Since published pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic models are often used by others for the purpose of simulations, enhanced clarity in reporting and clear statements regarding assumptions will improve the reproducibility of...

A physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of amlodipine: High enterocyte binding, not enterohepatic circulation, is responsible for the long Tmax
Amlodipine is a second generation calcium channel blocker that has been widely used in the therapy of hypertension and angina pectoris.

A Simulation and Estimation Platform for Malaria Model Evaluation
Accelerating clinical development of new compounds demands efficient systems for evaluation and interpretation of trial results. Systematizing trial evaluation methods yields efficiency and confidence in results.

Development of a Quantitative Systems Toxicology Model of Drug-Induced Cholangiocyte Injury in DILIsym
Cholangiocyte injury accounts for a quarter of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) cases and is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality than hepatocellular DILI (Chalasani et al., 2015).

Zonal Hepatic Stellate Cell (HSC) Activation in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Characterized by A Mathematical Model
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) represents a spectrum of pathophysiology, ranging from hepatic steatosis, through non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and hepatic fibrosis, and in rare cases resulting in cirrhosis and liver failure.

Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Supports Differentiated Liver Safety for a Next-in-Class Compound
Lixivaptan, a vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist, is under development for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), an orphan disease with minimal treatment options.
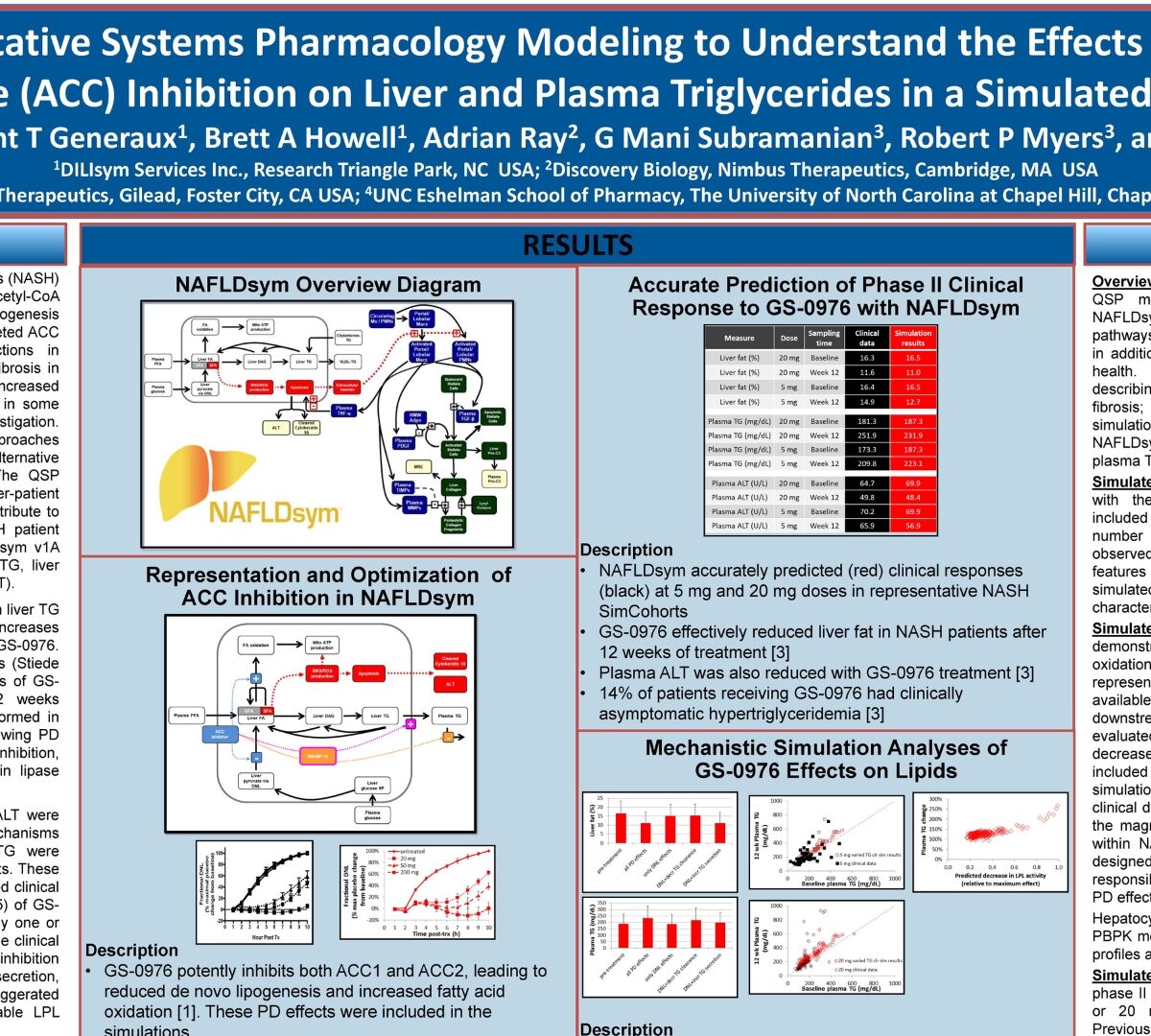
Using Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Modeling to Understand the Effects of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC) Inhibition on Liver and Plasma Triglycerides in a Simulated Population
Treatment options for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are limited. One approach targets hepatic acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), which influences de novo lipogenesis (DNL) and fatty acid oxidation.

In Vitro to In Vivo Extrapolation (IVIVE) of Itraconazole Precipitation using a Biphasic Dissolution Test and Mechanistic Absorption Model
Regulatory agencies have encouraged the use of mechanistic absorption (MAM) and physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling to reduce cost and time to market for new and generic drug products.

A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model of Rivaroxaban: Role of OAT3 and P-gp Transporters in Renal Clearance
Rivaroxaban is an oral anticoagulant which acts by inhibiting factor Xa of the coagulation network.

Liver Safety Comparison of Two Treatments for Autosomal-Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology Software (DILIsym)
Lixivaptan, a vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist, is being developed for the treatment of autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), an orphan disease that is an unmet medical need.

Assessing the Role of Intracellular Binding Protein in Drug-Induced Bile Acid Transporter Inhibition Using Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP) Modeling
Bile acid transporter inhibition has been shown to be an important mechanism of drug-induced liver injury (DILI), but the biophase responsible for the transporter inhibition is unclear.

A PBPK model of the negative effect of chitosan on acyclovir absorption: The mucus-chitosan interaction
A recent bioavailability study raises questions about the universality of the permeability enhancing effect of chitosan on poorly permeable drugs.

HTPK: Conducting PK modeling and simulations at high speed
In silico pharmacokinetic (PK) simulations are now routinely incorporated into drug development workflows, especially in the later stages.

Activation of CD8+ T Cells in the Context of Amodiaquine-Induced Liver Injury Advances Groundwork for Mathematical Representation of Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury (iDILI)
Extensive progress has been made in identifying mechanisms for dose-dependent drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and in developing screening assays to reduce its incidence.

Assessing Effects of BHV-0223 40 mg Zydis® Sublingual Formulation and Riluzole 50 mg Oral Tablet on Liver Function Test Parameters Utilizing DILIsym®
To quantitatively and mechanistically compare the liver toxicity potential of oral riluzole versus BHV-0223, combining clinical and mechanistic data, using DILIsym.

A Model-Based Approach to Bridging Plasma and Dried Blood Spot Concentration Data for Phase 3 Verubecestat Trials
Dried blood spot (DBS) pharmacokinetic (PK) sampling was investigated as a potential alternative to plasma sampling for Phase 3 verubecestat (MK-8931) trials due to several potential advantages (ie, reduced cost, reduced clinical site burden, and lower blood volume requirements)

Development of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Losartan and Its Active Metabolite E3174 – Ethnic Differences in Pharmacokinetics between Caucasian and Asian Populations
Losartan is a selective, competitive angiotensin 11 receptor type 1 (AT1) antagonist for hypertension treatment.

Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling Using DILIsym Suggests That Mitochondrial Biogenesis Could Explain Adaptation to Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI)
Resolution of elevations of the liver injury biomarker serum ALT despite continued drug dosing, termed “adaptation”, is commonly observed in clinical trials, but the underlying mechanisms behind this phenomenon remain unclear.

Representation of Crizotinib and Pazopanib-mediated Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST)
Crizotinib and pazopanib are oral receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).

Concentration-QT Analysis of Quizartinib in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory AML
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) is expressed in hematopoietic progenitor cells, and signaling through FLT3 promotes these cells’ proliferation and differentiation.
