patients with gout.

Impact of Composition and Morphology of Ketoconazole-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles on Intestinal Permeation and Gastroplus-Based Prediction Studies
Ketoconazole (KTZ) is a potential oral antifungal agent to control systemic and local infections.

From traditional to data-driven medicinal chemistry: A case study
Artificial intelligence (AI) and data science are beginning to impact drug discovery.

Machine Learning guided early drug discovery of small molecules
Machine learning (ML) approaches have been widely adopted within the early stages of the drug discovery process, particularly within the context of small-molecule drug...

Using GastroPlus to teach complex biopharmaceutical concepts
This report showcases the use of the software GastroPlus in an undergraduate-level pharmacy course.

Chronotherapy based on modified-release hydrocortisone to restore the physiological cortisol diurnal rhythm
In this inspirational note, we describe the development of an endocrine chronotherapy to restore the physiological rhythm of the essential adrenal stress hormone, cortisol.

The Use of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Analyses-in Biopharmaceutics Applications -Regulatory and Industry Perspectives
The use of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling to support the drug product quality attributes, also known as physiologically based biopharmaceutics modeling...

Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics Modeling for Hydroxychloroquine as a Treatment for Malaria and Optimized Dosing Regimens for Different Populations
Malaria is a severe parasite infectious disease with high fatality.

Comparing the Liver Safety Profiles of 4 Next-Generation CGRP Receptor Antagonists to the Hepatotoxic CGRP Inhibitor Telcagepant Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) signaling inhibitors have shown efficacy in both the acute and preventive treatment of migraine.

Molluskicidal activity of 3-aryl-2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinones against Biomphalaria glabrata
Schistosomiasis is the second most prevalent parasitic infectious disease after malaria, which affects millions of people worldwide and causes health and socioeconomic...

Discovery of new chemotypes of dual 5-HT2A/D2 receptor antagonists with a strategy of drug design methodologies
Aim: Through the application of structure- and ligand-based methods, the authors aimed to create an integrative approach to developing a computational protocol for the...

Evaluation of potential anticonvulsant fluorinated N-benzamide enaminones as T-type Ca2+ channel blockers
Trifluoromethylated N-benzamide enaminones have been identified as potential anticonvulsants for the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy.
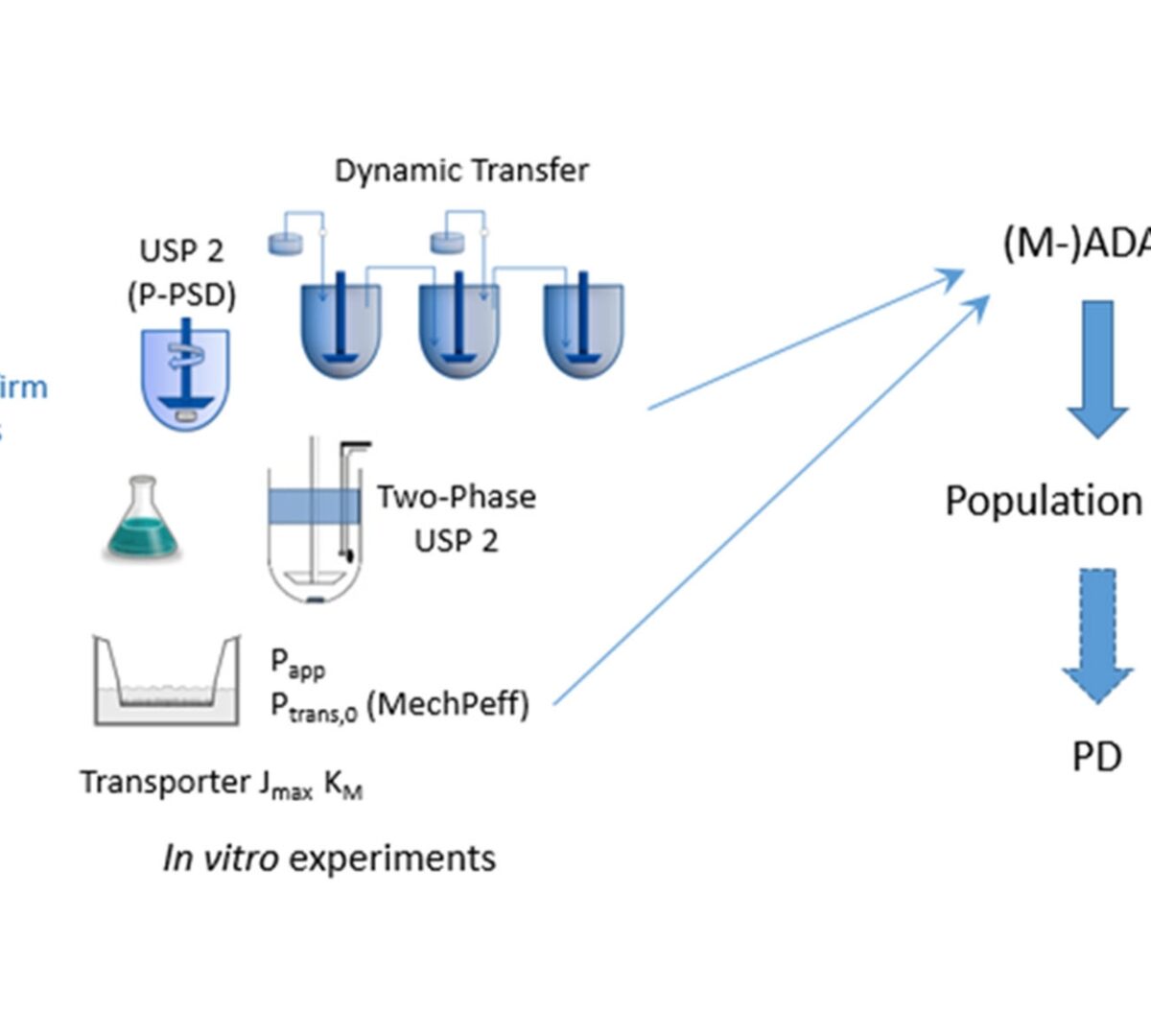
Developing Clinically Relevant Dissolution Specifications (CRDSs) for Oral Drug Products: Virtual Webinar Series
A webinar series that was organised by the Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences Biopharmaceutics focus group in 2021 focused on the challenges of developing clinically relevant...

Comparison of toxicological effects and exposure levels between triclosan and its structurally similar chemicals using in vitro tests for read-across case study
Read-across based on structural and biological similarities is expected to be a promising alternative method for assessing systemic toxicity.

Discovery of 2-((2-methylbenzyl)thio)-6-oxo-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile as a novel and effective bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) inhibitor for the treatment of sepsis
Sepsis has long been a major health problem worldwide.

Evaluating the pharmacokinetics of intrapulmonary administered ciprofloxacin solution for respiratory infections using in vivo and in silico PBPK rat model studies
Respiratory antibiotics have been proven clinically beneficial for the treatment of severe lung infections such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa.

A Mechanistic Absorption and Disposition Model of Ritonavir to Predict Exposure and Drug-Drug Interaction Potential of CYP3A4/5 and CYP2D6 Substrates
Due to health authority warnings and the recommended limited use of ketoconazole as a model inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 in clinical drug–drug interaction...

Evaluation of the Success of High-Throughput Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (HT-PBPK) Modeling Predictions to Inform Early Drug Discovery
Minimizing in vitro and in vivo testing in early drug discovery with the use of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling and machine learning (ML) approaches...

Exposure-efficacy analyses support optimal dosing regimens of ceftolozane/tazobactam in participants with hospital-acquired/ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia in ASPECT-NP
An exposure-efficacy analysis of the phase 3 ASPECT-NP trial was performed to evaluate the relationship between plasma exposure of ceftolozane and tazobactam and
