Odanacatib (MK-0822), a potent, orally-active inhibitor of cathepsin K, is under clinical development for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. This poster describes base model development of a…
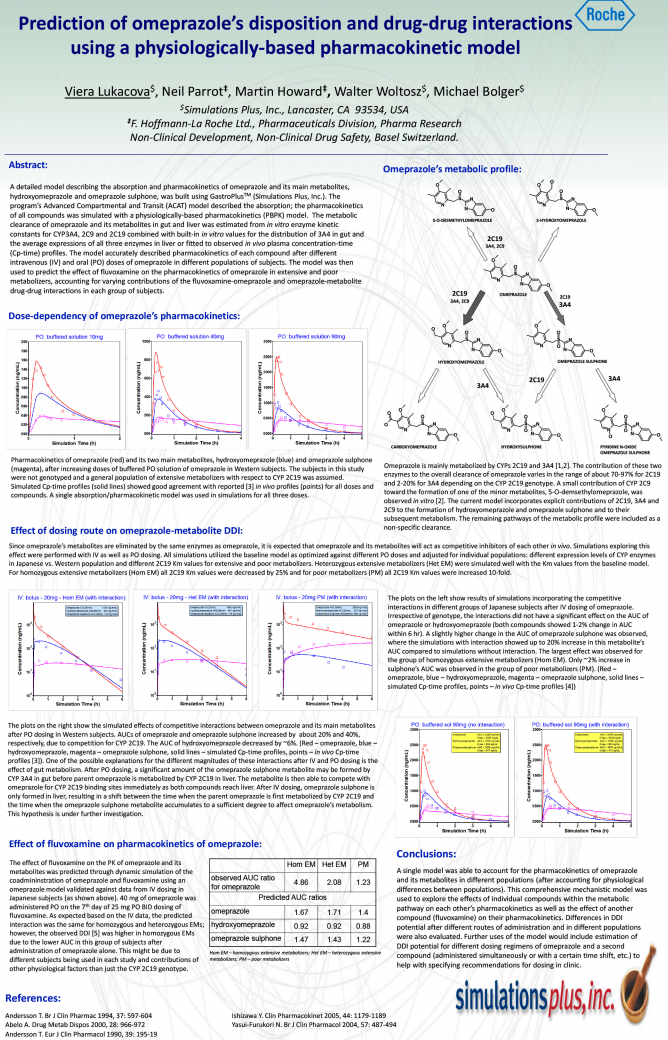
Prediction of Omeprazole’s Disposition and Drug-Drug Interactions Using A Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model
Download the poster presented at the ADMET Europe 2010 conference on the development of PBPK models and prediction of parent & metabolite DDIs with omeprazole.

Simulations of the Drug-Drug Interaction Between Atomoxetine and Quinidine in Poor and Extensive CYP2D6 Metabolizers
Atomoxetine is indicated for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children, adolescents and adults. It is metabolized to 4- hydroxy-atomoxetine primarily by CYP2D6, which is known to have…

Population Pharmacokinetics of Dexmedetomidine (DEX) During Long-Term Continuous Infusion in Critically Ill Patients
Dexmedetomidine (DEX), a selective alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist is approved for sedation. In this study, the population pharmacokinetics (PK) of DEX during long-term (> 24 hours) infusion was…

A Systems Approach to Resource Allocation in an Integrated Research and Development Environment
Typically, at the beginning of a project, the scope is defined along with the timelines and budget. As project team leaders negotiate with functional managers to recruit key team members, including…

Semi-mechanistic PK/PD Model of the Effect of Odanacatib, a Cathepsin K Inhibitor, on Bone Turnover to Characterize Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density in Two Phase II Studies of Postmenopausal Women
Odanacatib (MK-0822), a potent, orally-active inhibitor of cathepsin K, is under clinical development for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. This poster describes base model development of a...

Development of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for Predicting Deposition and Disposition follo · g Inhaled and Intranasal Administration
The selection of a biologically active molecule as a successful inhaled therapeutic agent depends on its pharmacokinetic and safety properties...

Modeling Drug Disposition of Timolol in Ocular Tissues of Rabbit following Topical Eye Drops
Recently, we reported the successful application of a novel mathematical model describing drug disposition in eye compartments to simulate disposition of clonidine after topical (eye drop) administration.

Modeling Fluconazole – a Case with Concentration-Dependent Liver:Plasma Partition Coefficient
Fluconazole is an antifungal agent widely used in the clinical setting for the treatment of candidiasis and meningitis. It undergoes minimal metabolism and is excreted renally.

PBPK Modeling of Fluoxetine and its Metabolite Norfluoxetine: Prediction of the Extent of Their Involvement in Drug Interactions
The aim of our study was to simulate the human pharmacokinetics of fluoxetine and its major metabolite, norfluoxetine, and predict the magnitude of their drug-drug interactions (DDIs) using physiologically…

A Pharmacokinetic Simulation-Based Comparison Of Varying Adherence Rates For Paliperidone ER And Risperidone In Patients With Schizophrenia
Medication adherence is important to successful management of • patients with schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders; patient nonadherence is documented in numerous studies (e.g., 30%-35%…

Simulation of Cilostazol Absorption and Pharmacokinetics
Cilostazol absorption and pharmacokinetics were simulated using GastroPlus™. The program’s Advanced Compartmental and Transit (ACAT) model described the absorption of the drug, while pharmacokinetics was…

Physiologically Based Model for Ketoconazole Disposition and Prediction of its Drug-Drug Interactions
Ketoconazole is a potent inhibitor of the major drug-metabolizing enzyme, CYP3A4 and, as the result of that, is involved in many drug-drug interactions. Pharmacokinetic (PK) information available for…

Forensic Pharmacometrics: Part 1 – Data Assembly
Pharmacometric modeling and simulation (M&S) is moving from merely describing pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) phenomena to informing critical drug development and regulatory decision-making…

Population PK/PD Modeling of Efficacy and Safety of CB1R Inverse Agonist Taranabant in Obese Patients
Taranabant is a cannabinoid-1 receptor (CB1R) inverse agonist, that was being developed by Merck and Co., Inc. as a potential treatment of obesity.

Simulation of Food Effect on Cilostazol Exposure in Human
For certain drugs, the time of administration respective to meal times can have a significant impact on exposure. The effect of food is usually attributed to increased solubility/dissolution rate and/or…

Improving the Efficiency and Ensuring the Quality of Data Assembly for Pharmacometric Analysis
Better tools and processes can improve the efficiency of data assembly and the quality of analysis-ready datasets for pharmacometric analyses.

Modeling and Simulation Approach to Pediatric Drug Development
Describe a process for determining pediatric drug doses using pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modeling and simulation.

Prediction of Dose-Dependent Intestinal and Liver First Pass Extraction for CYP3A4 Substrates
Cilostazol and midazolam absorption and pharmacokinetics were simulated using GastroPlus™. The program’s Advanced Compartmental and Transit model described the absorption and intestinal metabolism of both…

Physiologically-Based Model for Fluvoxamine Disposition and Prediction of Drug-Drug Interactions
Fluvoxamine absorption and pharmacokinetics were simulated using GastroPlus™. The program’s Advanced Compartmental and Transit model described the absorption; pharmacokinetics was simulated with a…
