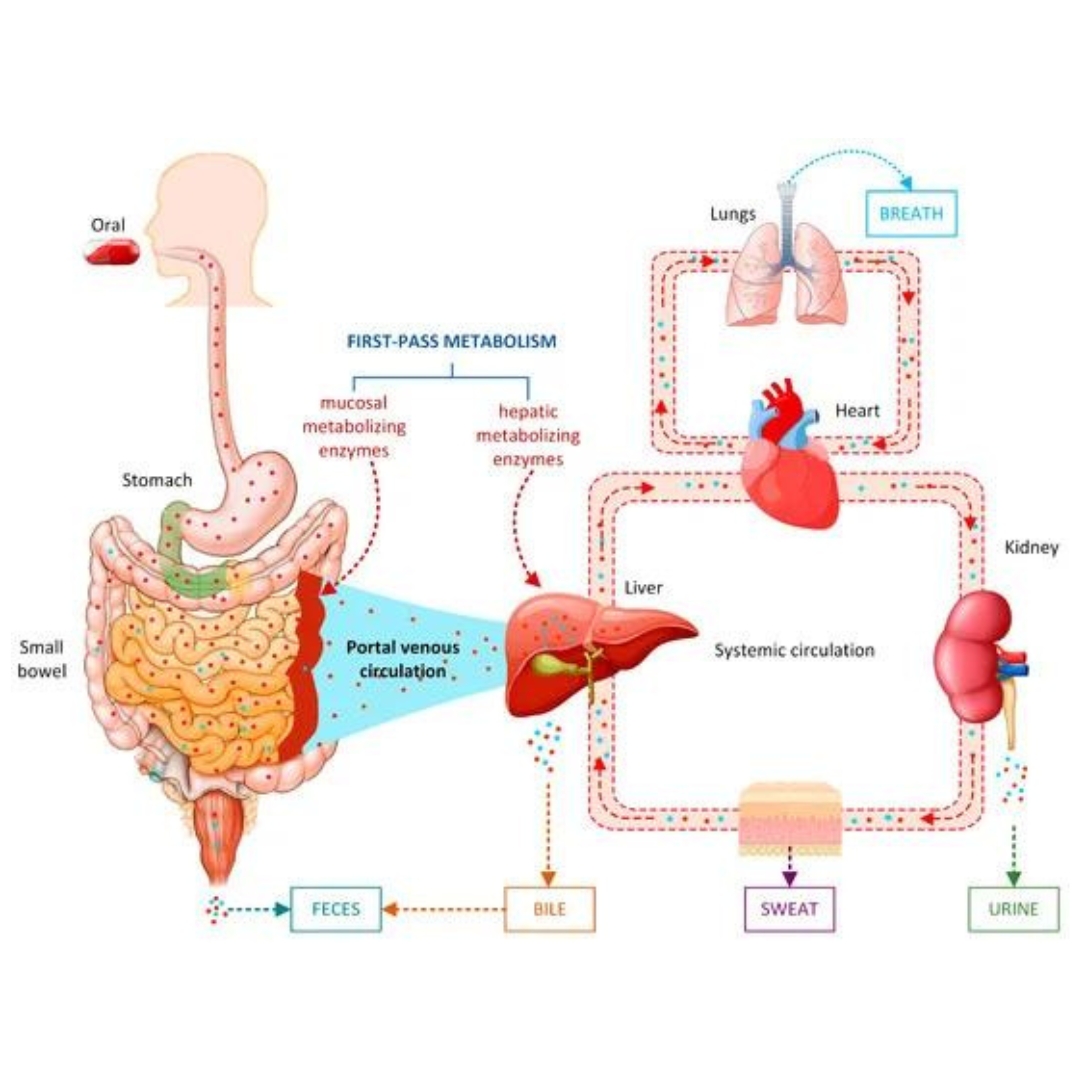
Drug metabolism and excretion play crucial roles in determining the efficacy and safety of drug candidates, and predicting these processes is an essential part of drug discovery and development.
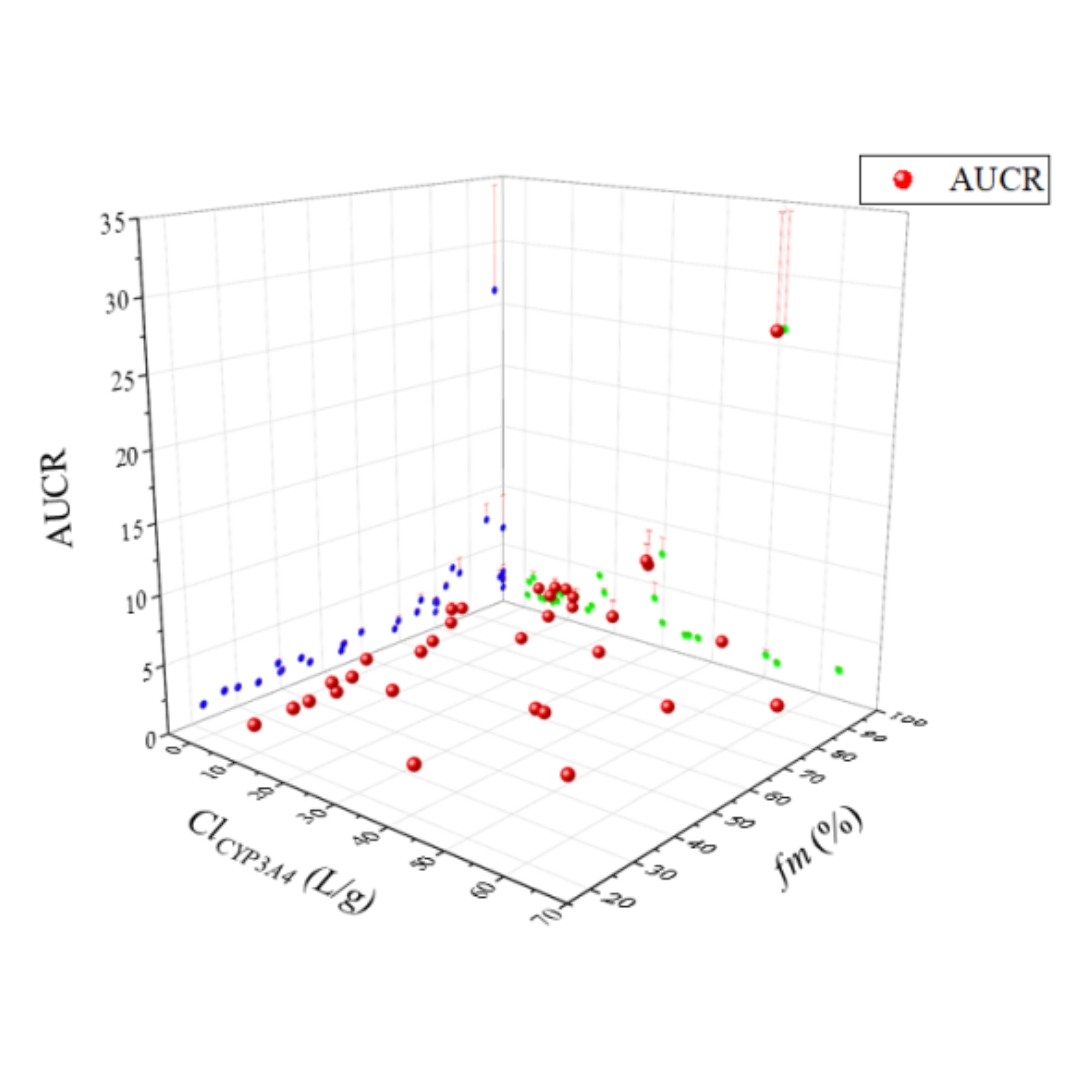
Enhancing Drug-Drug Interaction Prediction by Integrating Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model with Fraction Metabolized by CYP3A4
Enhancing the precision of drug-drug interaction (DDI) prediction is essential for mitigating potential drug interactions and enhancing drug safety and efficacy.
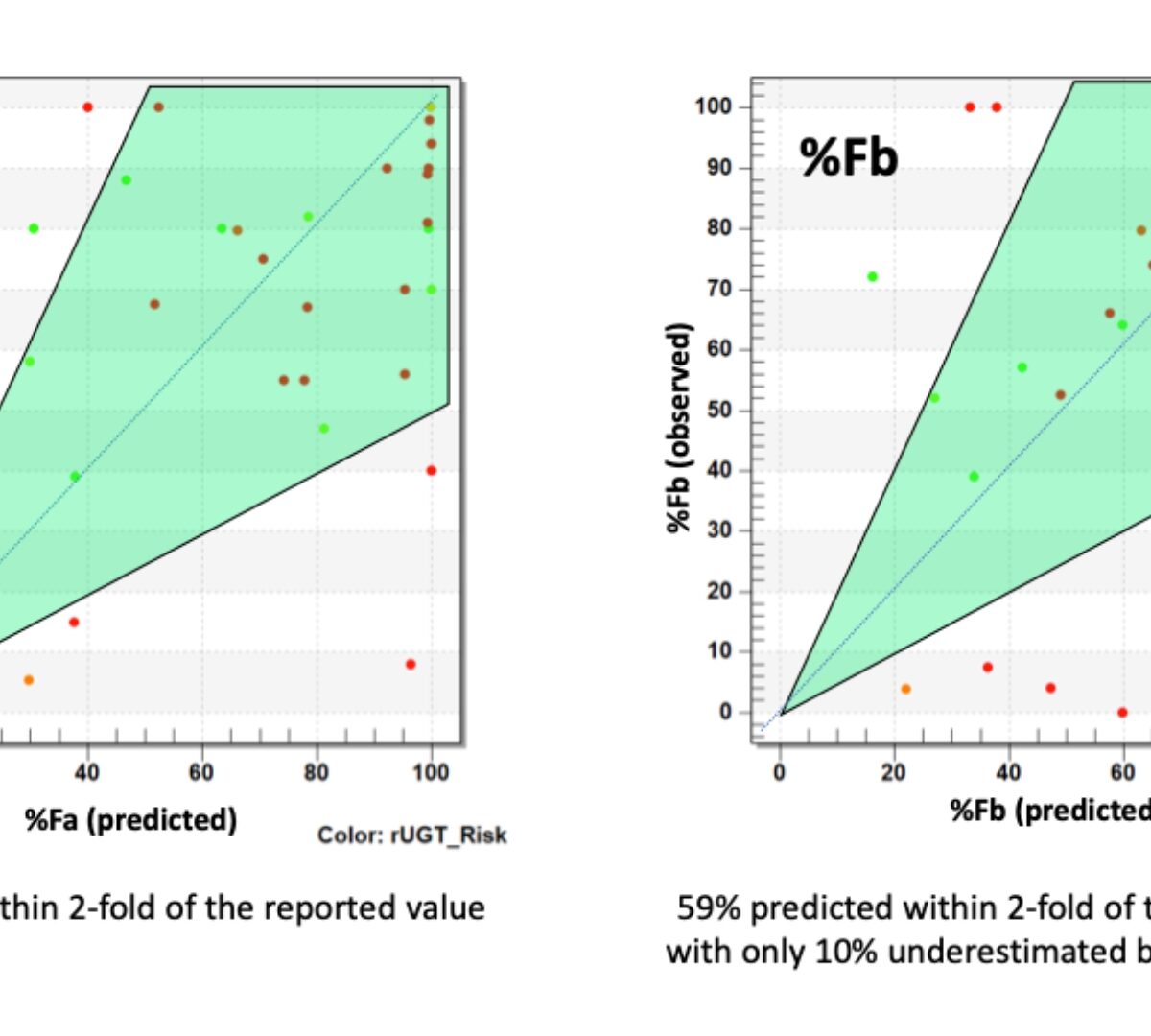
Model conception, parameterization using in silicomethods, and computational implementation
The PKB model structure depends on the problem, knowledge of the biokinetic mechanism, and availability of suitable data

The Involvement of Hypoxia in the Response of Neuroblastoma Cells to the Exposure of Atorvastatin
Cancer is a set of complex diseases, being one of the leading causes of death worldwide.

April 2023 GastroPlus Newsletter
Happy Spring! (for those of us that are North of the Equator)
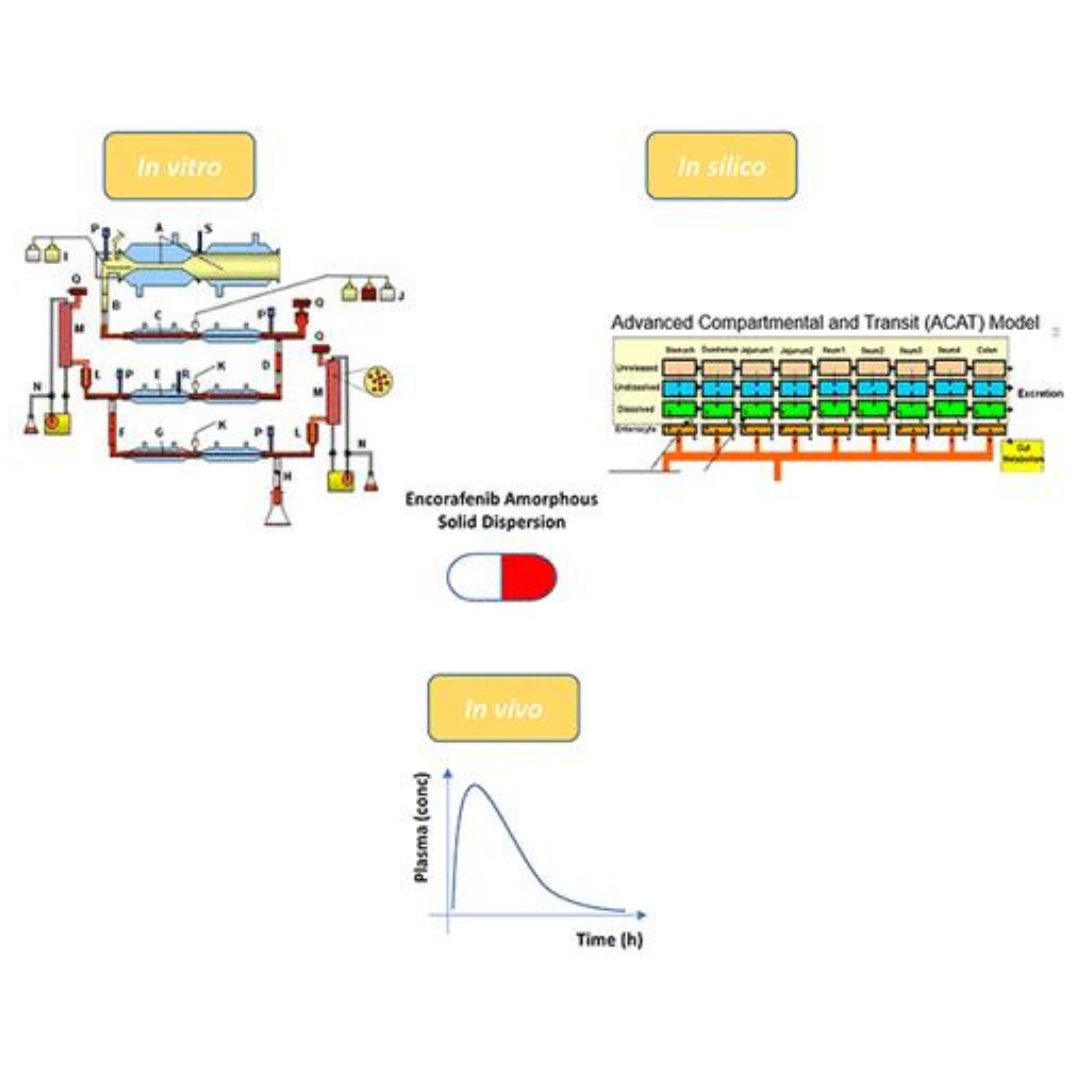
Effect of Food and a Proton-Pump Inhibitor on the Absorption of Encorafenib: An In Vivo–In Vitro–In Silico Approach
Encorafenib is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of patients with BRAF mutant melanoma and BRAF mutant metastatic colorectal cancer.

Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Modeling Using DILIsym Informed Safe Dose Selection of Emvododstat in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Patients
Clinical investigation of emvododstat for the treatment of solid tumors was terminated after two patients who were heavily...

Development of a Quantitative Systems Toxicology Model of Multidrug Resistance Protein 3 (MDR3) Inhibition to Predict Bile Acid Mediated Cholestatic Drug Induced Liver Injury
Multidrug resistance protein 3 (MDR3) translocates phospholipids (PLs) from the inner to the outer leaflet of the canalicular...

Simulations Plus Reports Second Quarter Fiscal 2023 Financial Results
Total revenue of $15.8 million; Diluted Earnings Per Share (EPS) of $0.20;
Maintains full-year revenue guidance of $59.3 - $62.0 million (+10-15%) and EPS Guidance of $0.63 - $0.67

April 2023 News/ Events
PBPK Summer Camp, FIH Predictions Workshops, and in-person conferences

Lunch & Learn – SOT 62nd Annual Meeting and ToxExpo
SOT 2023: Updates from Simulations Plus, Your Partner in Safety Assessment

Therapy with Allogeneic SARS-CoV-2-specific T-cells for Persistent COVID-19 in Immunocompromised Patients
We administered SARS-CoV-2 VST under emergency IND to 6 immunocompromised patients with persistent COVID-19 and characterized clinical and virologic responses: three patients had partial responses after failing other therapies but then died.
An integrated computational approach to infer therapeutic targets from Campylobacter concisus and peptidomimetic based inhibition of its pyrimidine metabolism pathway
Campylobacter concisus is a commensal of the human oral flora that has been allied with persistent diarrhea and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).

Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Probability of Target Attainment in Patients With Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia/ Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia
Probability of target attainment (PTA) analyses were conducted to support the recommended ceftolozane/tazobactam dosing regimens, adjusted for renal function, in patients with hospital-acquired/ventilator-associated...

Targeting Olokizumab-Interleukin 6 interaction interface to discover novel IL-6 inhibitors
The IL-6/IL-6R or IL-6/GP130 protein-protein interactions play a significant role in controlling the development of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis...

MIDD+ 2023 Panelists Discuss How to Increase Gender Equity for Women in Science
More than 150 people from around the world gathered virtually this past February for a panel discussion about how to move the needle on gender equity for women in science.
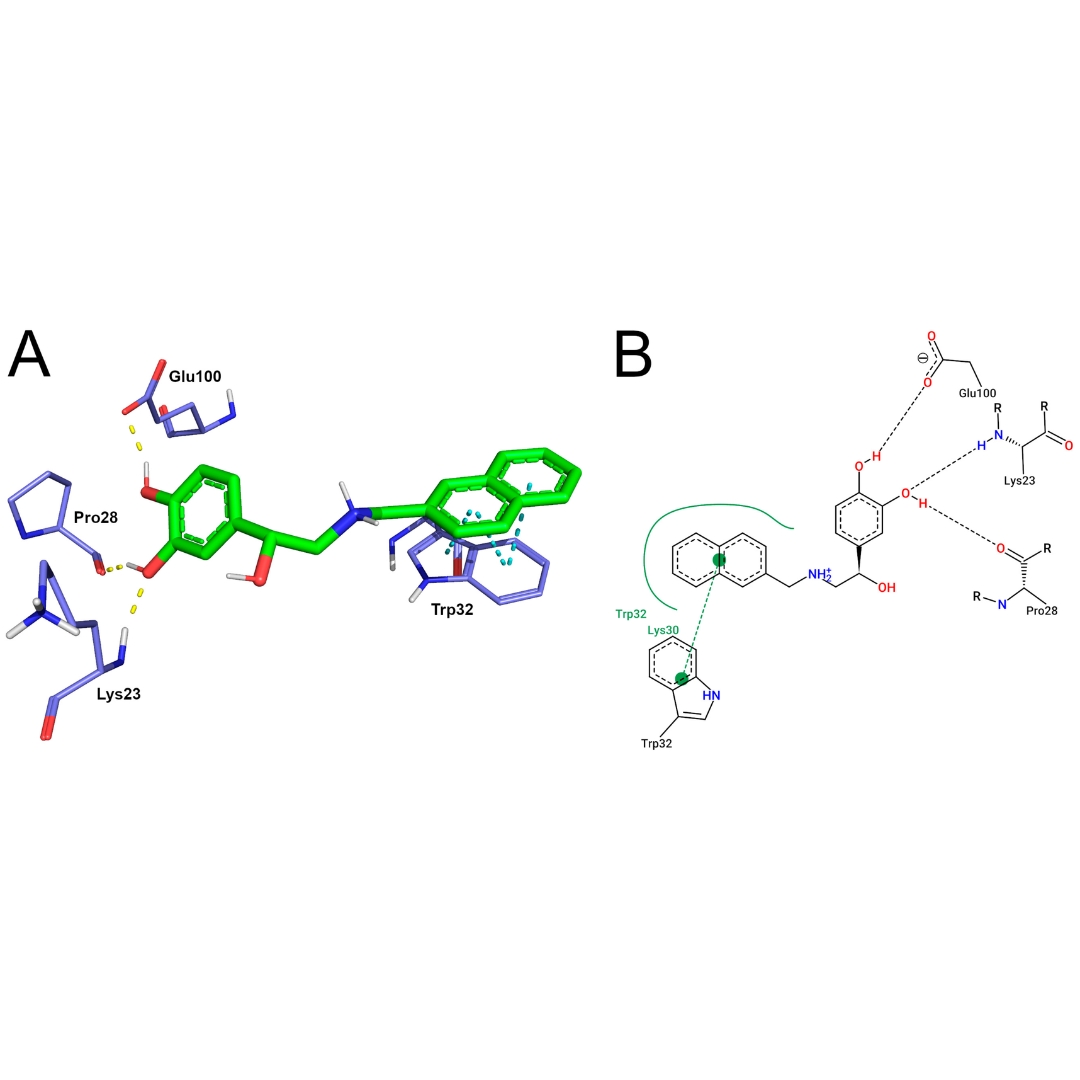
In Silico Analyses of a Promising Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Targeting Superoxide Dismutase I Protein
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the most prevalent motor neuron disorder in adults, which is associated with a highly disabling condition
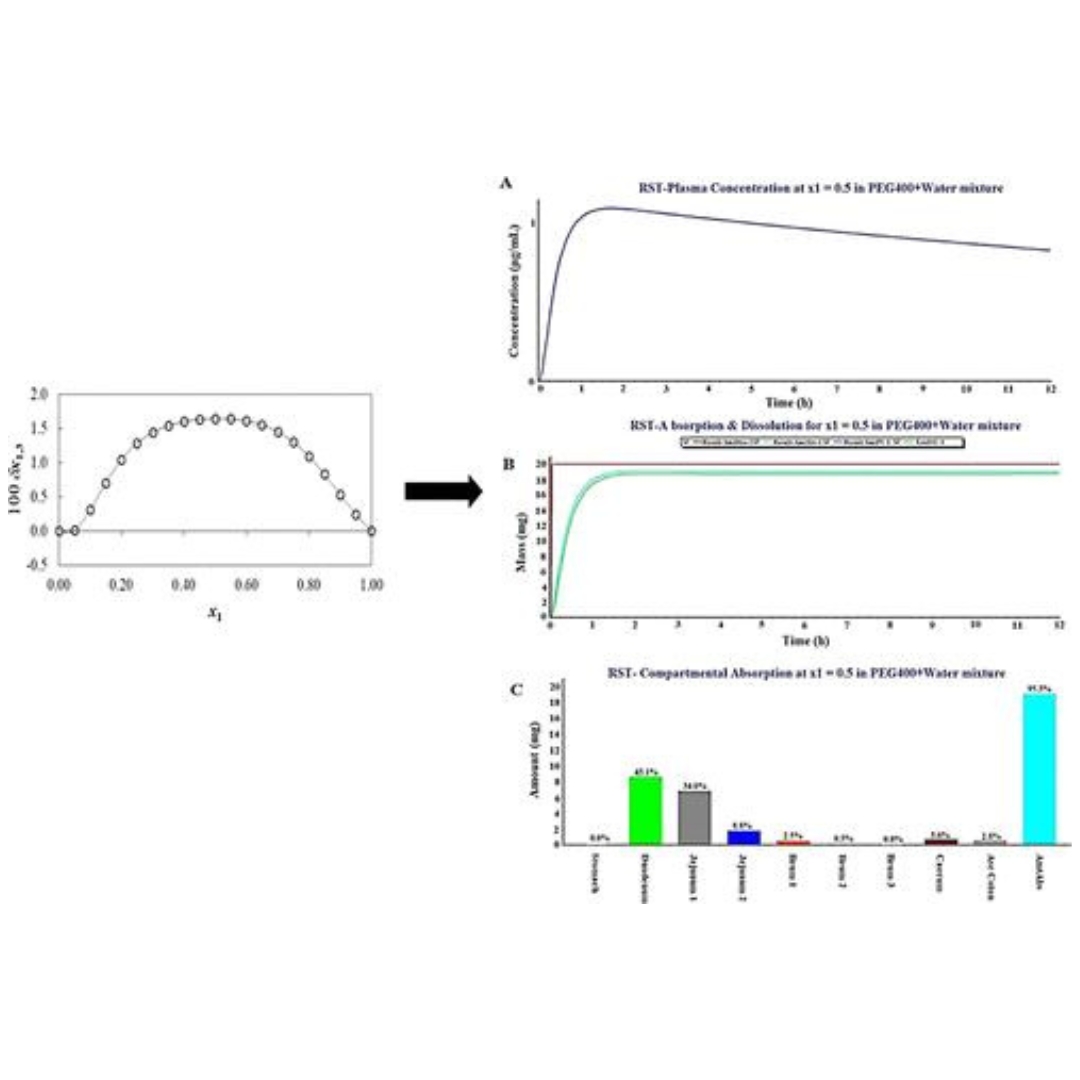
Preferential Solvation Study of Rosuvastatin in the {PEG400 (1) + Water (2)} Cosolvent Mixture and GastroPlus Software-Based In Vivo Predictions
Rosuvastatin (RST) is a poorly water-soluble drug responsible for limited in vivo dissolution and subsequently low oral systemic absorption (poor bioavailability).

Simulations Plus Enters New Strategic Collaboration to Discover Anticancer Therapies Through Its AI-Driven Drug Design Technology
Drug discovery services partnership with Sino-American Cancer Foundation focuses on the development of actionable hits against the MTHFD2 target