Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling requires understanding of chemical, physiologic, and pharmacokinetic principles.

Structural insights into the interaction of three Y-shaped ligands with PI3Kα
Class IA phosphoinositide 3-kinase alpha (PI3Kα) is an important drug target because it is one of the most frequently mutated proteins in human cancers.

Development of Extended-Release Formulations Containing Cyclobenzaprine Based on Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling and Bioequivalence Safe Space
The use of physiologically based biopharmaceutics modeling (PBBM) and bioequivalence safe space is increasingly common for immediate-release drug products.

Application of physiologically based pharmacokinetics modeling in the research of small-molecule targeted anti-cancer drugs
Physiologically based pharmacokinetics (PBPK) models are increasingly used in the drug research and development, especially in anti-cancer drugs.

Advanced In Vivo Prediction by Introducing Biphasic Dissolution Data into PBPK Models
Coupling biorelevant in vitro dissolution with in silico physiological-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) tools represents a promising method to describe...

Best Practices for Data Visualisation
Best Practices for Data Visualisation (for the Royal Statistical Society) contains insights, advice, and examples (with code) to make data outputs more impactful.

Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Models of CYP2D6 Substrate and Inhibitors Nebivolol, Cinacalcet and Mirabegron to Simulate Drug–Drug Interactions
Index substrates and inhibitors to investigate the role of the polymorphic enzyme, cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6, in the metabolism of new compounds have been proposed by regulatory agencies.

Ziritaxestat, a Novel Autotaxin Inhibitor, and Lung Function in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The ISABELA 1 and 2 Randomized Clinical Trials
There is a major need for effective, well-tolerated treatments for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).

Leveraging the use of in vitro and computational methods to support the development of enabling oral drug products: An InPharma commentary
Due to the strong tendency towards poorly soluble drugs in modern development pipelines, enabling drug formulations such as amorphous solid dispersions...

Therapeutic Potential and Predictive Pharmaceutical Modeling of Stilbenes in Cannabis sativa
Cannabis sativa is a plant used for recreational and therapeutic purposes; however, many of the secondary metabolites in the plant have not been thoroughly investigated.

Projection of Target Drug Particle Size in Oral Formulations Using the Refined Developability Classification System (rDCS)
Dissolution limitations to oral absorption can occur if the time required for dissolution is longer than the transit time across the small intestine and/or if dissolution is slower than the drug’s permeation through the gut wall.

Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling of oral drug absorption in older adults – an AGePOP review
The older population consisting of persons aged 65 years or older is the fastest-growing population group and also the major consumer of pharmaceutical products.

Biopolymer-Capped Pyrazinamide-Loaded Colloidosomes: In Vitro Characterization and Bioavailability Studies
This study aimed to prepare colloidosome particles loaded with pyrazinamide (PZA).

PBPK Modeling as an Alternative Method of Interspecies Extrapolation that Reduces the Use of Animals: A Systematic Review
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling is a computational approach that simulates the anatomical structure of the studied species...

Integrated in vitro – in vivo – in silico studies in the pharmaceutical development of propranolol hydrochloride mucoadhesive buccal films
In order to exploit the advantage of drug delivery through the buccal mucosa, mucoadhesive buccal films with propranolol hydrochloride based on polyethylene oxide...
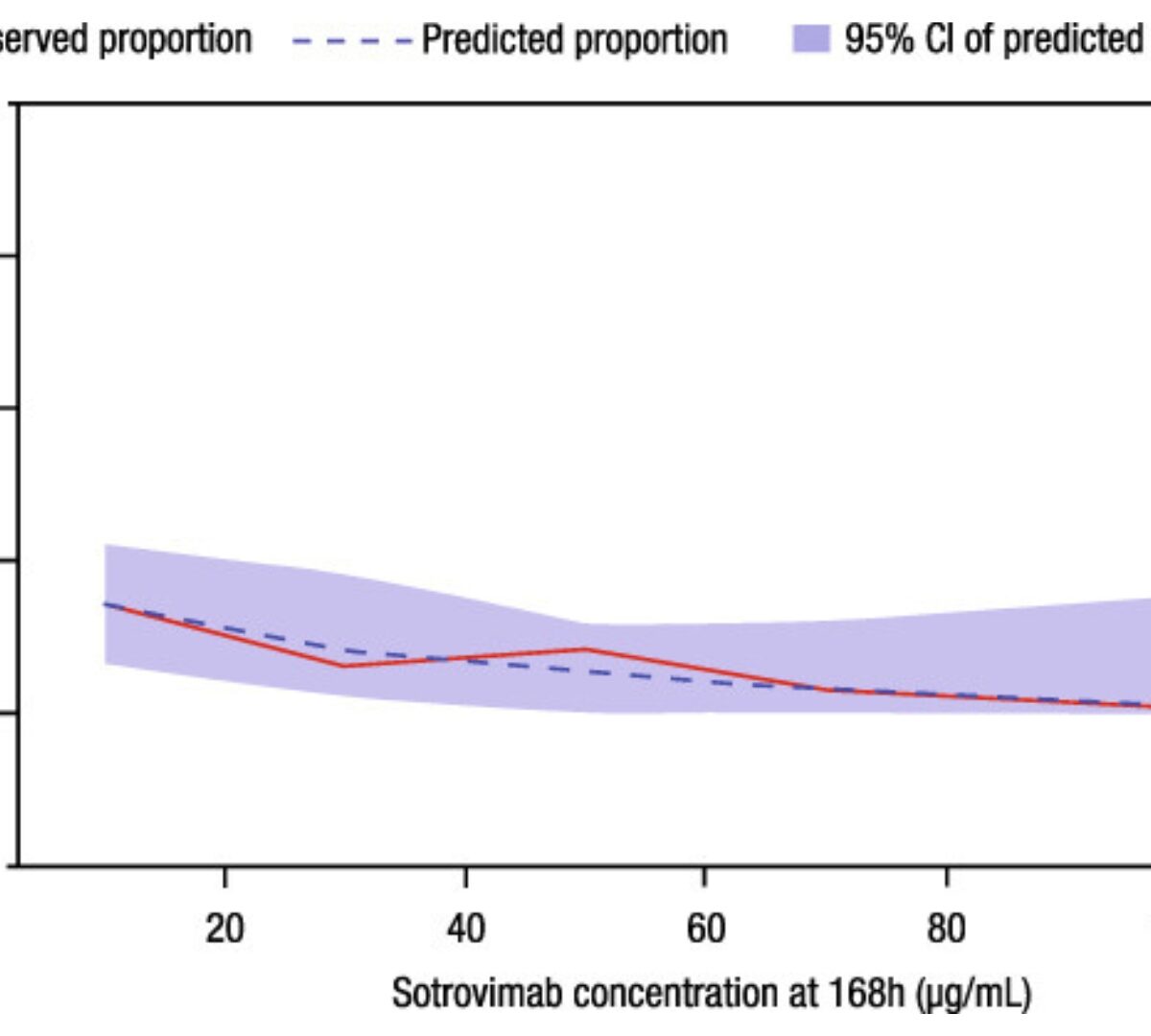
Population Pharmacokinetics and Exposure-Response Analysis of a Single Dose of Sotrovimab in the Early Treatment of Patients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19
Sotrovimab is a recombinant human monoclonal antibody that has been shown to prevent progression to hospitalization or death in non-hospitalized high-risk patients with mild to moderate...

Revisiting the in-vitro and in-vivo considerations for in-silico modelling of complex injectable drug products
Complex injectable drug products (CIDPs) have often been developed to modulate the pharmacokinetics along with efficacy for therapeutic agents used for remediation of chronic disorders.

Modeling Based Approaches to Support Generic Drug Regulatory Submissions-Practical Considerations and Case Studies
Model informed drug development (MiDD) is useful to predict in vivo exposure of drugs during various stages of the drug development process. This approach employs a variety of quantitative tools to assess the risks during the drug development process.
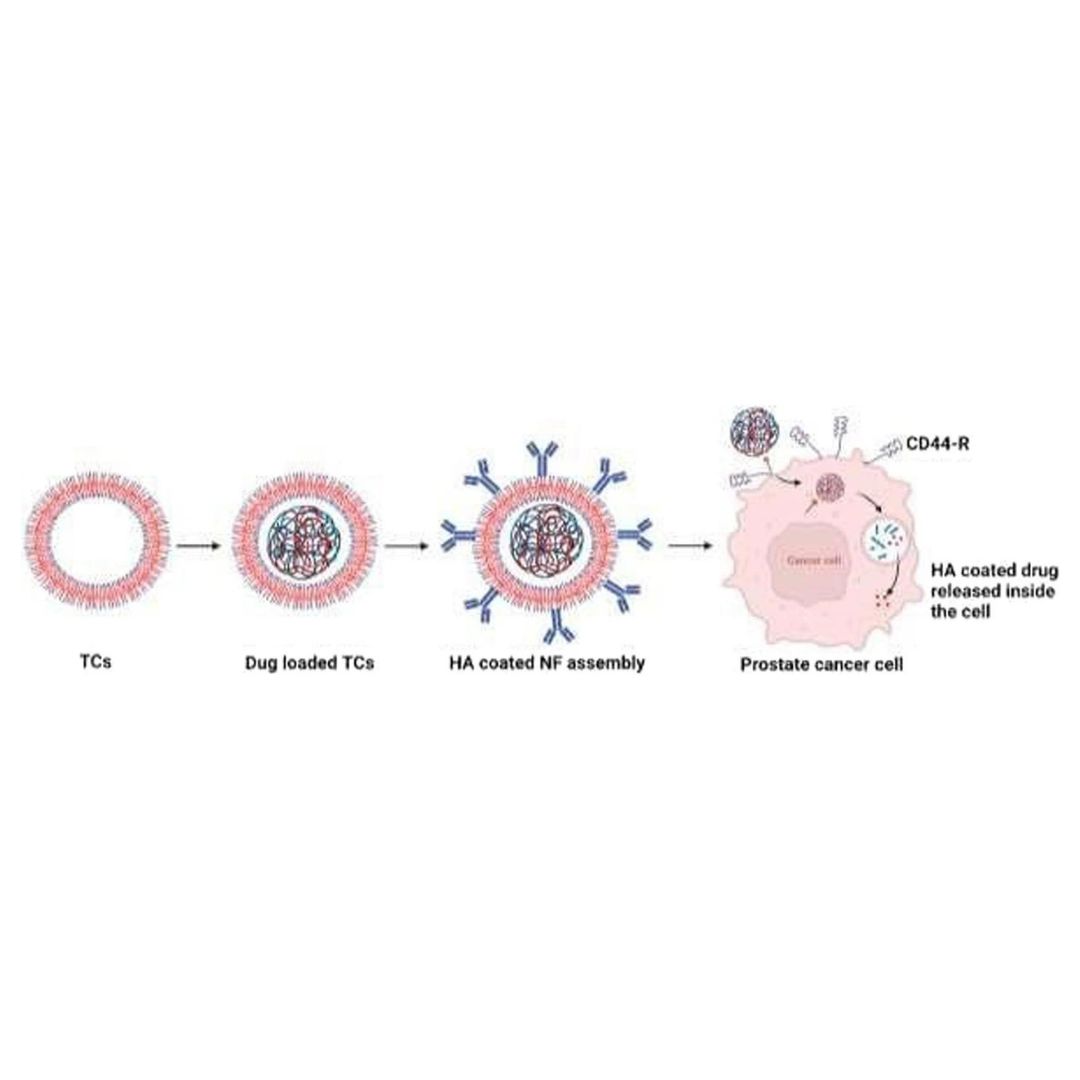
Evaluation of the anticancer potential of CD44 targeted vincristine nanoformulation in prostate cancer xenograft model: a multi-dynamic approach for advanced pharmacokinetic evaluation
The in vivo anticancer potential of vincristine (VC) loaded, thiolated chitosan-based nanoformulation (NFs) with an outer hyaluronic acid (VC-loaded in TCs-HA) coating was studied in prostate cancer (PC) xenograft in the immunosuppressed rat model induced by PC3 cell lines.

Development of a Discriminative Dissolution Method, Using In-Silico Tool for Hydrochlorothiazide and Valsartan Tablets
Hydrochlorothiazide (HTZ) and Valsartan (VAL) are poorly soluble drugs in BCS classes IV and II.
