The role of Physiologically Based Kinetic (PBK) modelling in assessing mixture toxicology has been growing for the last three decades. It has been widely used to investigate and address interactions in mixtures.

Quantitative prediction of oral bioavailability of a lipophilic antineoplastic drug bexarotene administered in lipidic formulation using a combined in vitro lipolysis/microsomal metabolism approach
For performance assessment of the lipid-based drug delivery systems (LBDDS), in vitrolipolysis is commonly applied because traditional dissolution tests do not reflect the complicated in vivo micellar formation and solubilisation processes.

Model-based drug development in pulmonary delivery: Pharmacokinetic analysis of novel drug candidates for treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection
Antibiotic resistance is a major public health threat worldwide. In particular, about 80% of cystic fibrosis patients have chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) lung infection resistant to many current antibiotics.

Galactosylated chitosan Triptolide nanoparticles for overcoming hepatocellular carcinoma: Enhanced therapeutic efficacy, low toxicity, and validated network regulatory mechanisms
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Current therapies present significant limitations.

Dibutyltin(IV) Complexes Derived from L-DOPA: Synthesis, Molecular Docking, Cytotoxic and Antifungal Activity
A series of organotin(IV) complexes was herein prepared and characterized. A one-pot synthetic strategy afforded reasonable to high yields, depending on the nature of the ligand.

Critical Evaluation of 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate Dermal Carcinogenicity Studies Using Contemporary Criteria
Skin tumors have been observed in C3H/HeJ mice following treatment with high and strongly irritating concentrations of 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (2-EHA).

Computer-aided drug discovery of Myc-Max inhibitors as potential therapeutics for prostate cancer
While Myc is an essential regulator of growth in normal cells, it is also frequently associated with cancer progression, therapy-resistance and lethal outcomes in most human cancers.

In silico scaling and prioritization of chemical disposition and chemical toxicity of 15,145 organic chemicals
This report describes the development and beta-test of methods that prioritize and scale in silico predictions of chemical disposition {(CD) intestinal absorption, membrane permeability...

Structural and functional pharmacokinetic analogs for physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model evaluation
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models enable simulations of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of chemicals from the body.

Virtual screening using covalent docking to find activators for G245S mutant p53
TP53 is the most mutated gene in all cancers. The mutant protein also accumulates in cells. The high frequency of p53 mutations makes the protein a promising target for anti-cancer therapy.

In Vivo Predictive Dissolution and Simulation Workshop Report: Facilitating the Development of Oral Drug Formulation and the Prediction of Oral Bioperformance
A 2-day workshop entitled “In Vivo Predictive Dissolution and Simulation” was held September 11–12, 2017 in Washington, DC, focused on the selection of applications, methodologies, and...

Exploring pharmacological mechanisms of Xueshuan-Xinmai-Ning tablets acting on coronary heart disease based on drug target-disease gene interaction network
Xueshuan-Xinmai-Ning Tablet (XXNT), a commercially available patent drug, has been extensively used in the treatment of coronary heart disease (CHD) with a satisfying therapeutic efficacy.

Study of degradation behaviour of montelukast sodium and its marketed formulation in oxidative and accelerated test conditions and prediction of physicochemical and ADMET properties of its degradation products using ADMET Predictor™
Study of oxidative stability of pharmaceutical actives and formulations is important as oxidation pathway is the second most significant route for the decay of pharmaceuticals.

Computational screening of known broad-spectrum antiviral small organic molecules for potential influenza HA stem inhibitors
With the emergence of new influenza virus strains that are resistant to current inhibitors such as oseltamivir (anti-neuraminidase (NA)) and amantadine (anti-M2 proton channel), influenza A viruses...
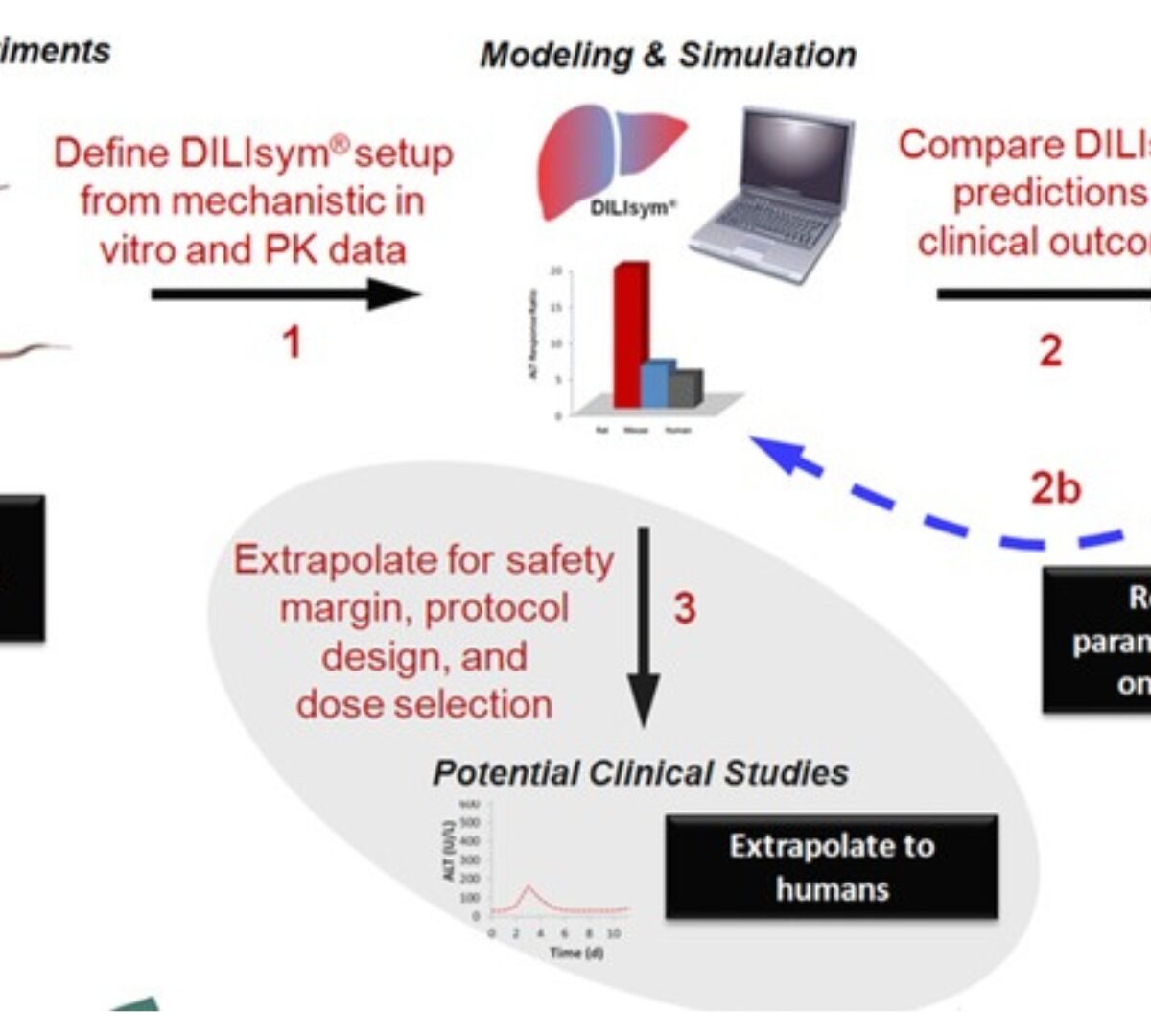
Prediction of Safety Margin and Optimization of Dosing Protocol for a Novel Antibiotic using Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Modeling
Elevations of liver enzymes have been observed in clinical trials with BAL30072, a novel antibiotic. In vitro assays have identified potential mechanisms for the observed hepatotoxicity, including...

Evaluation and Optimization of Pharmacokinetic Models for in Vitro to in Vivo Extrapolation of Estrogenic Activity for Environmental Chemicals
To effectively incorporate in vitro data into regulatory use, confidence must be established in the quantitative extrapolation of in vitro activity to relevant end...

Preclinical models for colonic absorption, application to controlled release formulation development
Oral controlled release (CR) formulations have many benefits and have become a valuable resource for the local and systemic administration of drugs.

Discussions on the hepatic well-stirred model: Re-derivation from the dispersion model and re-analysis of the lidocaine data
Roberts and Rowland explained the well-stirred model as an extreme case of the dispersion model when the dispersion number is infinity.

Characterization of solution stress degradation products of aliskiren and prediction of their physicochemical and ADMET properties
Forced degradation studies on aliskiren were carried out according to ICH and WHO guidelines. Six degradation products were formed in total in the solution state.

A bifunctional nociceptin and mu opioid receptor agonist is analgesic without opioid side effects in nonhuman primates
Misuse of prescription opioids, opioid addiction, and overdose underscore the urgent need for developing addiction-free effective medications for treating severe pain.
