Despite the importance of medication adherence for successful management of seizure disorders, nonadherence continues to be a significant problem in patients with epilepsy.
Computational Modeling of OATP1B1 Inhibitors
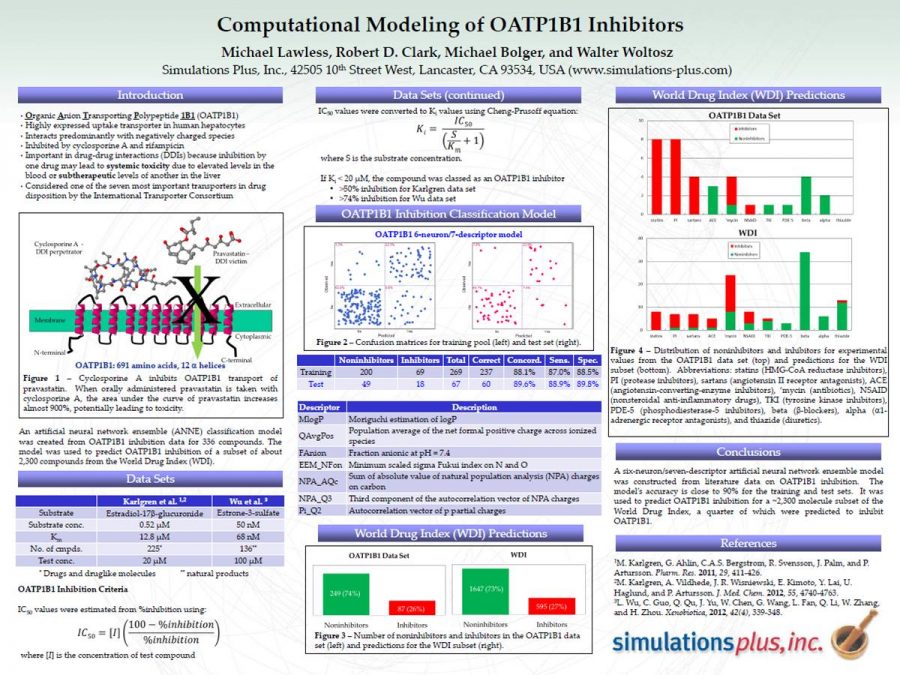
This poster was presented at the 2014 SOT meeting. It describes where the OATP1b1 data originated and the cutoff value. The model, including descriptors, is discussed.

Quantitative Modeling Uncovers a Potential Limitation in the Putative Mechanism of CCl4 Hepatotoxicity
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the leading causes of drug development failures and drug withdrawals. DILIsym® is being developed to identify and mitigate DILI risk through in silico…

Where top-down meets bottom-up: Combined population PK (PopPk) and PBPK approaches to evaluate the impact of food and gastric pH on the pharmacokinetics of GDC-0941
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (P13K) signaling pathway is deregulated in a wide variety of cancers. GDC-0941 is a potent and selective pan-inhibitor of class I P13K.

Population Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Eslicarbazepine Acetate for Adjunctive Therapy in Refractory Partial Onset Seizures
Eslicarbazepine acetate (ESL), a once-daily antiepileptic drug (AED), is converted to eslicarbazepine, the primary active metabolite of ESL, after oral administration. The population pharmacokinetics (PK)…

Design, Synthesis, and in vitro Testing of Novel COX-2/COX-1 Inhibitors
To design,synthesize,and test new lead molecules that inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 forms of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme, with higher affinity for COX-2 than for COX-1.

Prediction of Valsartan Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Population using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model
A method for transporter-based in vitro-in vivo extrapolation (IVIVE) was previously developed and demonstrated by predicting valsartan PK after i.v.administration [1]. The purpose of this study was to…

MembranePlus™: A Tool to Study in vitro/in vivo Transport and Drug-Drug Interaction
To develop a mechanistic mathematical model for analysis of in vitro permeability assays that accounts for all mechanisms contributing to observed apparent permeability: passive paracellular and…

Simulating the Disposition of Budesonide from Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs) and Nebulizers
Objective: To simulate and predict the absorption and pharmacokinetics (PK) of budesonide following orally‐inhaled (OIN) i.e. respiratory administration across multiple formulations and/or devices.

Modeling Disposition of Budesonide Following Intravenous and Oral Administration in Healthy Adult Subjects
Objective: To simulate and predict the absorption and pharmacokinetics(PK) of budesonide following intravenous(IV) and oral(PO) administrations.

Population Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Eslicarbazepine Acetate for Adjunctive Therapy in Refractory Partial Onset Seizures
Eslicarbazepine acetate (ESL) is a once-daily antiepileptic drug (AED) that is converted to eslicarbazepine, the primary active metabolite of ESL, after oral administration. A population…

Tedizolid Population Pharmacokinetics, Exposure-Response, and Target Attainment
Tedizolid phosphate is a novel antibiotic prodrug rapidly converted by phosphatases to its active moiety tedizolid after administration. Tedizolid is 4-16 fold more potent in vitro than linezolid against…

Reduction in Interindividual Variability and Clinical Significance Ratio in Covariate Assessment
Covariate analysis has become a customary and expected part of population pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modeling.1 The covariate submodel describes, explains, and…

A Population PK Model for Cariprazine and the Metabolites
Cariprazine (CAR) is a potent dopamine D3/D2 receptor partial agonist with preferential binding to D3 receptors. Cariprazine was originally discovered by Gedeon Richter Plc. in Budapest, Hungary, and is…

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Amoxicillin in Neonates and Infants
An amoxicillin PBPK model was previously developed and validated in healthy adults as well as adults with altered renal function [1-2]. The purpose of this study was to explore the utility of the model in...

The Role of Paracellular and Carrier-Mediated Pathways in the Nonlinear Absorption of BCS Class III Substrates for Influx and Efflux Transporters
Mechanistic oral absorption simulation of nonlinear dose dependence for BCS Class III transporter substrates is an important objective in preclinical development of NCEs as well as in generic formulation…

Computational Exploration of the Role of a Prototypical Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern (DAMP) Molecule in Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a major source of acute liver failure and is one of the leading causes of drug development failures. As such, there remains an important unmet need for earlier...

Pharmacokinetic Profile of an Ascending-Dose, Estrogen/Progestin Combination Oral Contraceptive
The estrogen component of oral contraceptives provides stability to the endometrium so that irregular shedding and unwanted breakthrough bleeding are minimized. An ascending-dose, extended-regimen…

The PK/PD Relationship of Ethinyl Estradiol and Unscheduled Bleeding or Spotting for an Ascending-dose, Estrogen/Progestin Combination Oral Contraceptive (OC)
The estrogen component of OCs provides stability to the endometrium so that irregular shedding and unwanted breakthrough bleeding are minimized. An ascending-dose, extended-regimen ethinyl estradiol…

Mechanistic Modeling Reveals the Most Important Unknowns in Bile Acid-Mediated DILI
BSEP inhibition and consequent bile acid (BA) buildup has been proposed to be an important mechanism in druginduced liver injury (DILI). There are many gaps in the knowledge of BA homeostasis and its…
