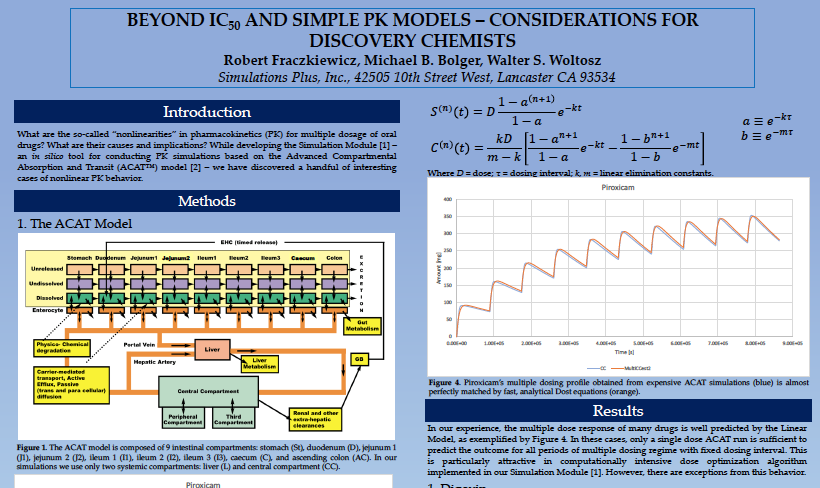
While developing the Simulation Module [1] – an in silico tool for conducting PK simulations based on the Advanced Compartmental Absorption and Transit (ACAT™) model [2] – we have discovered a handful of...

Innate immune signaling through differential RIPK1 expression promote tumor progression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a devastating disease for which new treatments, such as immunotherapy are needed.

Mechanistic Modeling Predicts Drug-Induced HyperbilirubinemiaThat Involves Inhibition Of Enzymes And Transporters
Elevated serum ALT and bilirubin indicates high risk of fatal drug-induced liver injury. However, drugs also can increase serum bilirubin in the absence of hepatic injury by inhibiting enzymes and/or transporters.

A historical perspective from Alison Boeckmann
Prior to 1978, PK data was obtained from drugs that were tested on healthy young volunteers (typically medical students).

in silico Prediction of Oral Bioavailability
Oral bioavailability (F%) is an important pharmacokinetic property that can determine the fate of a compound in clinical trials. Predicting F% directly from the 2D structure of the molecule prior to first…

Pharmacokinetic evaluation of cefdinir-loaded floating alginate beads in rabbits using LC–MS/MS
The present investigation aims to compare the pharmacokinetic parameters of Cefdinir in rabbits, from floating alginate (an anionic polysaccharide obtained from cell walls of brown algae) beads and...

Unified dissolution / precipitation model and its use predicting absorption
This webinar will focus on the description of a novel mechanistic mathematical model developed to describe in vitro dissolution and precipitation data and how the model can be used in a wider PBPK framework...

Disease specific modeling: simulation of the pharmacokinetics of meloxicam and ibuprofen in disease state vs. healthy conditions
Studies have shown altered pharmacokinetic patterns (PK) in patient suffering from acute pain.

Comparative human in-vivo study of an immediate release tablet over-encapsulated by gelatin and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose capsules – impact of dissolution rate on bioequivalence
Rapid and consistent in-vivo drug dissolution is critical for drug absorption. In-vitro dissolution tests are used to predict in-vivo disintegration and dissolution properties of drug products.

Efficacy, safety, tolerability and population pharmacokinetics of tedizolid, a novel antibiotic, in Latino patients with acute bacterial skin and skin
Acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections are caused mainly by Gram-positive bacteria which are often treated with intravenous vancomycin, daptomycin, or linezolid, with potential step down to oral linezolid for outpatients.

A First-in-Human Phase I Study of the Oral p38 MAPK Inhibitor, Ralimetinib (LY2228820 Dimesylate), in Patients with Advanced Cancer
Purpose: p38 MAPK regulates the production of cytokines in the tumor microenvironment and enables cancer cells to survive despite oncogenic stress, radiotherapy, chemotherapy...

Regulatory Perspectives on Strength-Dependent Dissolution Profiles and Biowaiver Approaches for Immediate Release (IR) Oral Tablets in New Drug Applications
Dissolution profile comparisons are used by the pharmaceutical industry to assess the similarity in the dissolution characteristics of two formulations

Development of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic / Pharmacodynamic Model to Predict the Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Represented by Receptor / Transporter Occupancy of Central Nervous System Drugs
Genetic polymorphisms are major determinants of individual variability in a drug’s efficacy and safety, which is one of the main challenges in current clinical practice and drug development.

Design and synthesis of some new 1-phenyl-3/4-[4-(aryl/heteroaryl/alkyl-piperazine1-yl)-phenyl-ureas as potent anticonvulsant and antidepressant agents
A series of 1-phenyl-3/4-[4-(aryl/heteroaryl/alkyl-piperazine1-yl)-phenyl-urea derivatives (29–42) were designed, synthesized and evaluated for their anticonvulsant activity by using maximal electroshock (MES)...

Discovery of novel S1P 2 antagonists, part 3: Improving the oral bioavailability of a series of 1, 3-bis (aryloxy) benzene derivatives
The structure of the S1P2 antagonist 1 has been modified with the aim of improving its oral bioavailability.

Ferulic acid-carbazole hybrid compounds: combination of cholinesterase inhibition, antioxidant and neuroprotection as multifunctional anti-Alzheimer agents
In order to search for novel multifunctional anti-Alzheimer agents, a series of ferulic acid–carbazole hybrid compounds were designed and synthesized.
![N-(3, 4- Dimethylisoxazol -5-yl) piperazine-4-[4-(2-fluoro-4-[11C] methylphenyl) thiazol-2-yl] -1-carboxamide: a promising positron emission tomography ligand for fatty acid amide hydrolase](https://www.simulations-plus.com/wp-content/themes/simulations-plus/library/dist/img/default_square-large.jpg)
N-(3, 4- Dimethylisoxazol -5-yl) piperazine-4-[4-(2-fluoro-4-[11C] methylphenyl) thiazol-2-yl] -1-carboxamide: a promising positron emission tomography ligand for fatty acid amide hydrolase
To visualize fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) in brain in vivo, we developed a novel positron emission tomography (PET) ligand N-(3,4-dimethylisoxazol-5-yl)piperazine-4-[4-(2-fluoro...

Provenance of Computers in Pharmacy
Computers in pharmacy are used for the information of drug data, records and files, drug management (creating, modifying, adding and deleting data in patient files to generate reports), business details.

Utility of PBPK Absorption Modeling to Guide Modified Release Formulation Development of Gaboxadol, a Highly Soluble Compound with Region-Dependent Absorption
Given the complexity of controlled release (CR) formulations, selecting the right preclinical tools is important to enable decision making on the in vivo performance of these formulations during development.