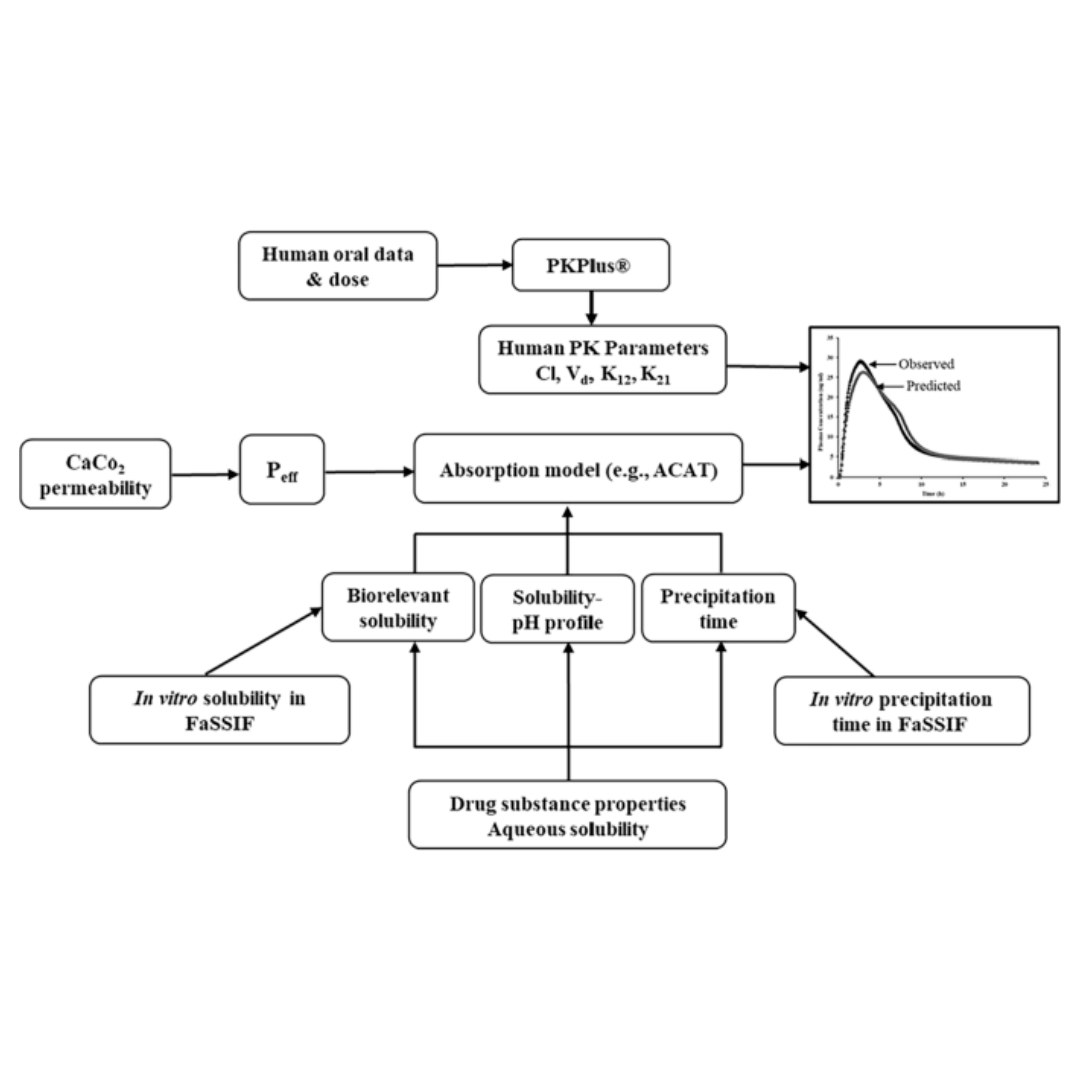
Poorly water-soluble weak base molecules such as cinnarizine often exhibit pH-dependent solubility within the gastrointestinal tract.

Simulations Plus Launches New Integrated Pulmonary Software and Services Package to Streamline Drug Development and Improve Patient Outcomes
Simulations Plus, Inc. (Nasdaq: SLP), a leading provider of modeling and simulation software and services for pharmaceutical safety and efficacy, today announced the release of a new integrated pulmonary software and services package.

May 2023 GastroPlus Newsletter
Happy Spring… even though this year I have experienced the most severe case of “hay fever” ever.

DDDPlus™ Product Brochure
Simulations software for the in vitro dissolution experiment of pharmaceutical dosage forms
Subtractive sequence-mediated therapeutic targets from the conserved gene clusters of Campylobacter hyointestinalis and computational inhibition assessment
Campylobacter hyointestinalis is a causative agent of enteritis, proctitis, human gastroenteritis, and diarrhea.
Pan-genome mediated therapeutic target mining in Kingella kingae and inhibition assessment using traditional Chinese medicinal compounds: an informatics approach
Kingella kingae causes bacteremia, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, meningitis, spondylodiscitis, and lower respiratory tract infections in pediatric patients
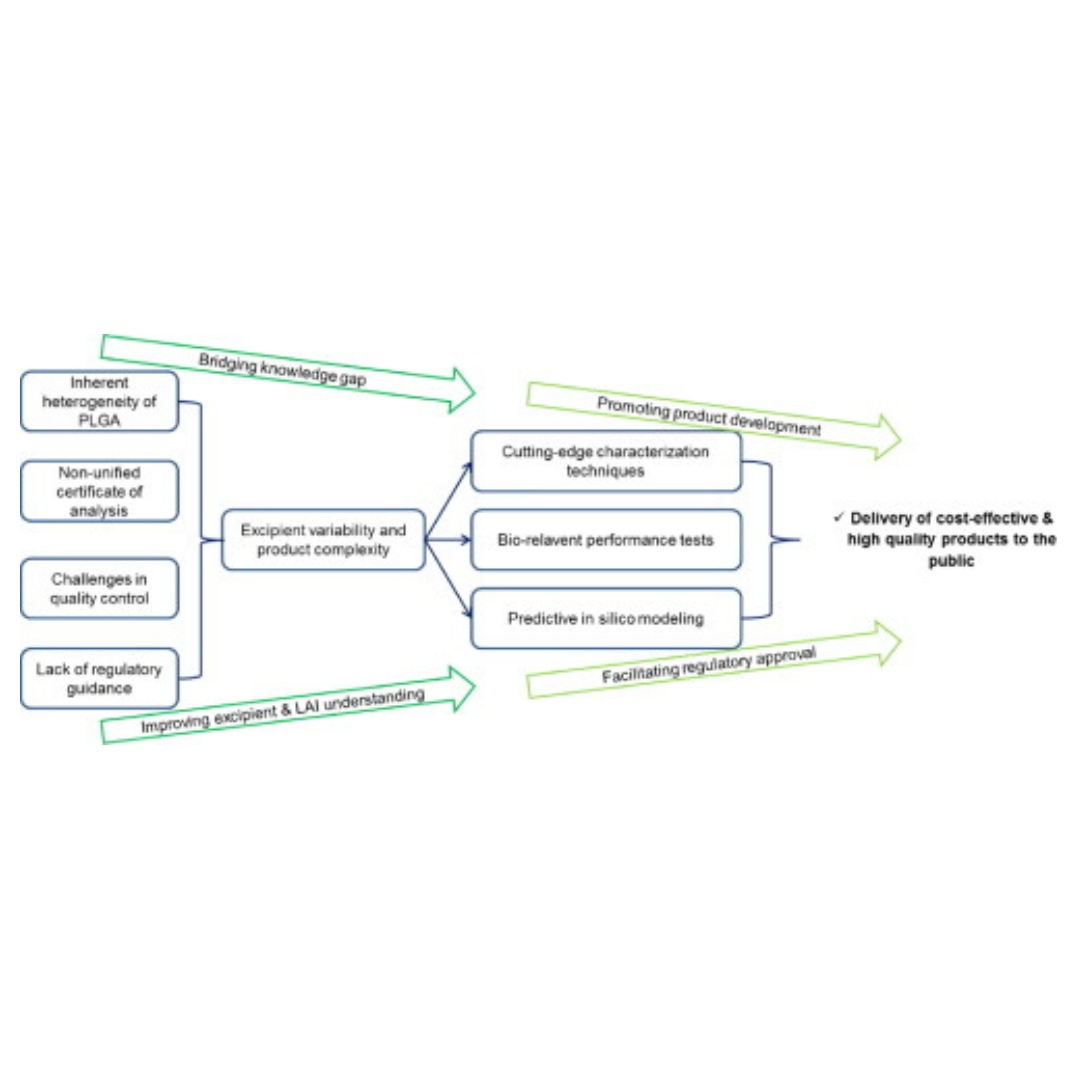
Long-acting PLGA microspheres: Advances in excipient and product analysis toward improved product understanding
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres are a sustained-release drug delivery system with several

May 2023 News/Events
Early Drug Discovery Application, FIH Predictions Workshops, and new software & consulting bundles

Rapid emergence of potentially transmissible SARS-CoV-2 with resistance to combination monoclonal antibody therapy
Prolonged COVID-19 may generate new viral variants.
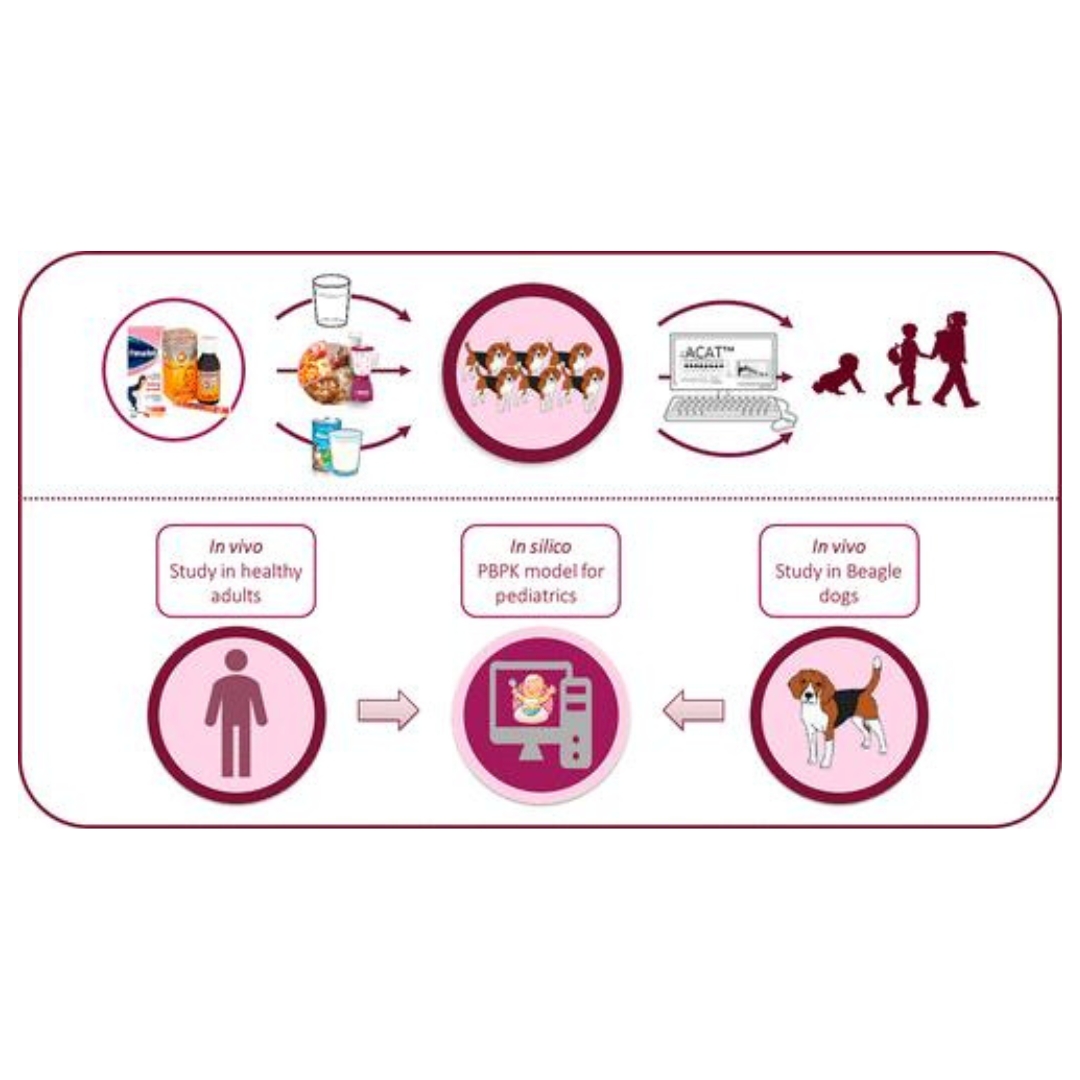
Usefulness of the Beagle Model in the Evaluation of Paracetamol and Ibuprofen Exposure after Oral Administration to Pediatric Populations: An Exploratory Study
The present study aimed to explore the usefulness of beagle dogs in combination with physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling...
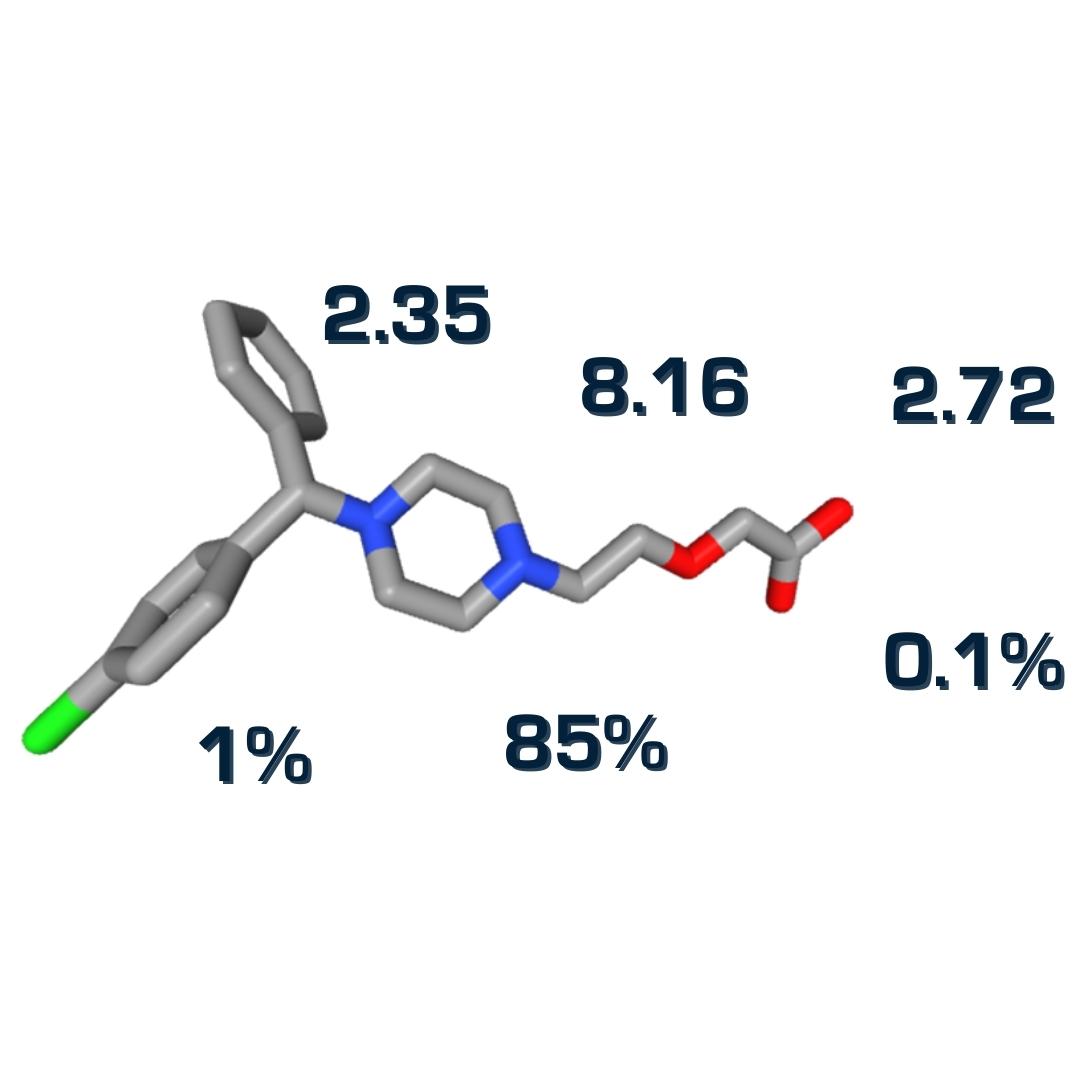
pK50─A Rigorous Indicator of Individual Functional Group Acidity/Basicity in Multiprotic Compounds
In this work, we show that the apparent pKa measured by standard titration experiments is an insufficient measure of acidity...

Using GastroPlus®, PBBM and PKPD to Define Dissolution Safe Space in Support of Registration Specifications
If you’re curious how GastroPlus could be used to define dissolution safe space for your own projects, stream now.

PBPK Modeling for Identifying and Mitigating Absorption Risks in Early Drug Development
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models represent animals and humans virtually as a collection of organs and tissues, each defined by a system of mathematical equations
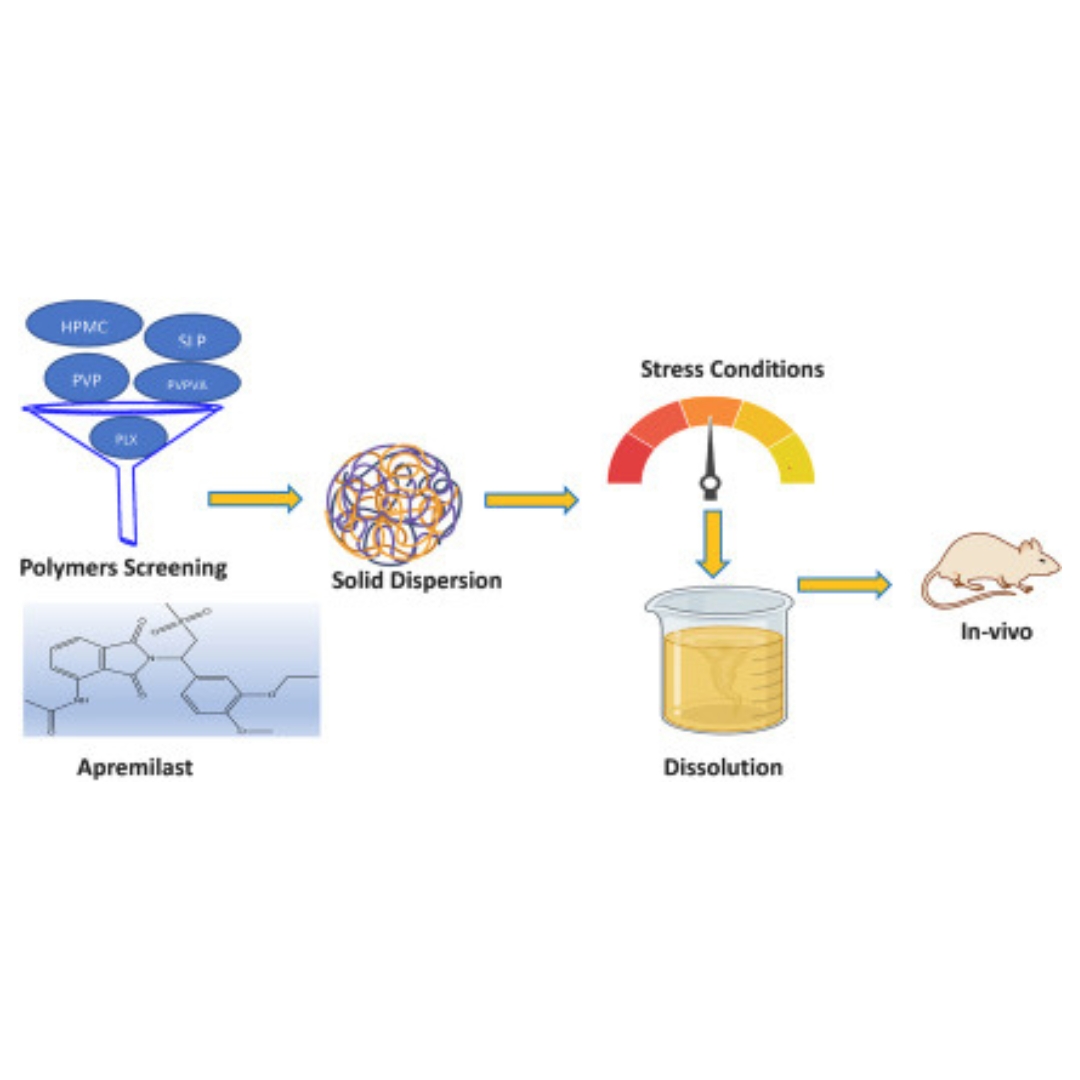
Investigating the influence of the type of polymer on sustaining the supersaturation from amorphous solid dispersions of Apremilast and its pharmacokinetics
Apremilast, a BCS class IV drug, has minimal solubility in aqueous medium which results in poor bioavailability.
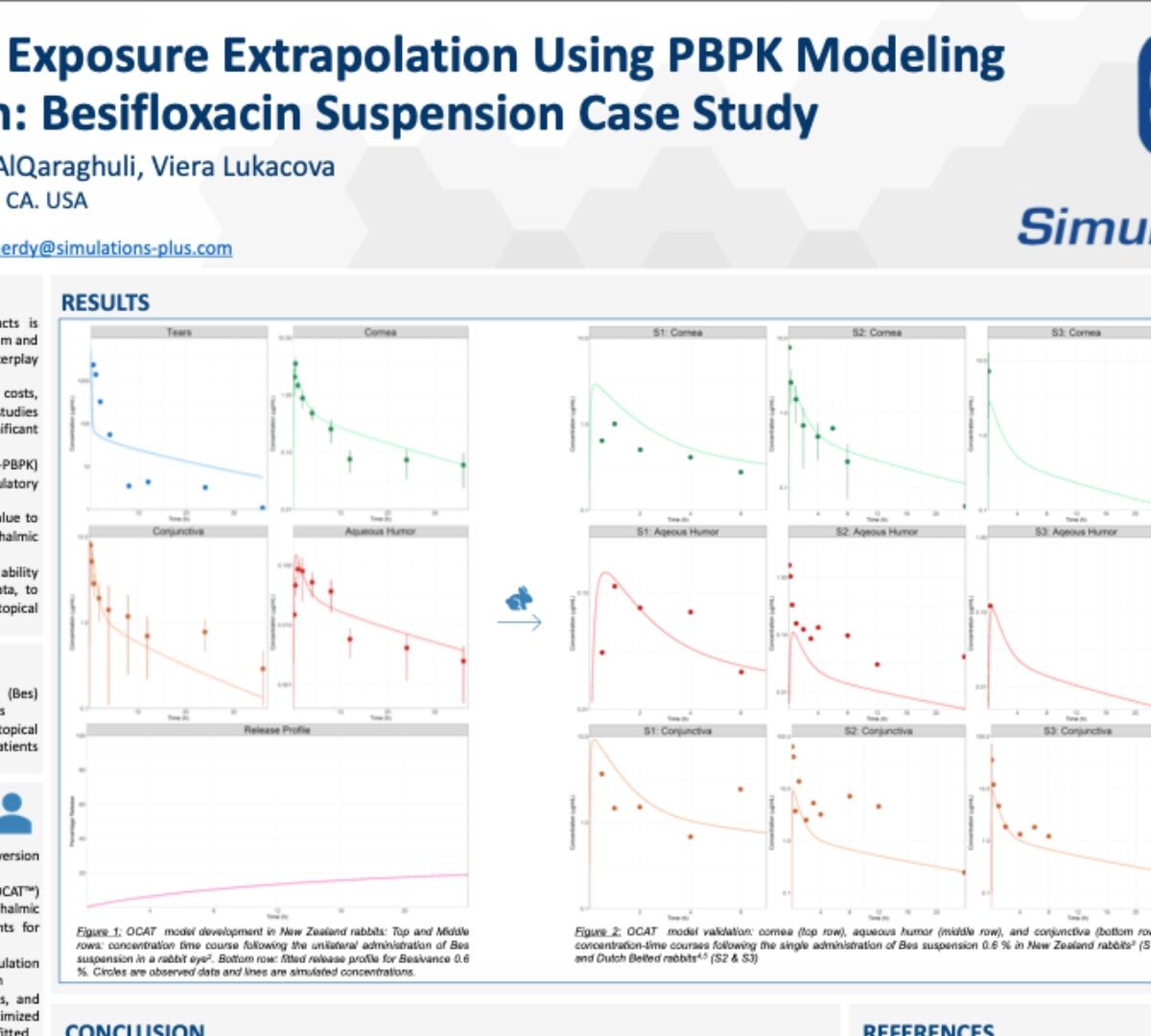
Clinical Ocular Exposure Extrapolation Using PBPK Modeling and Simulation: Besifloxacin Suspension Case Study
The purpose of this research is to demonstrate the ability of O-PBPK models, validated against rabbit PK data, to predict clinical ocular exposure, following topical administration of ophthalmic suspensions
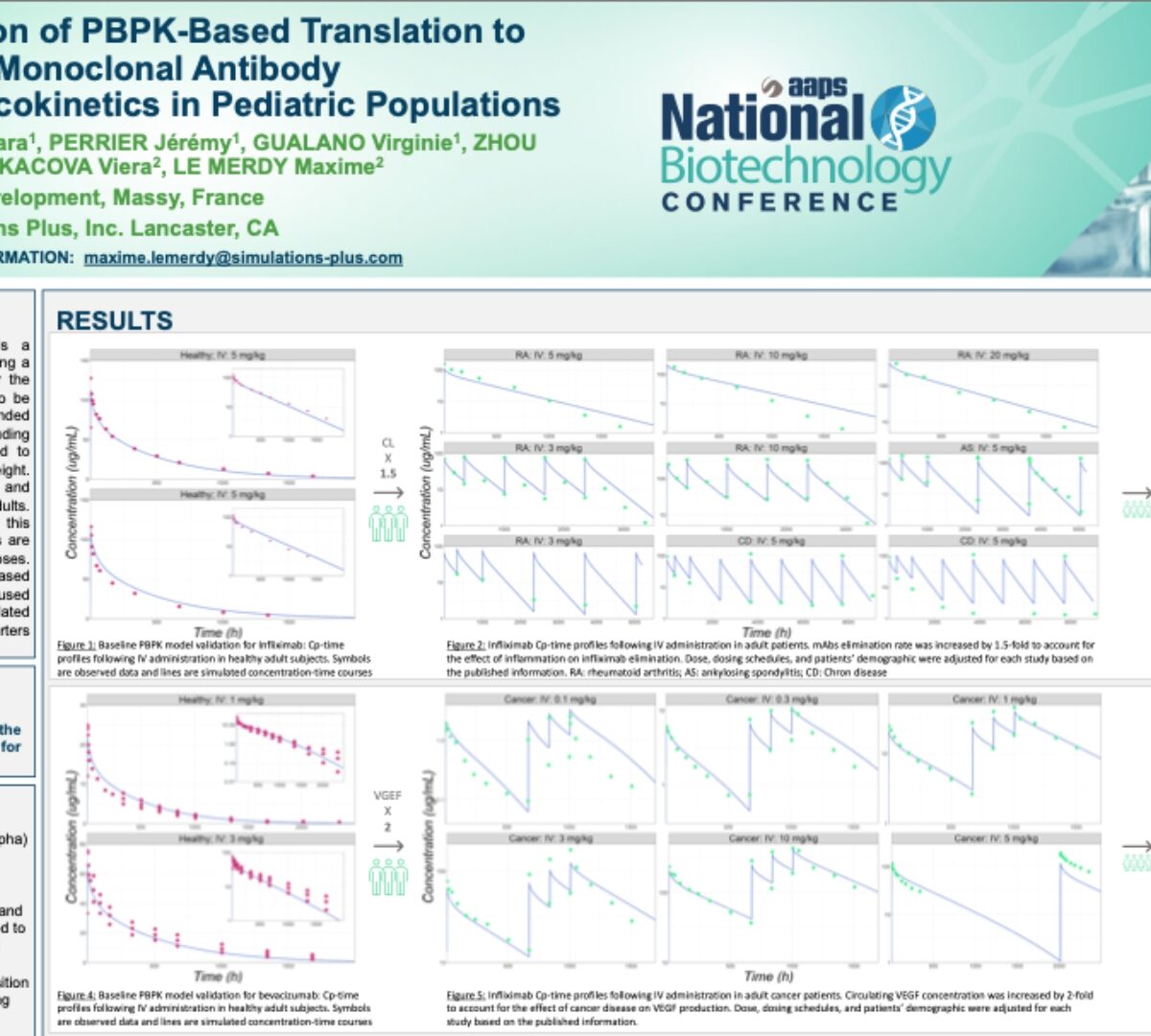
Validation of PBPK-Based Translation to Predict Monoclonal Antibody Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Populations
Accurate prediction of the pediatric dose is a necessity before conducting a clinical trial or using a drug product in standard clinical practices.

Next generation risk assessment of human exposure to estrogens using safe comparator compound values based on in vitro bioactivity assays
In next generation risk assessment (NGRA), the Dietary Comparator Ratio (DCR) can be used to assess the safety of chemical exposures to humans in a 3R compliant approach.
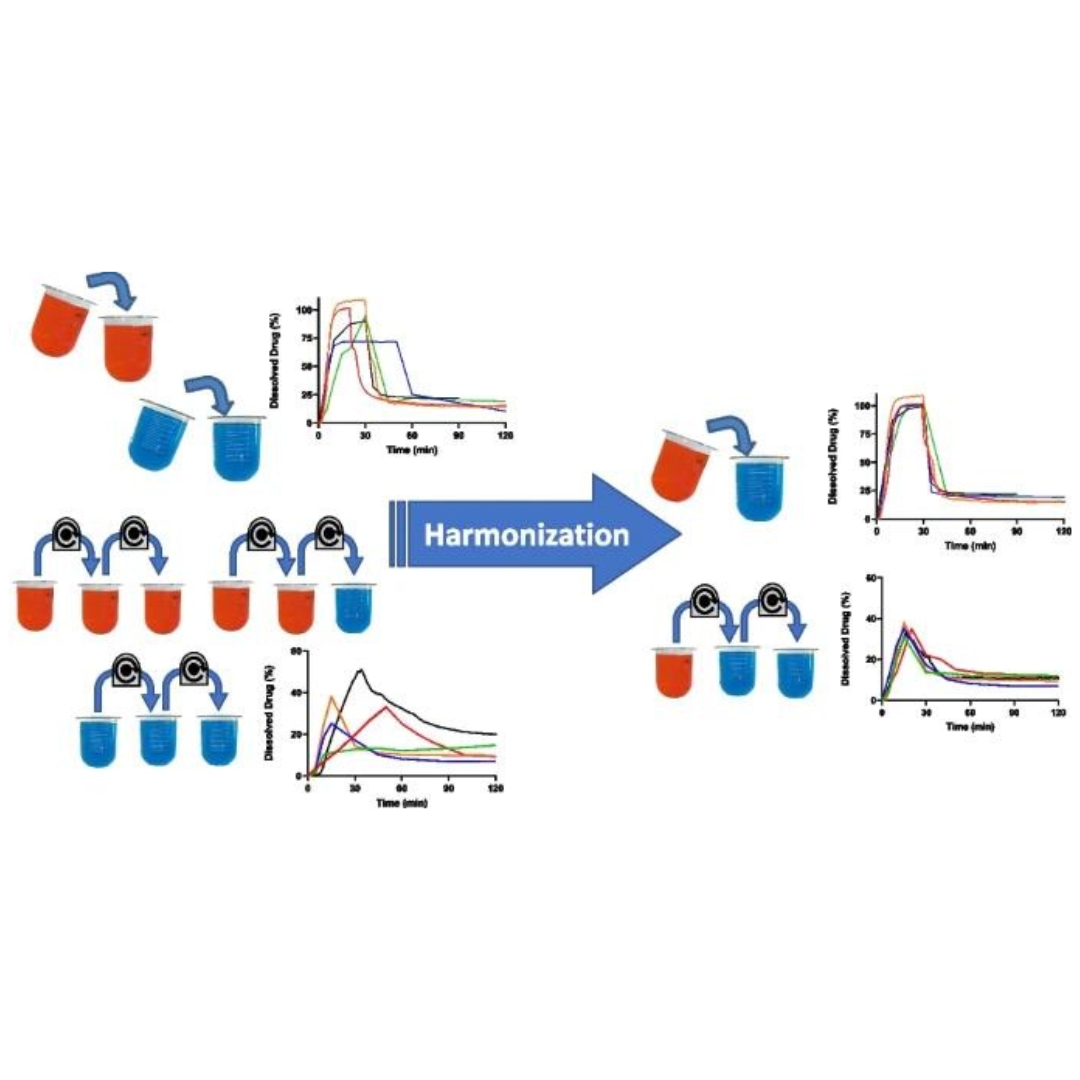
Harmonizing Biopredictive Methodologies Through the Product Quality Research Institute (PQRI) Part I: Biopredictive Dissolution of Ibuprofen and Dipyridamole Tablets
Assessing in vivo performance to inform formulation selection and development decisions is an important aspect of drug development.

Simulations Plus Receives U.S. FDA Renewal for DILIsym Software Licenses
Provides FDA with software tools to investigate drug-induced liver injury in clinical trials

Pulmonary Package
Breathe Easy with our Pulmonary Package