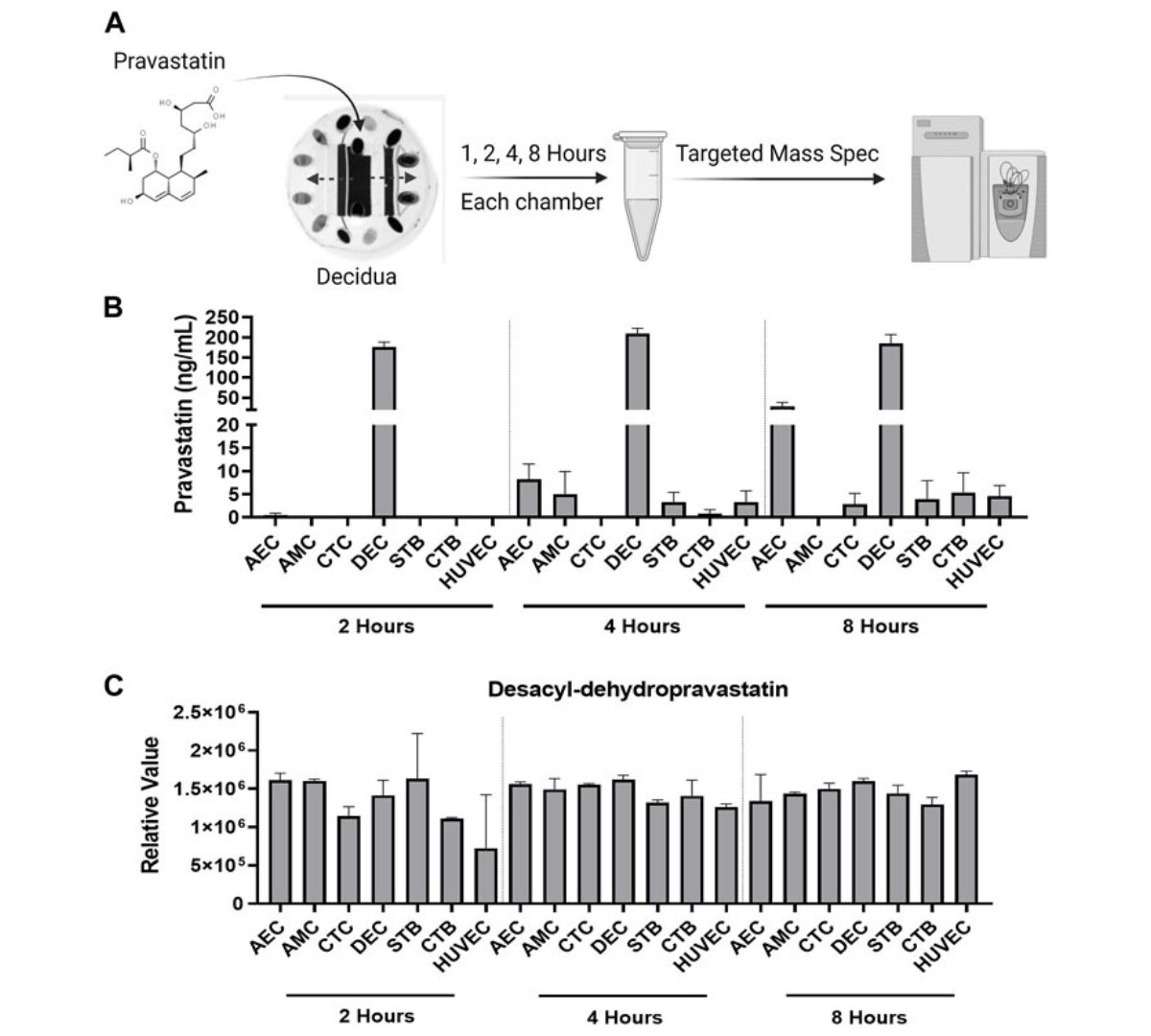
Preterm birth rates and maternal and neonatal mortality remain concerning global health issues, necessitating improved strategies for testing therapeutic compounds during pregnancy.
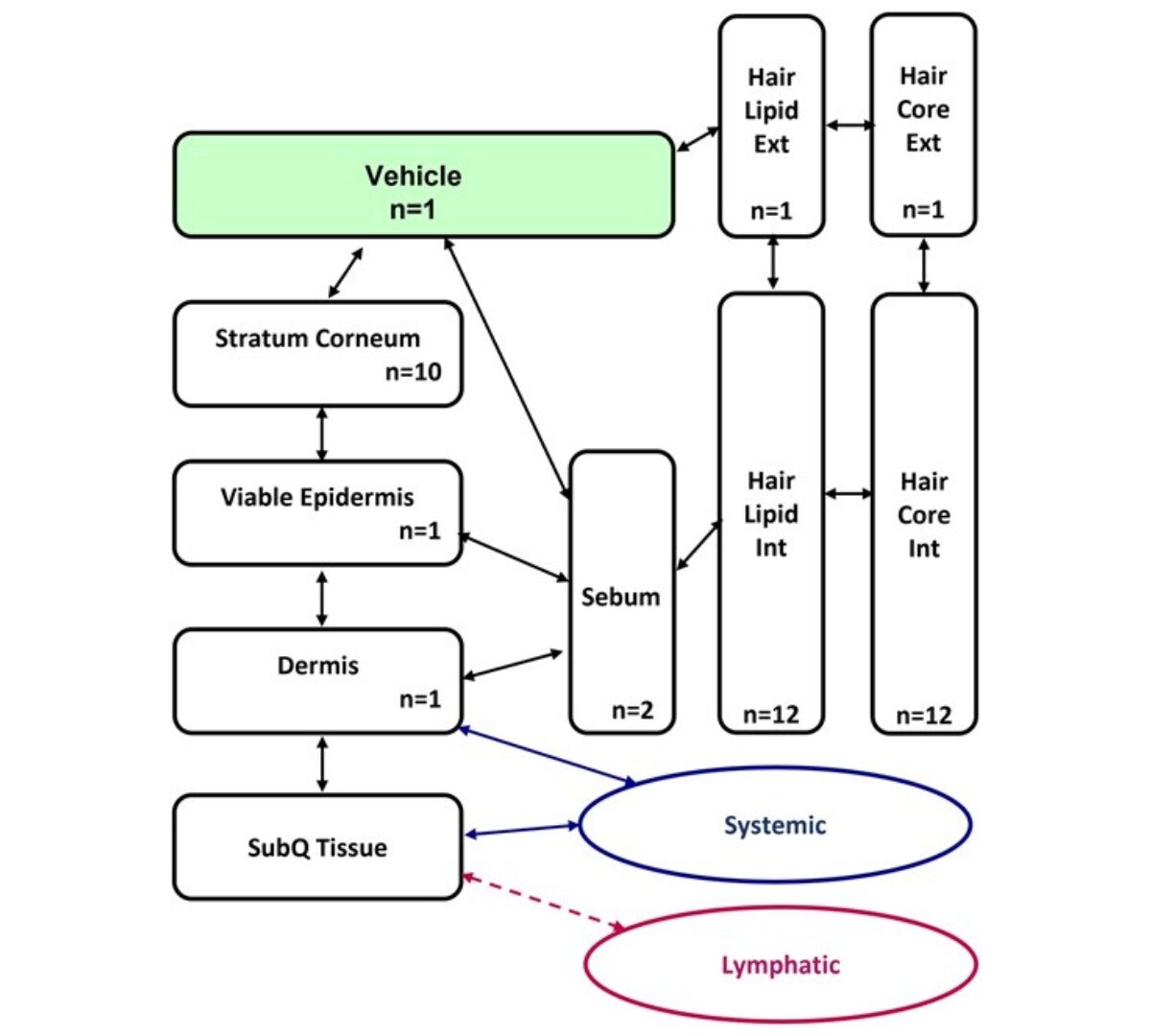
ADME characterization and PBK model development of 3 highly protein-bound UV filters through topical application
Estimating human exposure in the safety assessment of chemicals is crucial. Physiologically based kinetic (PBK) models which combine information on exposure, physiology, and chemical properties...

AIDD, an interactive AI-driven drug design system that uses molecular evolution and mechanistic pharmacokinetic simulation to optimize multiple property objectives simultaneously
Computer-aided drug design has advanced rapidly in recent years, and multiple instances of in silico designed molecules advancing to the clinic have...
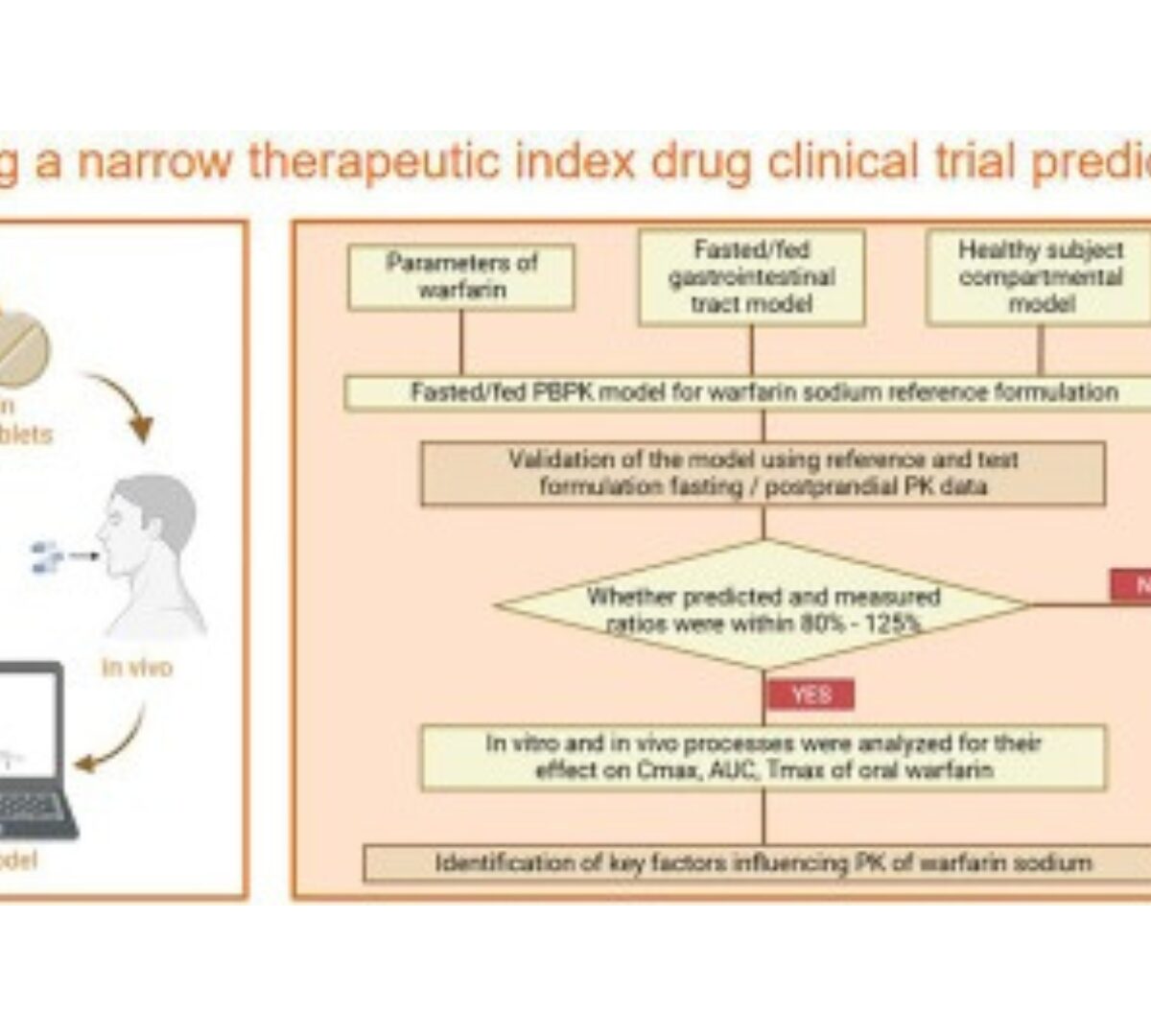
Predicting bioequivalence and developing dissolution bioequivalence safe space in vitro for warfarin using a Physiologically-Based pharmacokinetic absorption model
Bioequivalence (BE) studies support the approval and clinical use of both new and generic drug products.

Training the next generation of pharmacometric modelers: a multisector perspective
The current demand for pharmacometricians outmatches the supply provided by academic institutions and considerable investments are made to develop the competencies of these scientists on-the-job.

Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model combined with reverse dose method to study the nephrotoxic tolerance dose of tacrolimus
Nephrotoxicity is the most common side effect that severely limits the clinical application of tacrolimus (TAC), an immunosuppressive agent used in kidney transplant patients.
The In Vitro, In Vivo, and PBPK Evaluation of a Novel Lung-Targeted Cardiac-Safe Hydroxychloroquine Inhalation Aerogel
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was repurposed for COVID-19 treatment. Subtherapeutic HCQ lung levels and cardiac toxicity of oral HCQ were overcome...

PB2205: A Mechanistic Absorption and Pharmacokinetic Model of Covalent BTK Inhibitor TL-895: Influence of Food and Acid Reducing Agents
L-895 is a highly potent, orally available, selective, covalent inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) and bone marrow tyrosine kinase X-linked (BMX)...

Quantitative Systems Toxicology identifies independent mechanisms for hepatotoxicity and bilirubin elevations due to AKR1C3 Inhibitor BAY1128688
BAY1128688 is a selective inhibitor of AKR1C3, investigated recently in a trial that was prematurely terminated due to drug-induced liver injury. These...

Assessing Liver Effects of Cannabidiol and Valproate Alone and in Combination Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology
In clinical trials of cannabidiol (CBD) for the treatment of seizures in patients with Dravet syndrome, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, and tuberous sclerosis complex, elevations in serum alanine...

Discovering Negative Allosteric Modulators of Frizzled 4 Receptor Using the NPASS Database
The class F G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) consists of the Smoothened receptor (SMO) and 10 Frizzled receptors (FZDs).

The Organophosphate Esters Used as Flame Retardants and Plasticizers Affect H295R Adrenal Cell Phenotypes and Functions
Adverse effects associated with exposure to brominated flame retardants have led to regulations for their use and their replacement with organophosphate esters (OPEs).

In Silico Modeling Approaches Coupled with In Vitro Characterization in Predicting In Vivo Performance of Drug Delivery System Formulations
Optimization of the in vivo performance of dosage forms in humans is essential in developing not only conventional formulations but also drug delivery system (DDS) formulations.

Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to assess the drug-drug interactions of anaprazole with clarithromycin and amoxicillin in patients undergoing eradication therapy of H. pylori infection
This study aimed to assess the pharmacokinetic (PK) interactions of anaprazole, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin using physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models.

Comparison and summary of in silico prediction tools for CYP450-mediated drug metabolism
The cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzyme system is responsible for the metabolism of more than two-thirds of xenobiotics.

Biopharmaceutics Risk Assessment—Connecting Critical Bioavailability Attributes with In Vitro, In Vivo Properties and Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling to Enable Generic Regulatory Submissions
Quality risk assessment following ICH Q9 principles is an important activity to ensure optimal clinical efficacy and safety of a drug product.

Progressive tools and critical strategies for development of best fit PBPK model aiming better in vitro–in vivo correlation
Nowadays, conducting discriminative dissolution experiments employing physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling (PBPK)...

Power of integrating PBPK with PBBM (PBPK-BM): a single model predicting food effect, gender impact, drug-drug interactions and bioequivalence in fasting & fed conditions
Over the past few years, PBPK and PBBM modelling have proven their significance in drug development. PBPK modelling is traditionally used to predict..

Development of Successful Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Models
Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling is a strong mathematical tool that integrates body physiology, drug physicochemical properties...

In silico modeling-based new alternative methods to predict drug and herb-induced liver injury: A review
New approach methods (NAMs) have been developed to predict a wide range of toxicities through innovative technologies.