Sitaxsentan and ambrisentan are highly selective endothelin-1 type A receptor antagonists which were developed for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.

Cognitive Engineering – The Tools, Mindset, and Strategy for an Integrated Development Standard
Internet technology facilitates connectedness but often fails to foster collaboration. Advanced modeling techniques can provide insight for development discussions, but in many cases, these tools…

Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Gatilfoxacin in Plasma and Sinus Aspirate Drug Treatment of Maxiliary Sinusitis
A novel approach to collect sinus exudate was utilized and the time course of gatifloxacin (GAT) in the blood and at the primary infection site were assessed during treatment for acute maxillary sinusitis (AMS).

Pharmacokinetics And Exposure-Response Relationships Of Dasotraline In The Treatment Of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder In Adults
To characterize the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data to explore the time course and exposure response relationships in Phase 2 to define dasotraline benefit to risk relationship in adult Attention...

Characterization of Population Pharmacokinetics of Cariprazine and Its Major Metabolites
Population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis was undertaken to describe the concentration‑time profiles of cariprazine and its 2 major metabolites of similar pharmacological activity, desmethyl‑cariprazine...

IVIVC using in silico and PBPK methods for inhaled drug product development
The physiologically based model of the lung included in GastroPlus™ was used to simulate the absorption, distribution, and pharmacokinetics of two APIs from an inhaled combination product.

Modeling of Active Transport and Metabolism for Hepatocyte Assays with Application of In Vitro to In Vivo Extrapolation (IVIVE)
Sandwich and suspended hepatocyte cultures are routinely used to assess either active transport and/or metabolism of drug molecules.

Development of In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation for Long Acting Injectable Microsphere Formulations
The concept of in vitro-in vivo correlations (IVIVCs) for long-acting injectable (LAI) microsphere formulations has gained more significance in the past decade.

Application of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Models in Predicting Drug Pharmacokinetics for Different Ethnic Groups
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of PBPK models to predict the pharmacokinects (PK) of different compounds in two ethnic groups, Caucasian and Chinese.

Robust Uncertainty Estimates for Unbalanced Data Sets
Mathematical models of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs) play a key role in qualifying synthesis ideas, drug candidates and leads.

Population Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Exposure-Efficacy Analyses of Nivolumab in Subjects with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Nivolumab is a fully human immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody (mAb) that selectively binds to the programmed death-1 (PD-1) membrane receptor. PD-1 is a negative regulatory molecule expressed...

Population Pharmacokinetics and Exposure-Response Analyses for Abatacept in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Polyarticular-course juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA) is the most common chronic rheumatic disorder in children and one of the leading causes of childhood-acquired disability. Treatment with biologic...

Systemization of Time-to-Event Analyses for Pharmacometric Applications
In addition to the values of efficacy and safety endpoints, the timing of such endpoints relative to the start of treatment is often of interest. A commonly used statistical methodology for analyzing such...

Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Dose Selection for Pediatric Patients (Birth to <18 years)
Ceftolozane/tazobactam is a combination of the novel cephalosporin, ceftolozane, and the beta-lactamase inhibitor, tazobactam. It is approved for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI)...

Prospective Liver Safety Comparison of Two Treatments for Autosomal-Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling
The main objective of this research was to prospectively compare the potential for lixivaptan to cause liver toxicity to a comparator drug in the same class, tolvaptan, which has produced off-target liver signals in clinical trials.

Simulation of in vitro Dissolution and Degradation of Orntide-loaded PLGA Microspheres
An in vitro dissolution model has been developed to describe the drug release from orntide-loaded PLGA microspheres.

Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Compound A and Its Metabolite in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
Compound A is a potent and highly selective non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist being developed for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy and other potential indications.
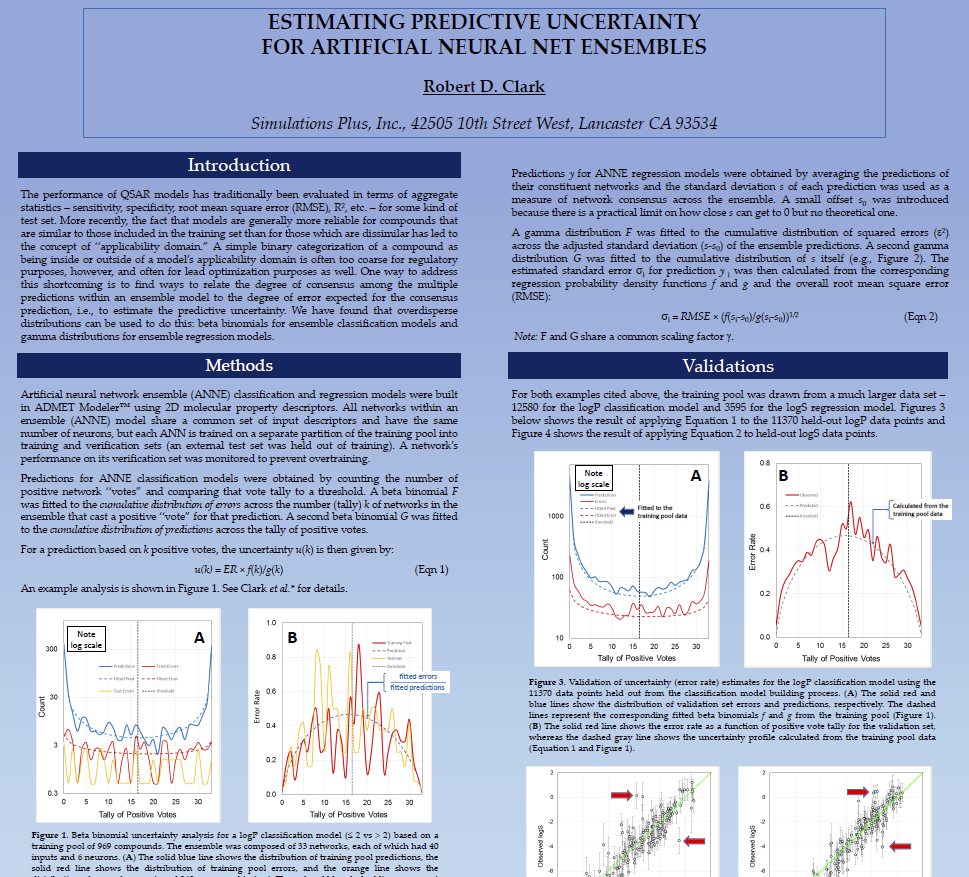
Estimating Predictive Uncertainty for Artificial Neural Net Ensembles
The performance of QSAR models has traditionally been evaluated in terms of aggregate statistics – sensitivity, specificity, root mean square error (RMSE), R2, etc. – for some kind of test set.
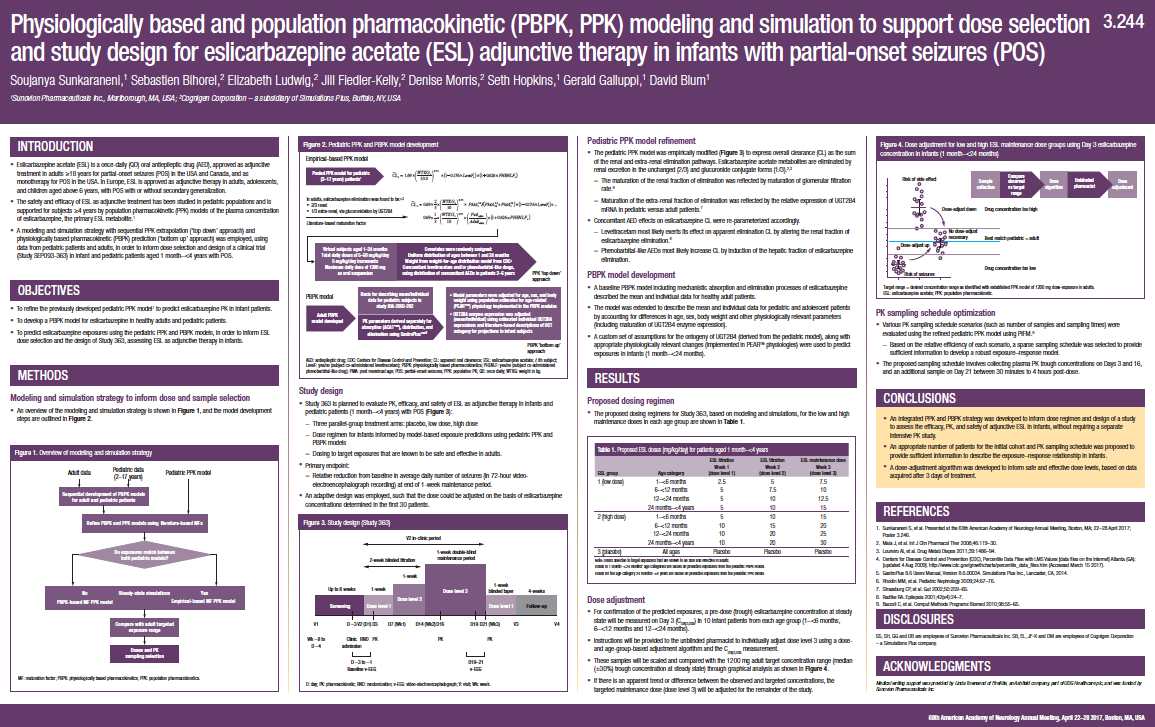
Physiologically Based and Population Pharmacokinetic (PBPK, PPK) Modeling and Simulation to Support Dose Selection and Study Design for Eslicarbazepine Acetate (ESL) Adjunctive Therapy in Infants with Partial-Onset Seizures (POS)
Eslicarbazepine acetate (ESL) is a once-daily (QD) oral antiepileptic drug (AED), approved as adjunctive treatment in adults ≥18 years for partial-onset seizures (POS) in the USA and Canada, and as...
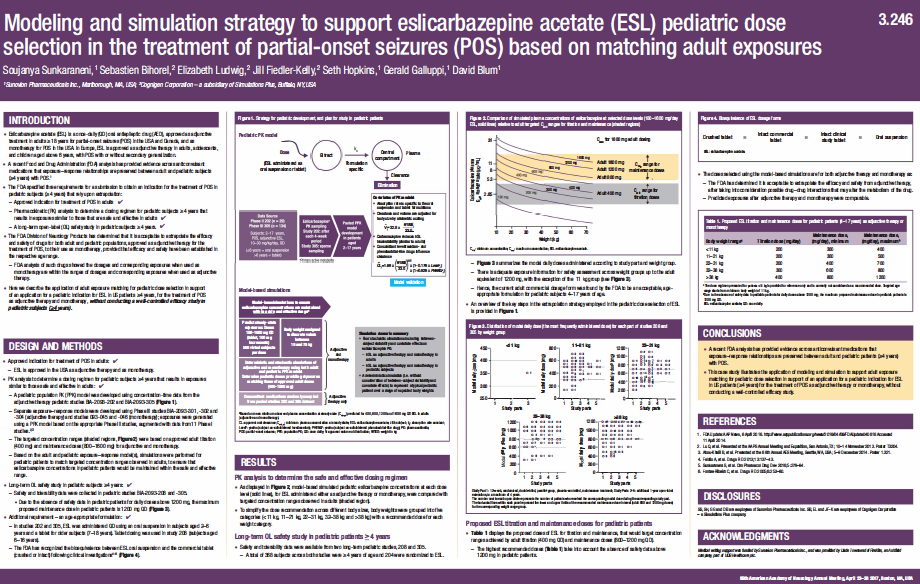
Modeling and Simulation Strategy to Support Eslicarbazepine Acetate (ESL) Pediatric Dose Selection in the Treatment of Partial-Onset Seizures (POS) Based on Matching Adult Exposures
Eslicarbazepine acetate (ESL) is a once-daily (QD) oral antiepileptic drug (AED), approved as adjunctive treatment in adults > years for partial-onset seizures (POS) in the USA and Canada, and as monotherapy...
