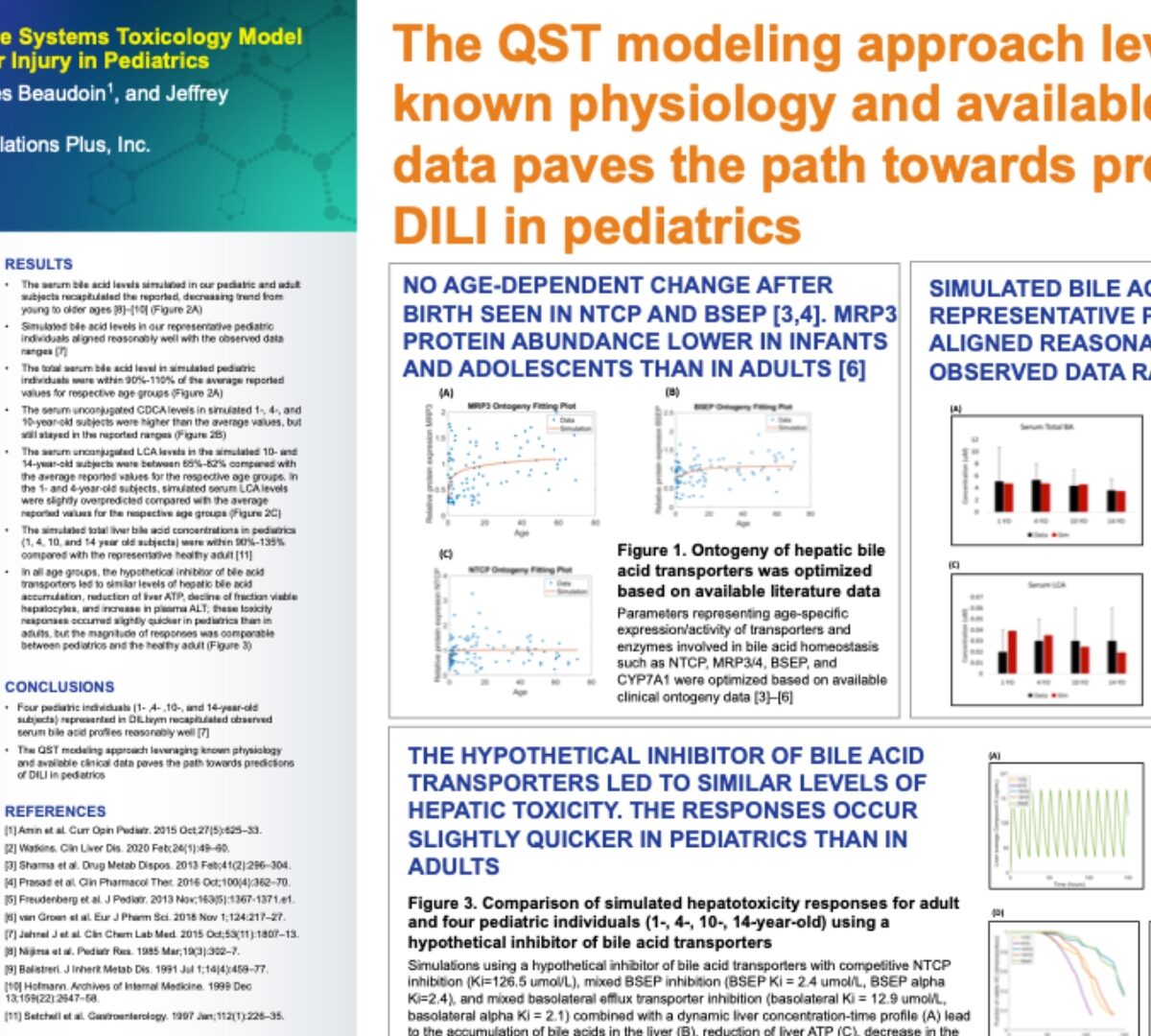
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is an underrecognized cause of pediatric liver disease which accounts for almost...
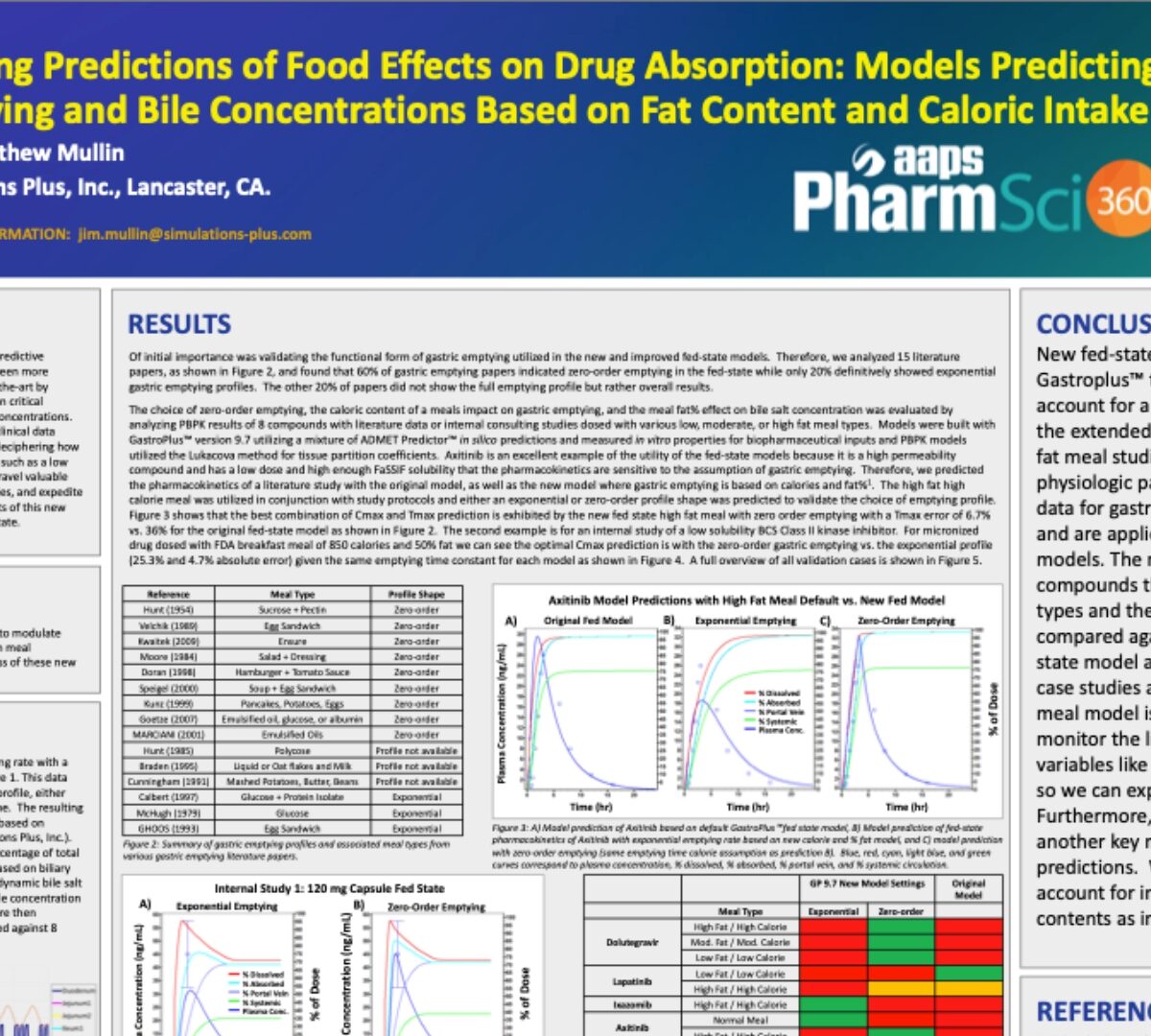
Refining Predictions of Food Effects on Drug Absorption: Models Predicting Gastric Emptying and Bile Concentrations Based on Fat Content and Caloric Intake
In the realm of pharmaceutical R&D, the quest for enhanced predictive accuracy and efficiency for Fed State PBPK models has never been more pressing.
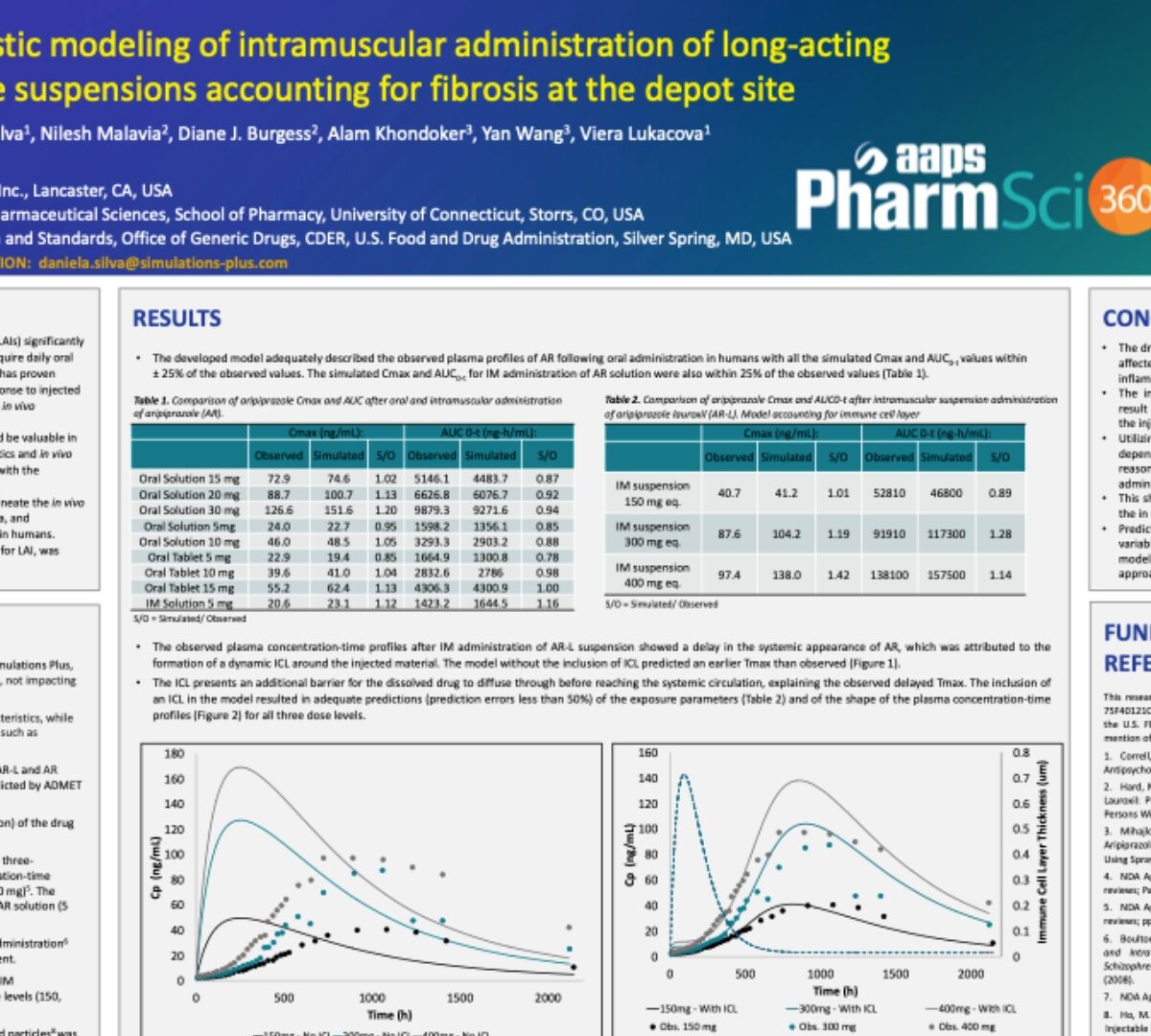
Mechanistic Modeling of Intramuscular Administration of Long-Acting Injectable Suspensions Accounting for Fibrosis at the Depot Site
Antipsychotic drugs formulated as long-acting injectables (LAIs) significantly improve patient compliance compared to regimens that require daily oral administration.
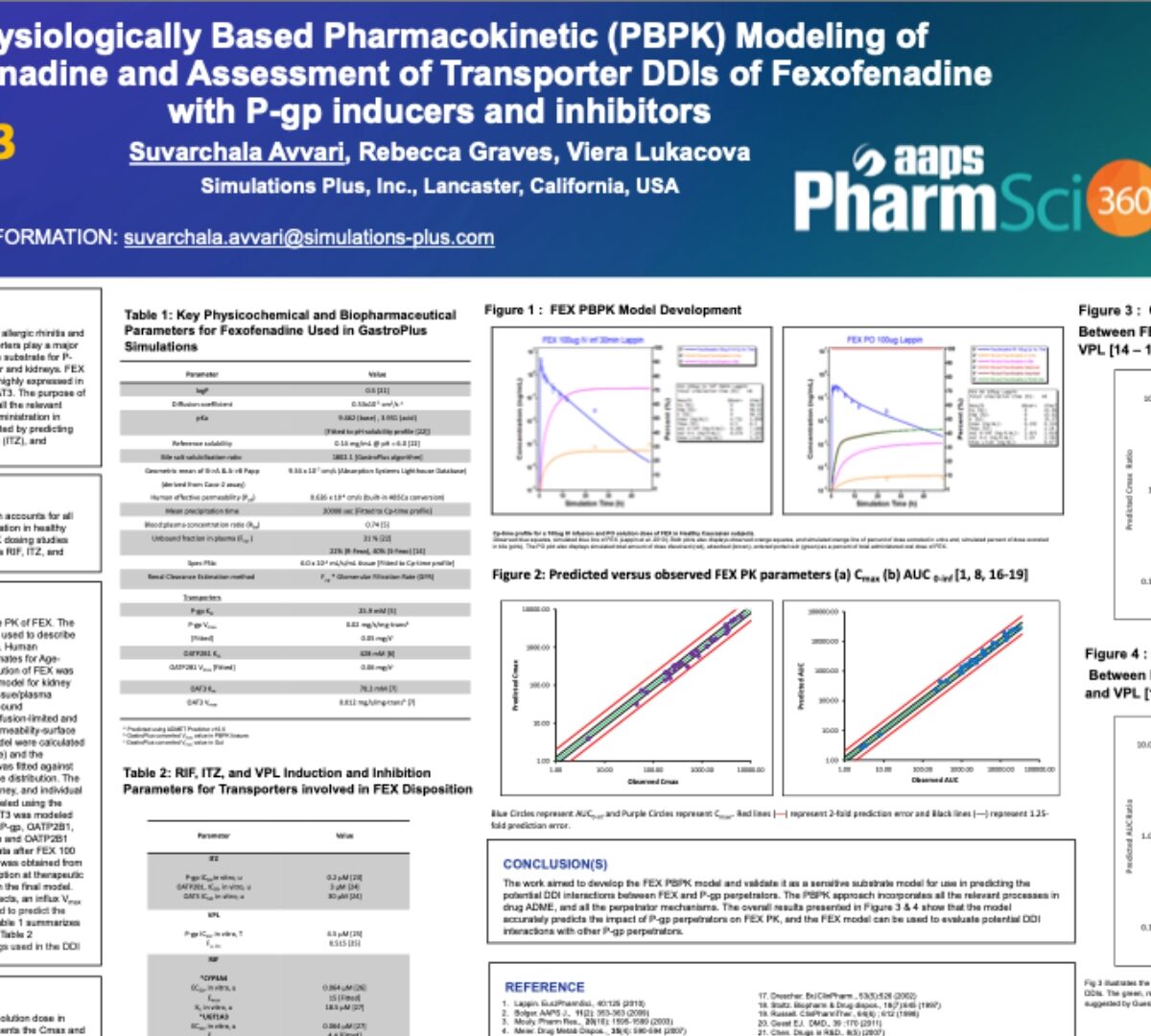
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Fexofenadine and Assessment of Transporter DDIs of Fexofenadine with P-gp inducers and inhibitors
Fexofenadine (FEX), a H1-receptor antagonist used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria, undergoes minimal metabolism and transporters play a major role in its absorption and disposition.
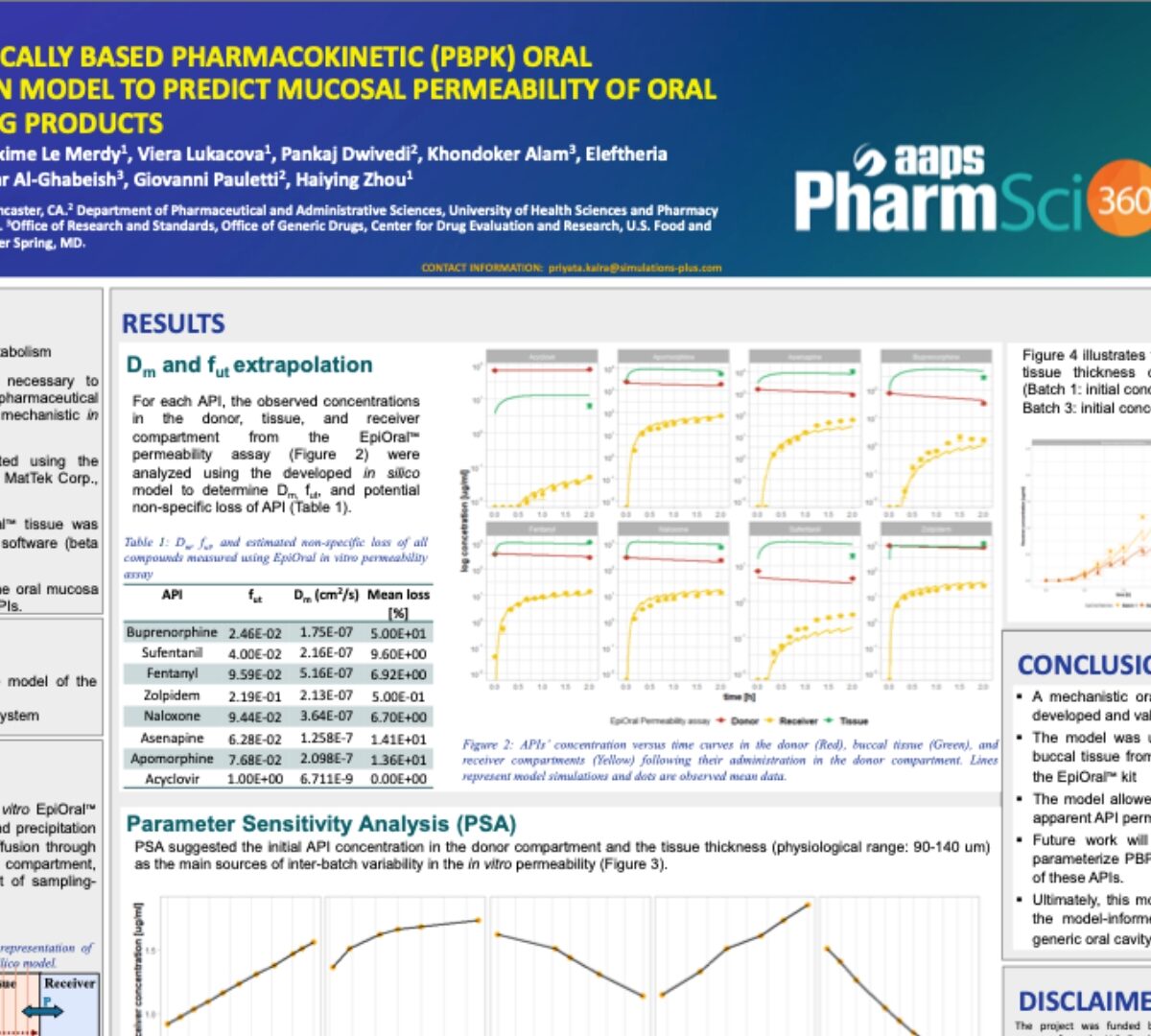
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (Pbpk) Oral Absorption Model To Predict Mucosal Permeability of Oral Cavity Drug Products
Buccal delivery allows bypassing first-pass metabolism
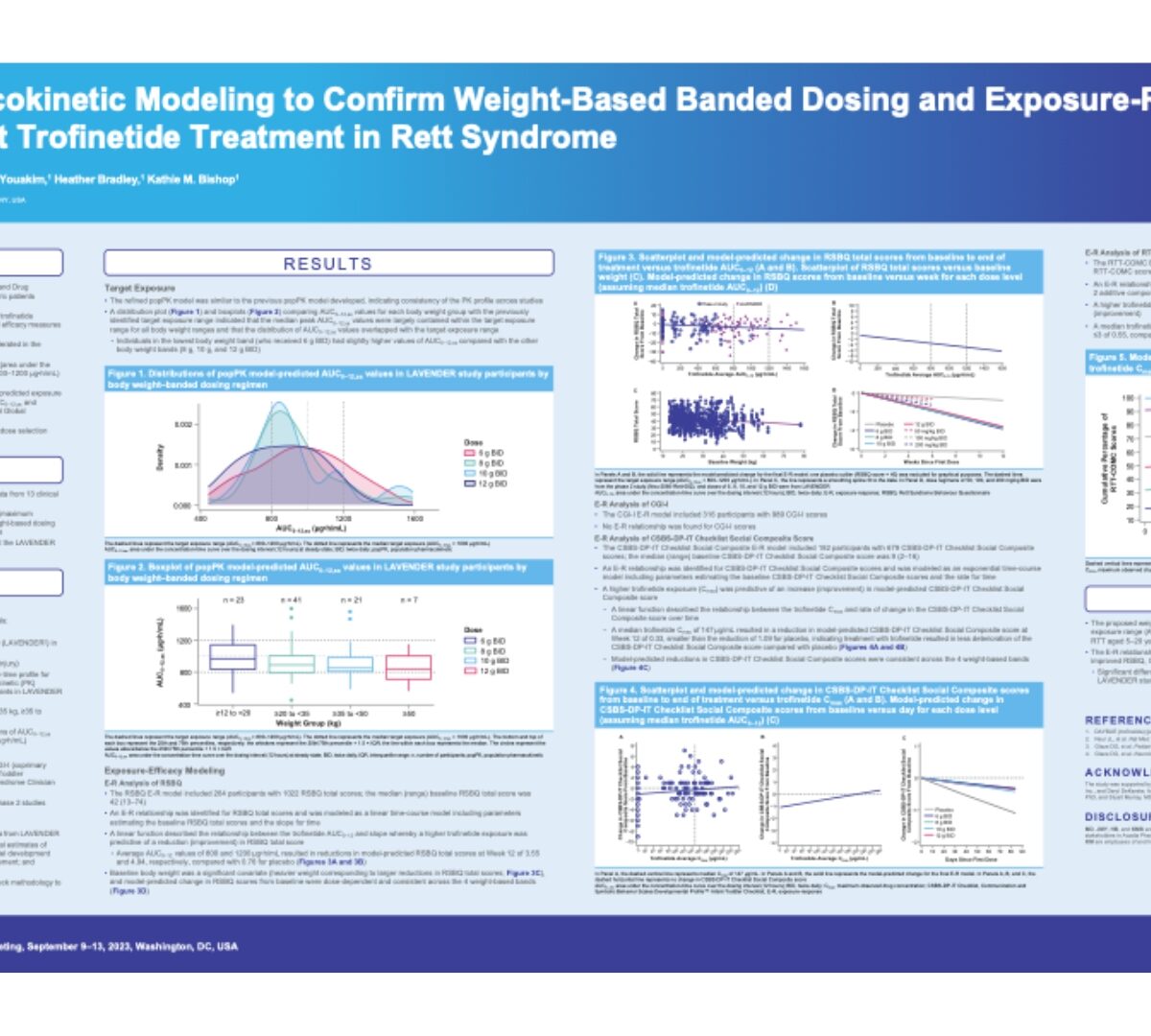
Population pharmacokinetic modelling to confirm weight-based banded dosing and exposure-response efficacy analyses to support trofinetide treatment in rett syndrome
Trofinetide, a synthetic analog of glycine-proline-glutamate, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in March 2023 for the treatment of...
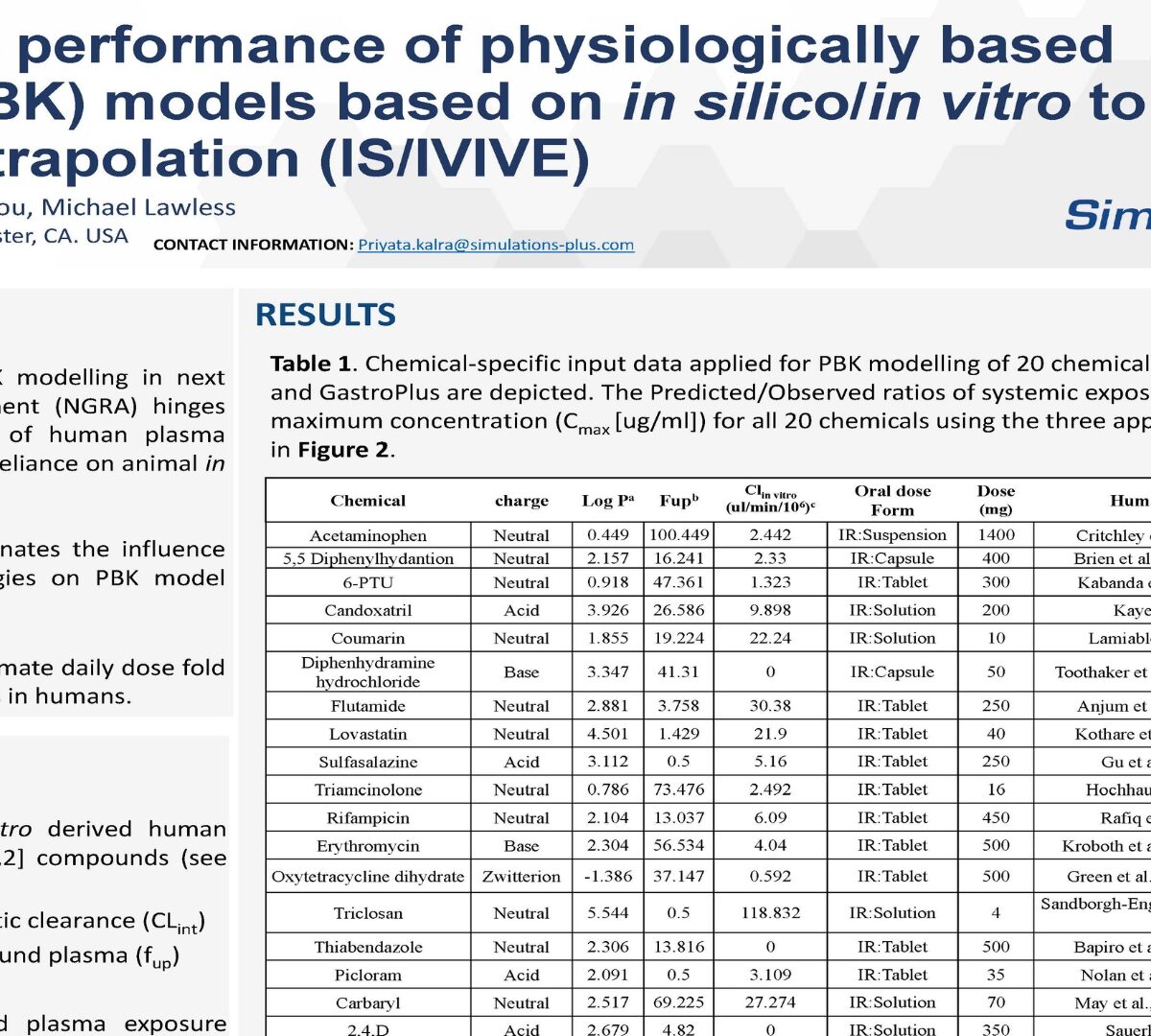
Predictive performance of physiologically based kinetic (PBK) models based on in silic o/ in vitro to in vivo extrapolation (IS/IVIVE)
The applicability of PBK modelling in next generation risk assessment ( hinges on accurate prediction of human plasma concentrations without reliance on animal in vivo kinetics data.
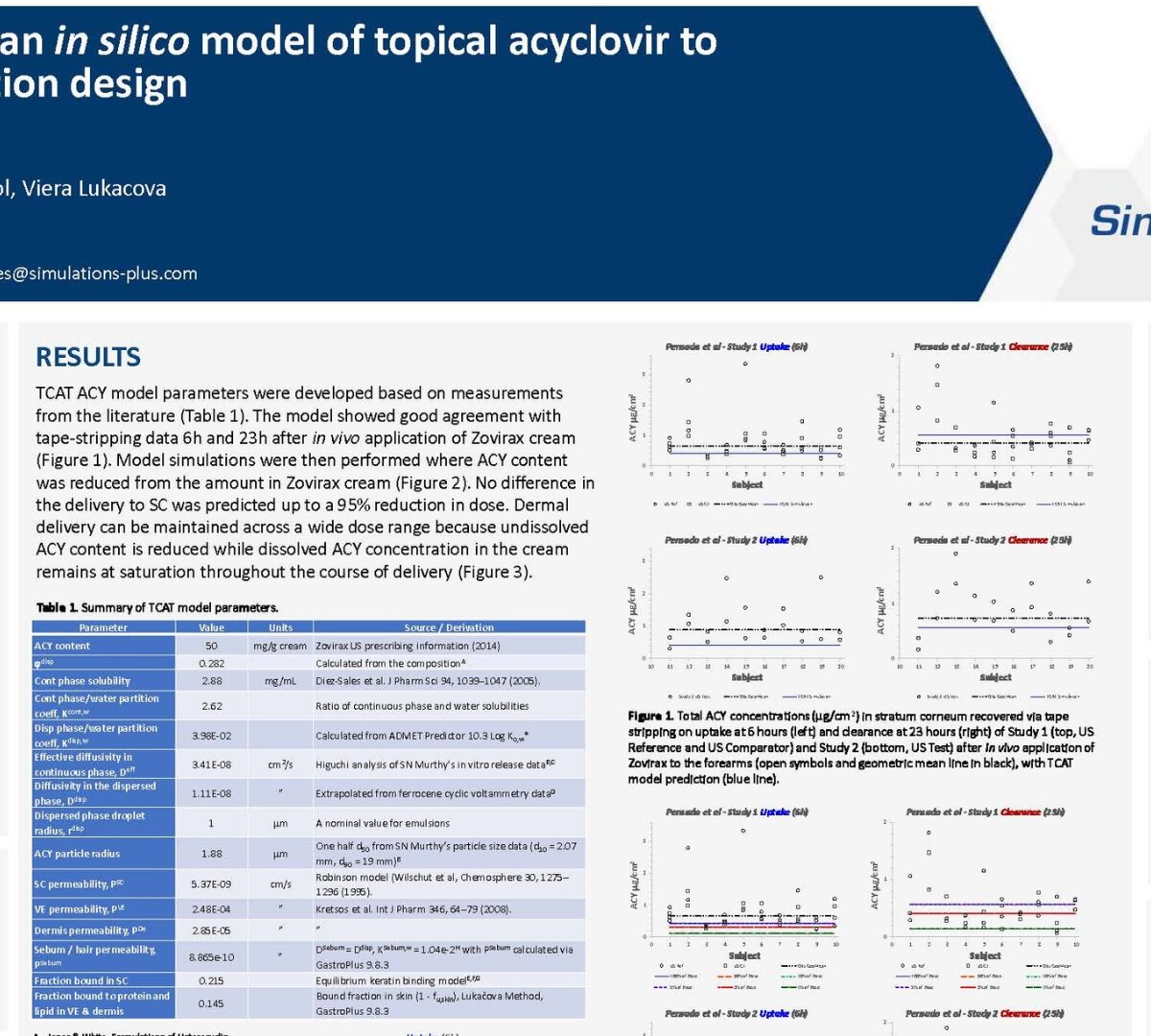
Development of an in silico model of topical acyclovir to explore formulation design
Acyclovir (ACY) creams are used for local treatment of HSV-1 infections in the basal epidermis.
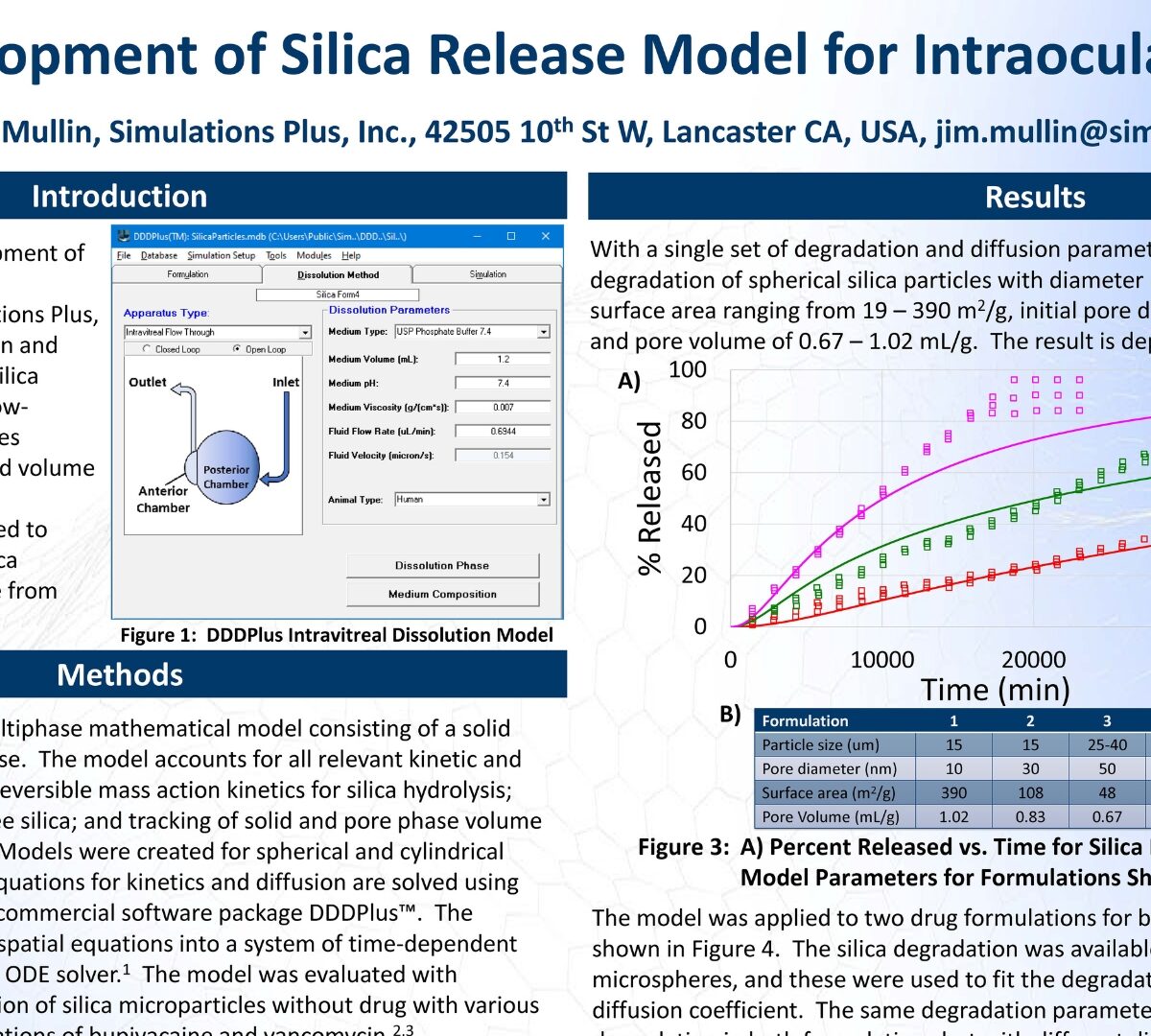
Development of Silica Release Model for Intraocular Injections
This poster reviews the development of a numerical framework within DDDPlus™ (Version 6.0, Simulations Plus, Inc.) to simulate the degradation and drug...
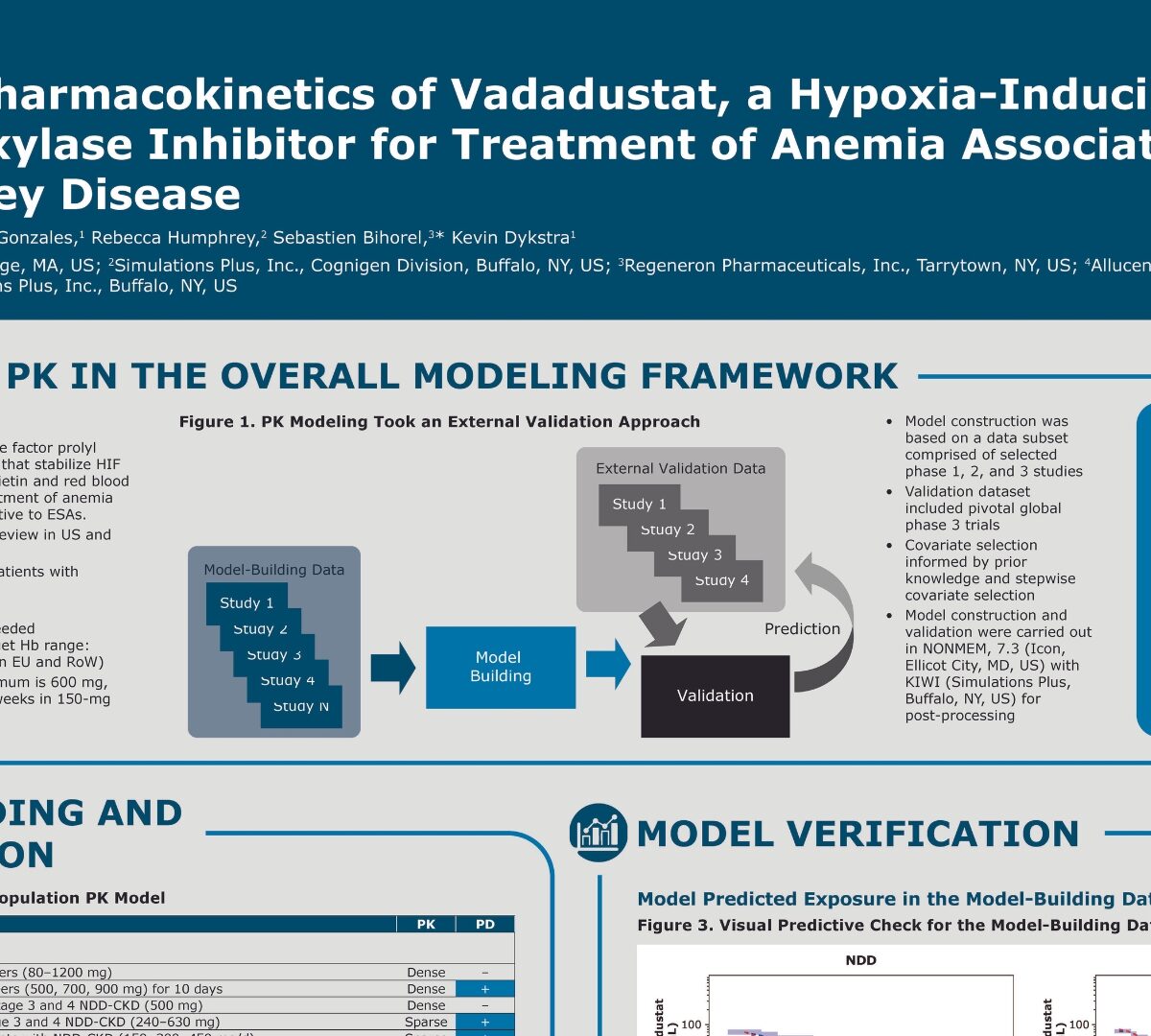
Population pharmacokinetics of vadadustat, a hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor for treatment of anemia associated with chronic kidney disease
Vadadustat is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, a class of...
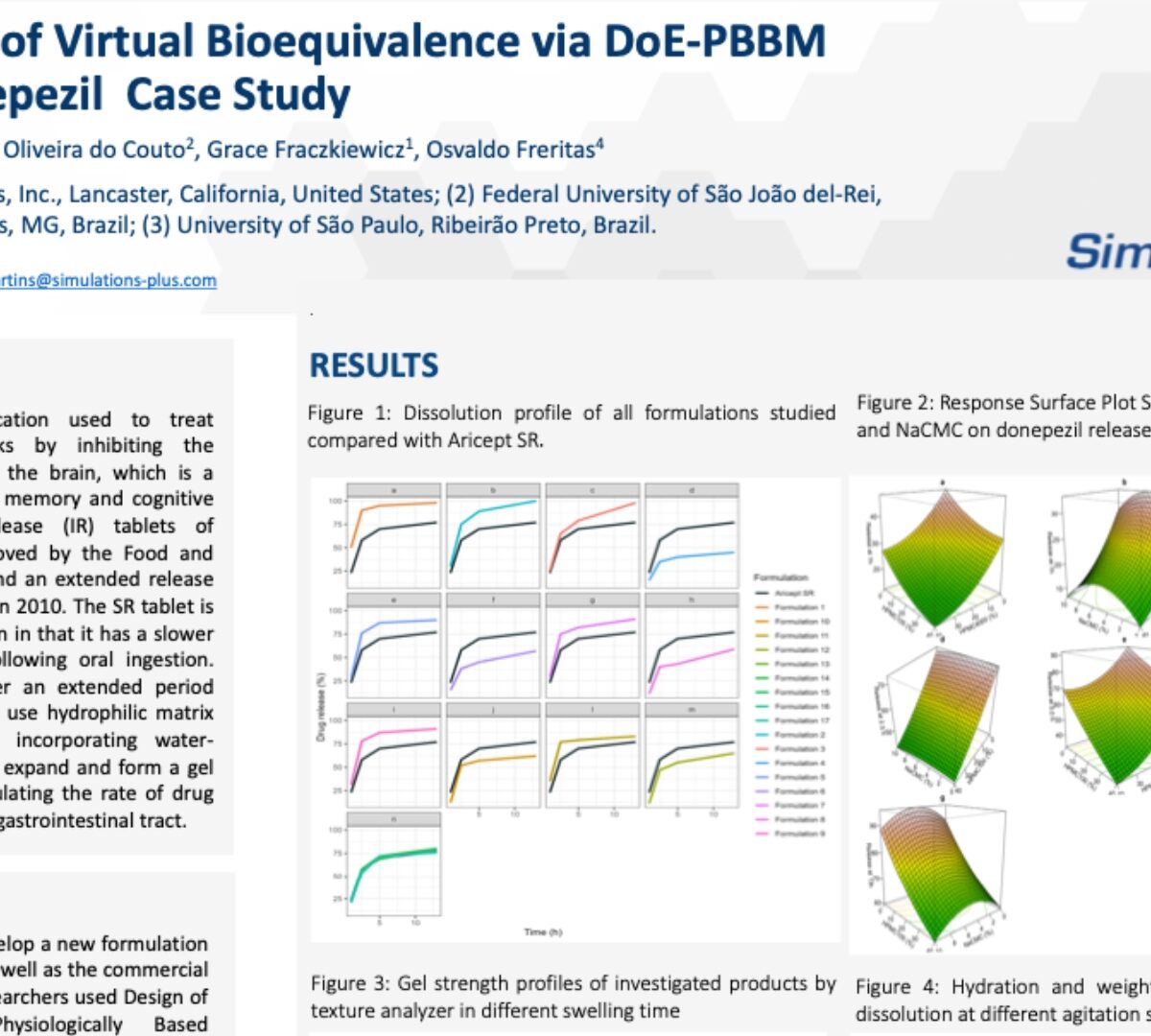
Establishment of Virtual Bioequivalence via DoE-PBBM Model: A Donepezil Case Study
Donepezil (DZP) is a medication used to treat Alzheimer's disease.

The application of AI-driven Drug Discovery technology for molecular optimization of nuclear receptor ligands
Nuclear receptors (NRs) are a superfamily of transcription factors whose activity is regulated upon the binding of a specific ligand.
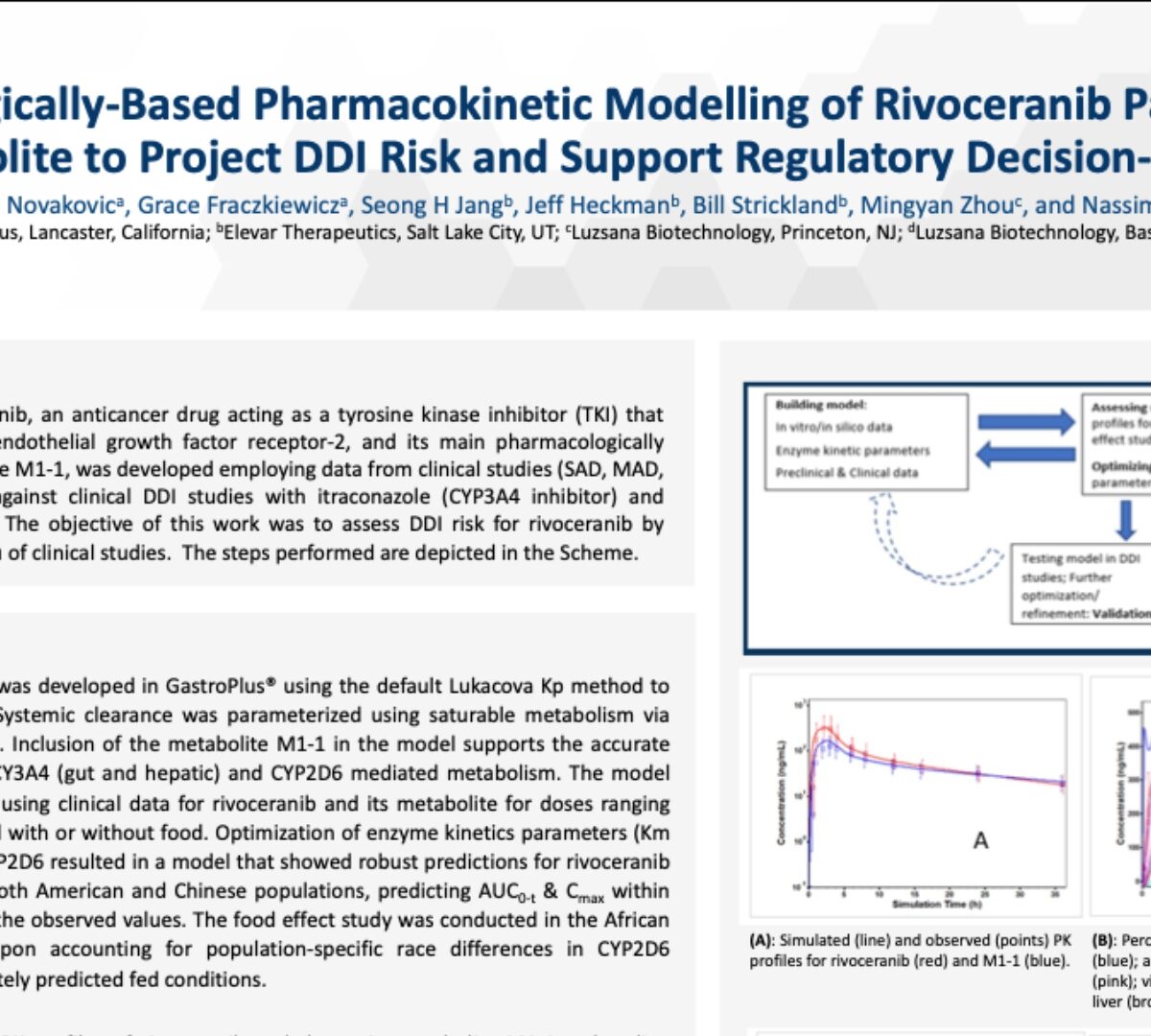
Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modelling of Rivoceranib Parent and Metabolite to Project DDI Risk and Support Regulatory Decision-Making
The PBPK model for rivoceranib, an anticancer drug acting as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that selectively targets vascular...
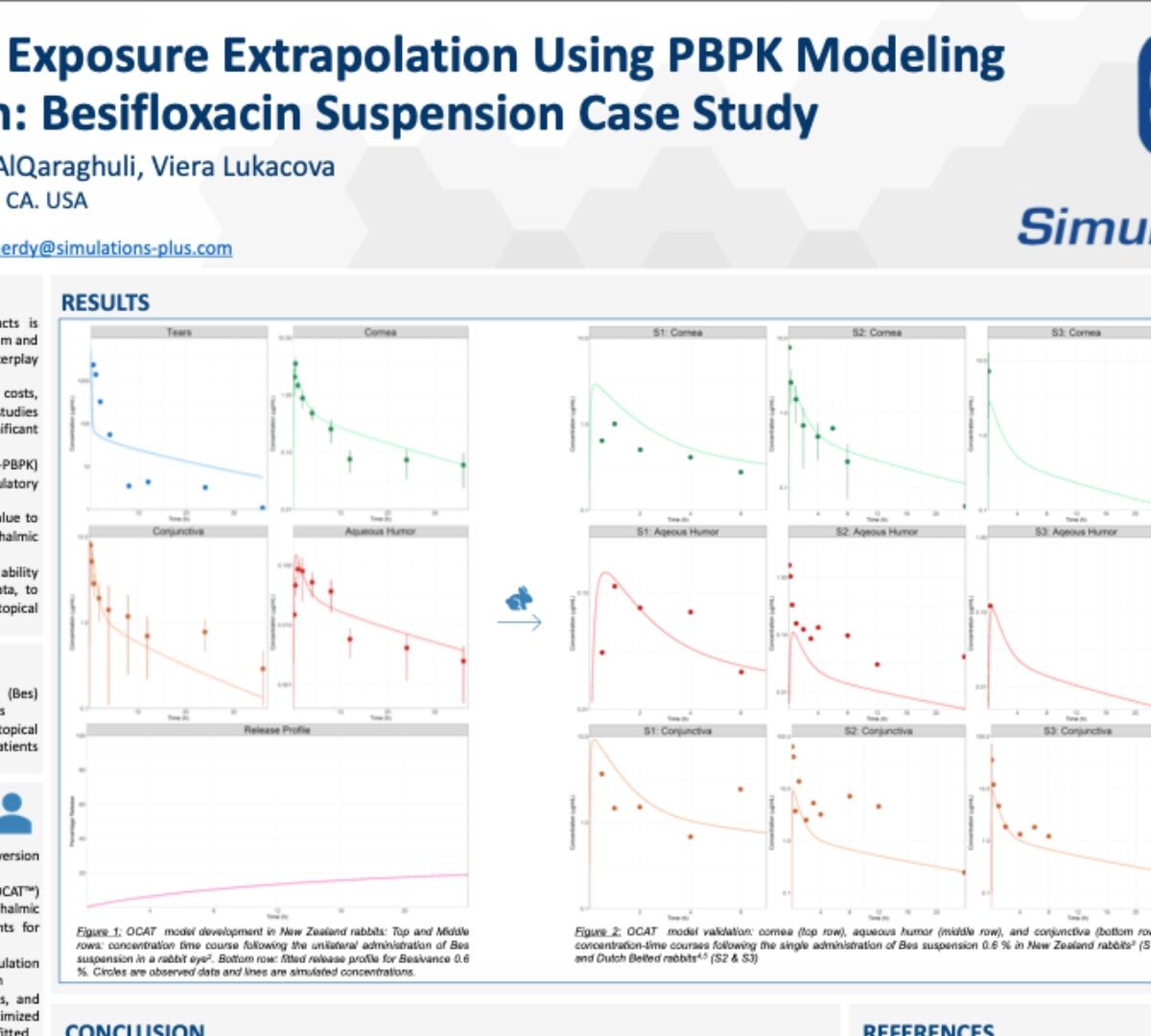
Clinical Ocular Exposure Extrapolation Using PBPK Modeling and Simulation: Besifloxacin Suspension Case Study
The purpose of this research is to demonstrate the ability of O-PBPK models, validated against rabbit PK data, to predict clinical ocular exposure, following topical administration of ophthalmic suspensions
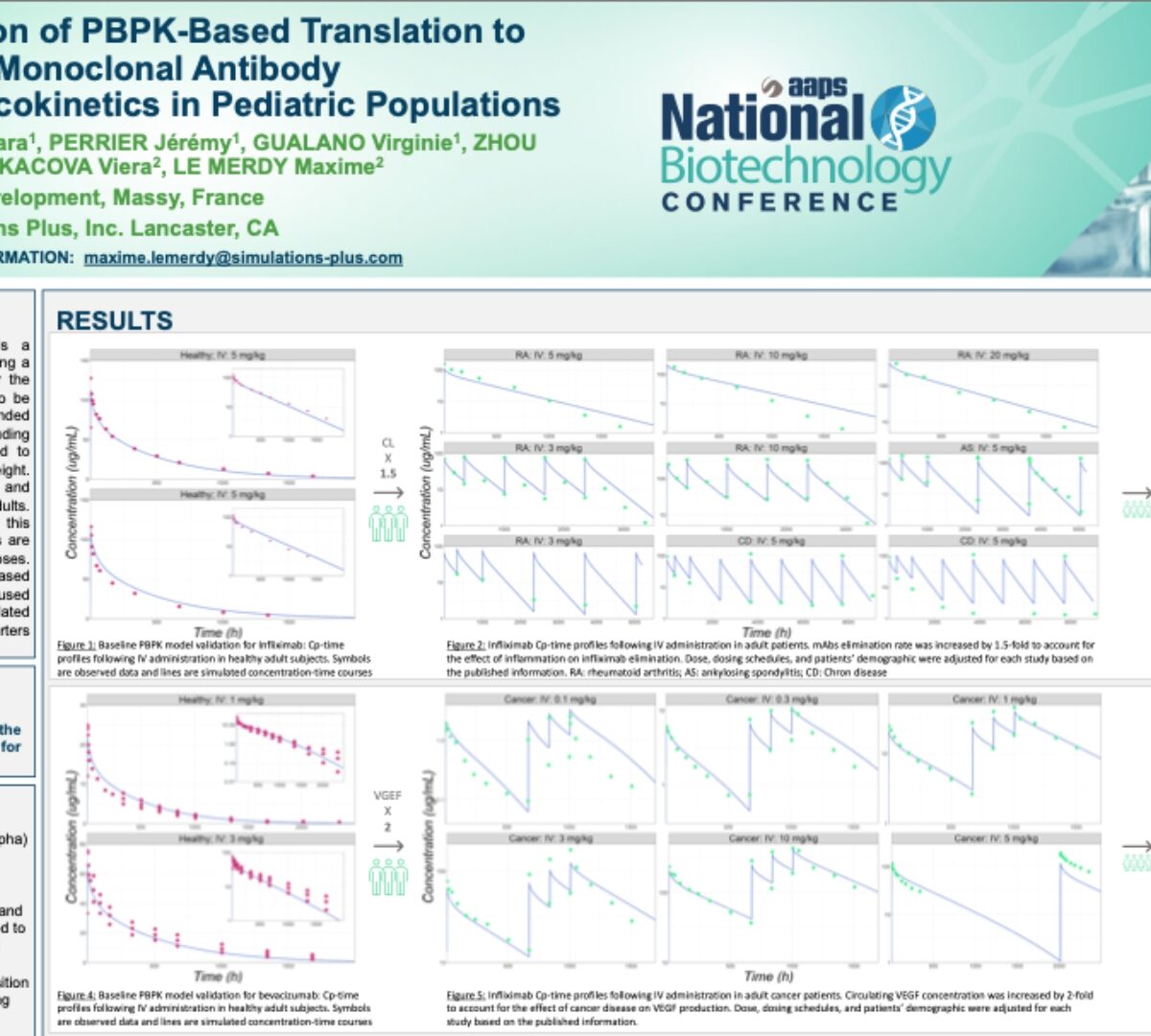
Validation of PBPK-Based Translation to Predict Monoclonal Antibody Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Populations
Accurate prediction of the pediatric dose is a necessity before conducting a clinical trial or using a drug product in standard clinical practices.
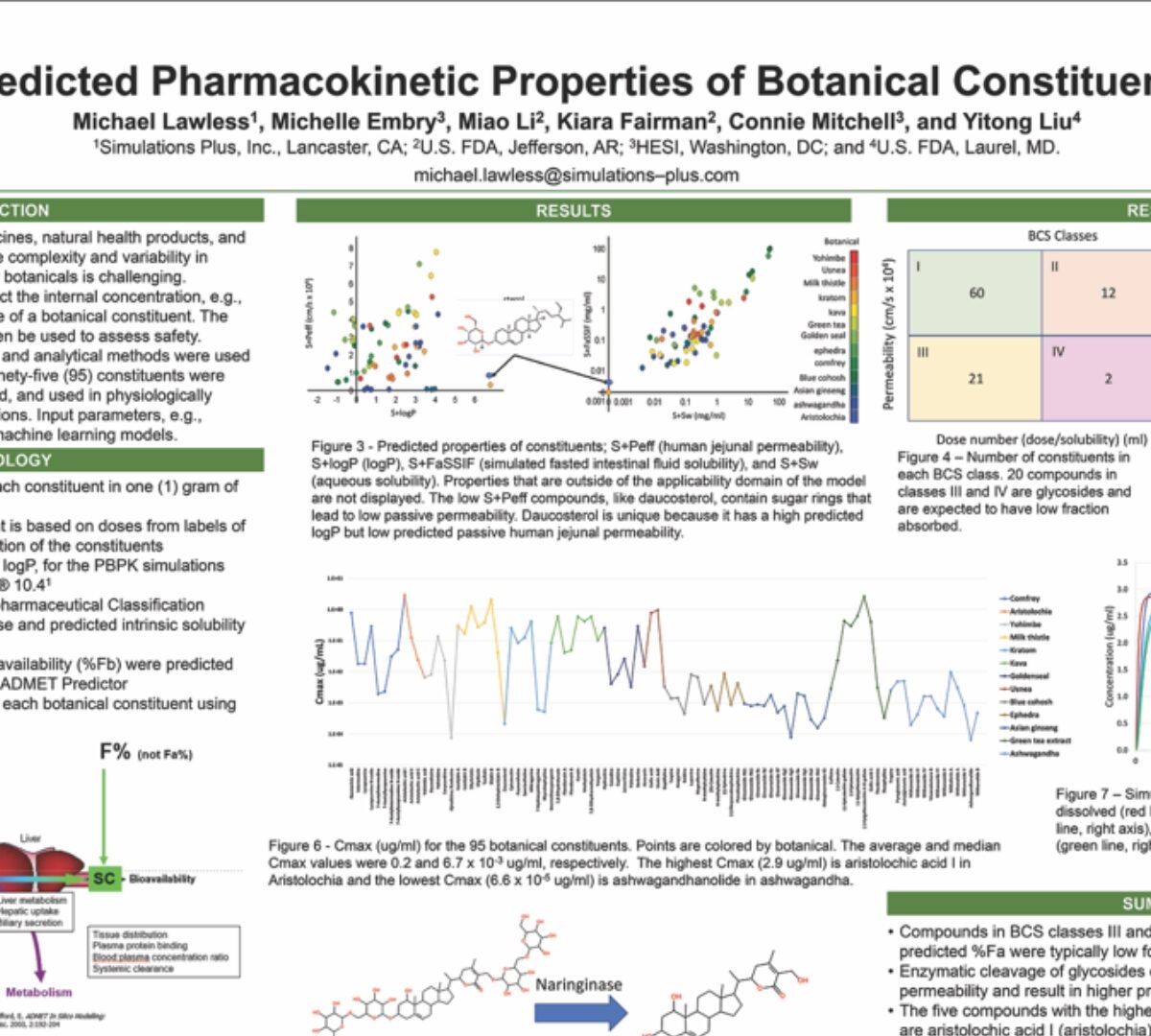
Predicted Pharmacokinetic Properties of Botanical Constituents
Botanicals are used as traditional medicines, natural health products, and dietary supplements globally.
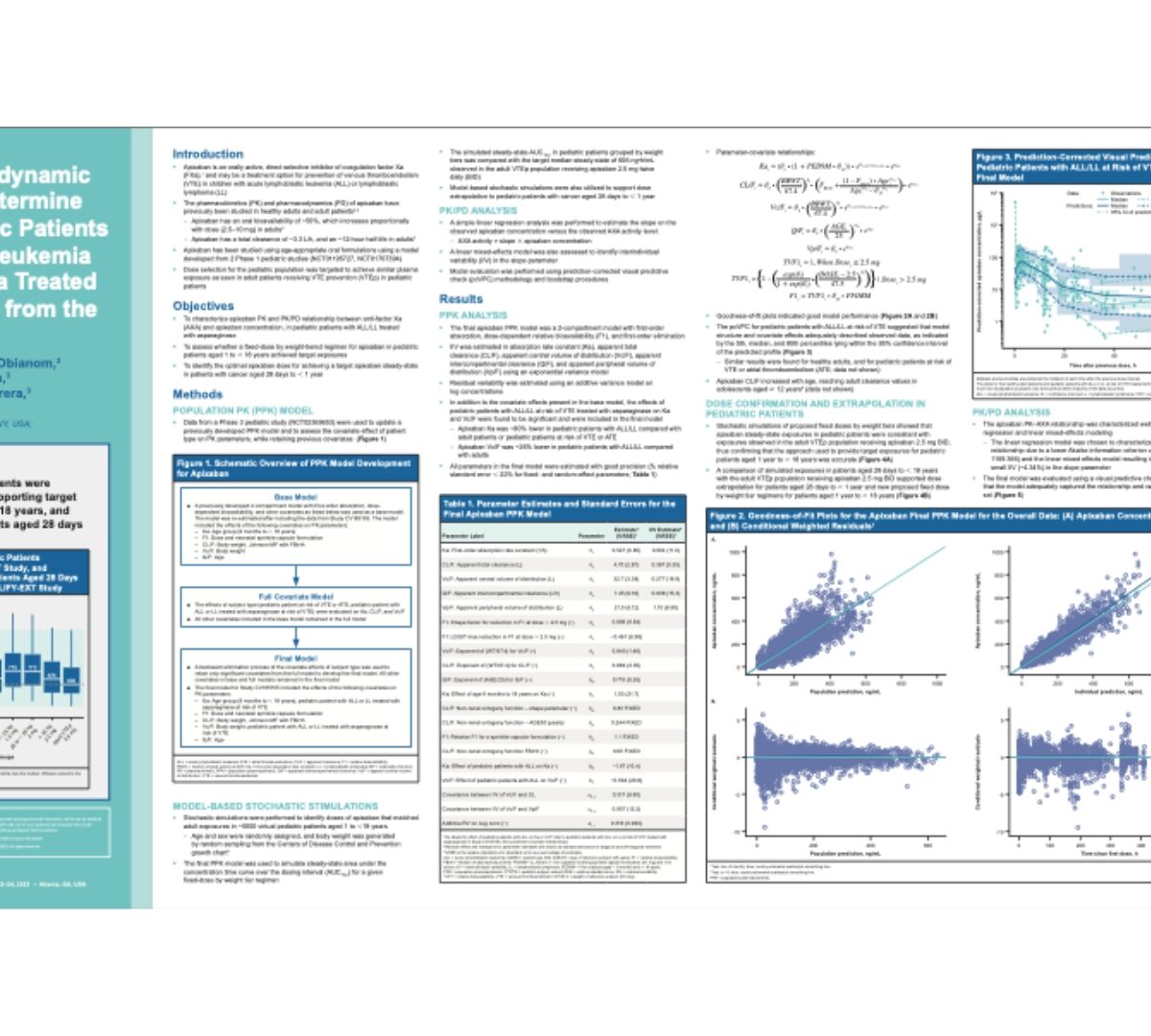
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis of apixaban to determine dosing regimens for pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia or lymphoblastic lymphoma treated with asparaginase: analysis from the PREVAPIX study
Apixaban is an orally active, direct selective inhibitor of coagulation factor Xa (FXa),1 and may be a treatment option for prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in children with...
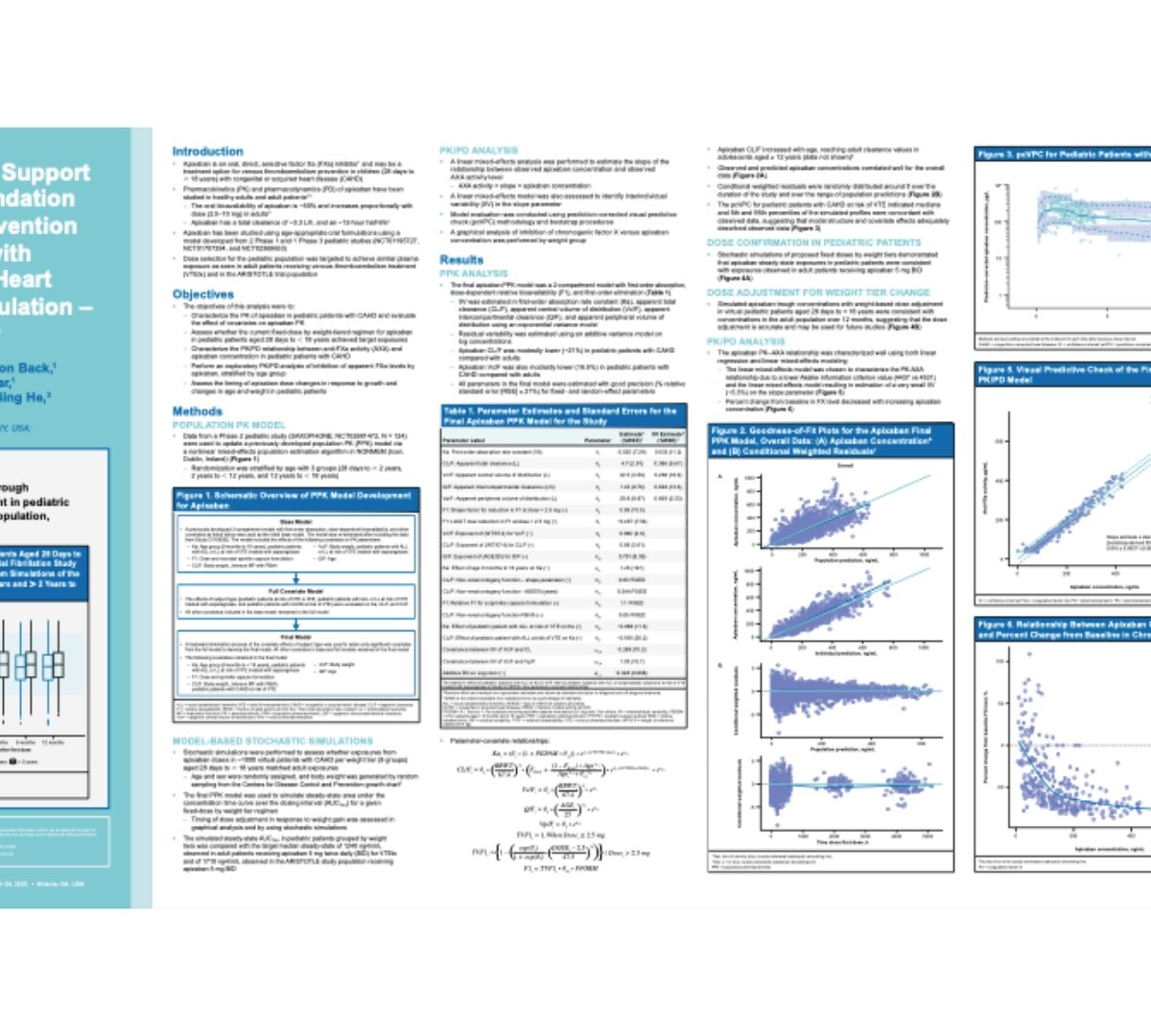
Modeling and simulation to support apixaban dose recommendation for thromboembolism prevention in pediatric subjects with congenital or acquired heart disease requiring anticoagulation–saxophone study
Apixaban is an oral, direct, selective factor Xa (FXa) inhibitor1 and may be a treatment option for venous thromboembolism prevention in...
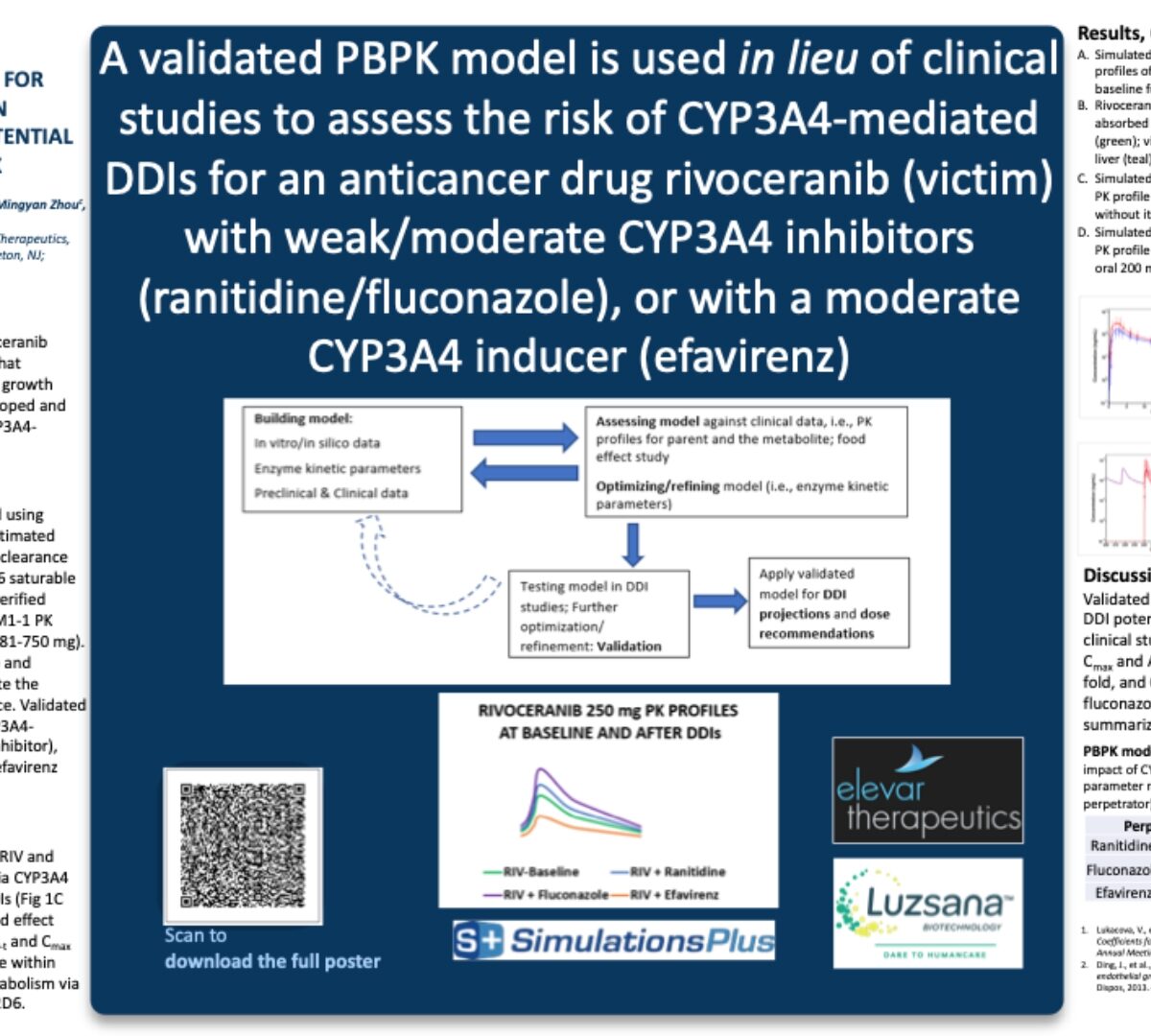
A validated PBPK model is used in lieu of clinical studies to assess the risk of CYP3A4-mediated DDIs for an anticancer drug rivoceranib (victim) with weak/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (ranitidine/fluconazole), or with a moderate CYP3A4 inducer (efavirenz)
A PBPK model for anticancer drug rivoceranib (RIV), a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that selectively targets vascular endothelia growth factor...

Attenuations in adiponectin production over time restrict simulated efficacy for pegbelfermin in F3 NASH patients
Patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis do not currently have options for...