Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Software for Predicting and Explaining Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI)
The Impact of Simulation-Based Learning on Study Acceleration: Spoken from the Sponsor who Converted
Enhancing Training to be a personalized, representative and interactive strategic asset

Expanding ADMET Predictor®’s Chemical Space: Enhanced bRo5 and Chameleon Molecule Predictions for HTPK
ADMET Predictor has been enhanced to accurately predict properties of beyond Rule-of-Five (bRo5) molecules, including macrocycles and PROTACs.

Formulation and Evaluation of Poly(Jasmine Lactone) Based Micelles for Improving the Oral Permeability of Acyclovir
Acyclovir (ACV), an antiviral drug, belongs to the BCS class III drug with intermediate solubility and low permeability.

Simulation-Guided Dissolution Testing: Coupling DDDPlus™ and GastroPlus® to Predict Aripiprazole Oral Bioperformance
Orally administered weakly basic compounds like aripiprazole (ARI) can precipitate in the small intestine due to limited solubility at intestinal pH.

Sensitivity Analysis of the Inputs for Bioactivity-Exposure Ratio Calculations in a NAM-based Systemic Safety Toolbox
To support regulatory decision-making without animal testing, Next-Generation Risk Assessment (NGRA) frameworks leverage New Approach Methodologies (NAM).

3 Mistakes We’re Still Making with Study Training (and How to Fix Them)
Training is one of the most critical parts of study start-up and yet, we often treat it like a box to check rather than the foundation of trial quality.

Applications of PBPK Models to Predict Tissue Residues and Extralabel Withdrawal Times of Drugs in Food Animals: Perspectives from the Food Animal Residue Avoidance Databank (FARAD) Program
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models are commonly used in human drug discovery and development and human health risk assessment of environmental chemicals.
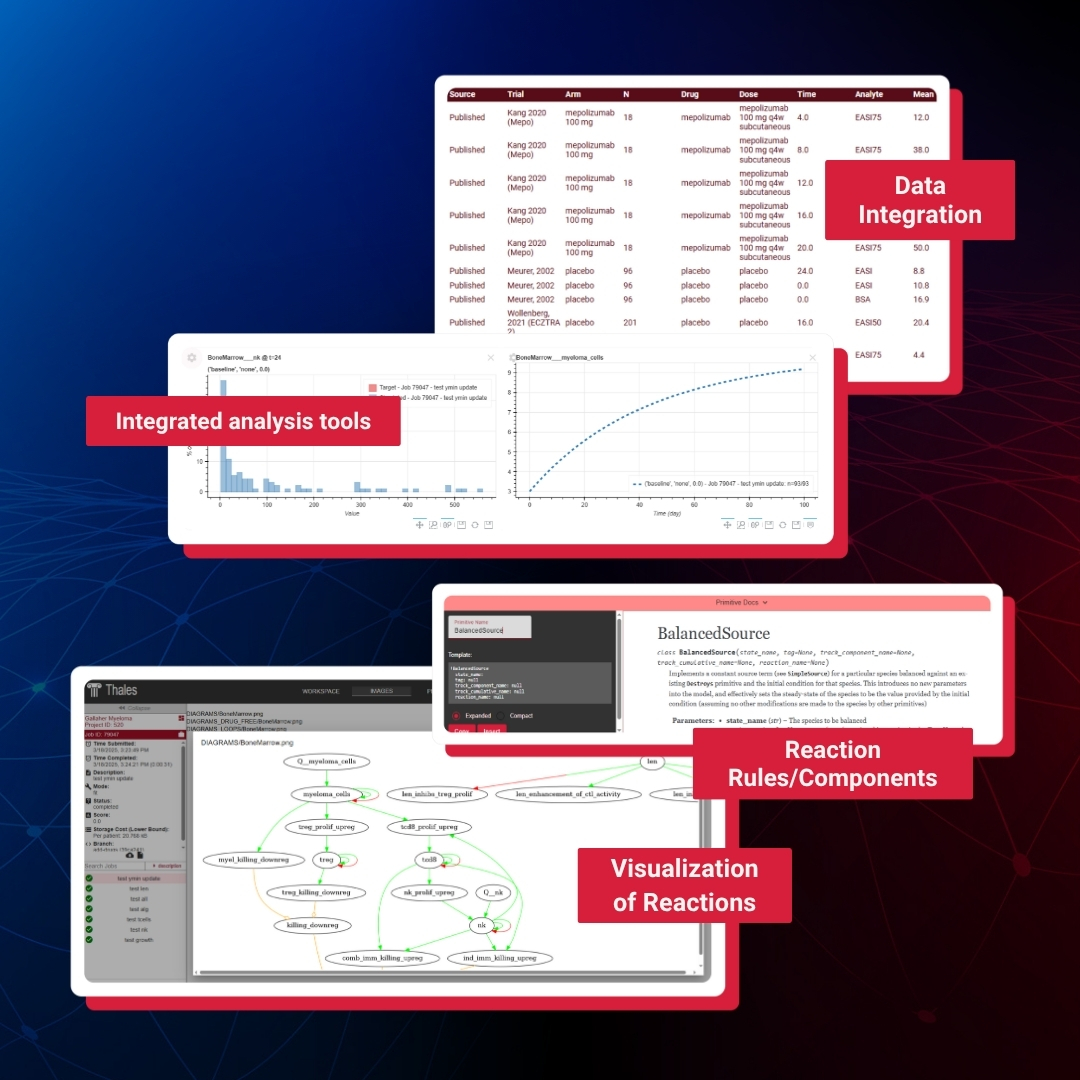
Thales™ Product Brochure
Accelerate your model development
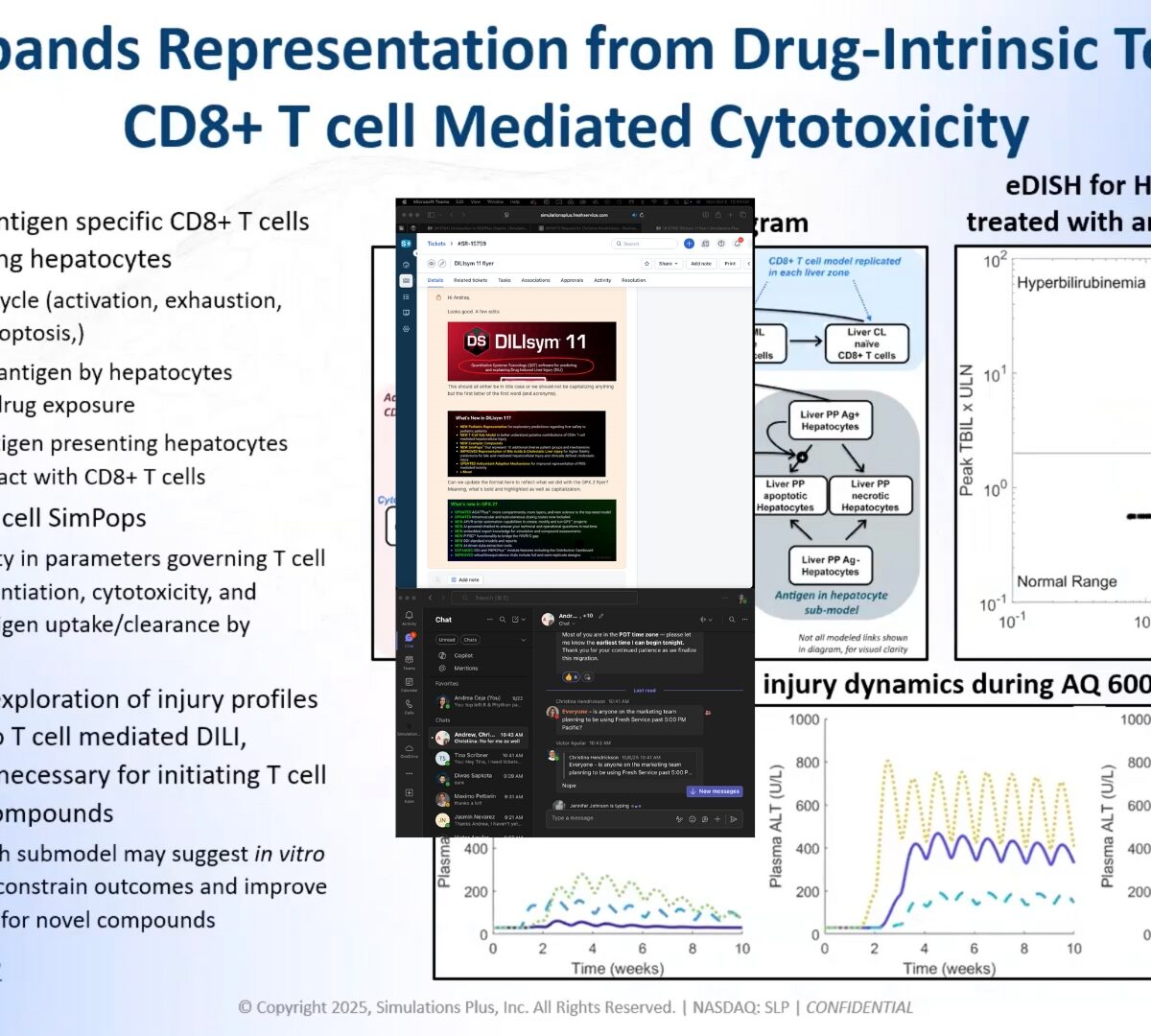
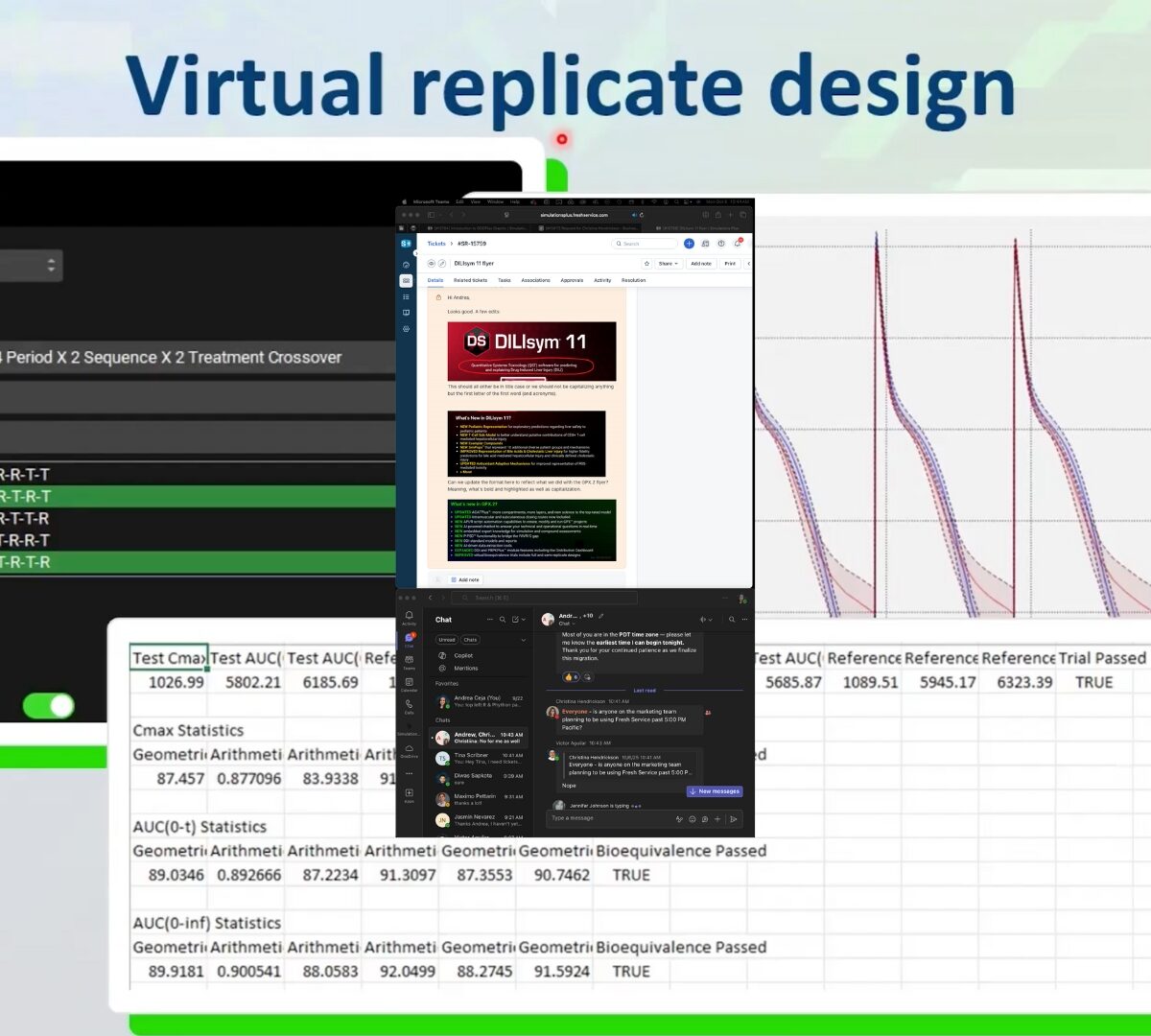
Unlocking the Power of Predictive Toxicology: What’s New in DILIsym® 11
Introducing DILIsym® 11, the latest evolution of the industry’s leading quantitative systems toxicology (QST) platform.
GastroPlus® X.2: The Deep Dive Webinar Series – How ACATPlus™ Can Be Used to Mechanistically Understand Local Drug Disposition in the Gastrointestinal Tract
Our ACAT™ model has been trusted by scientists for years, and the highly anticipated update—ACATPlus—is here.
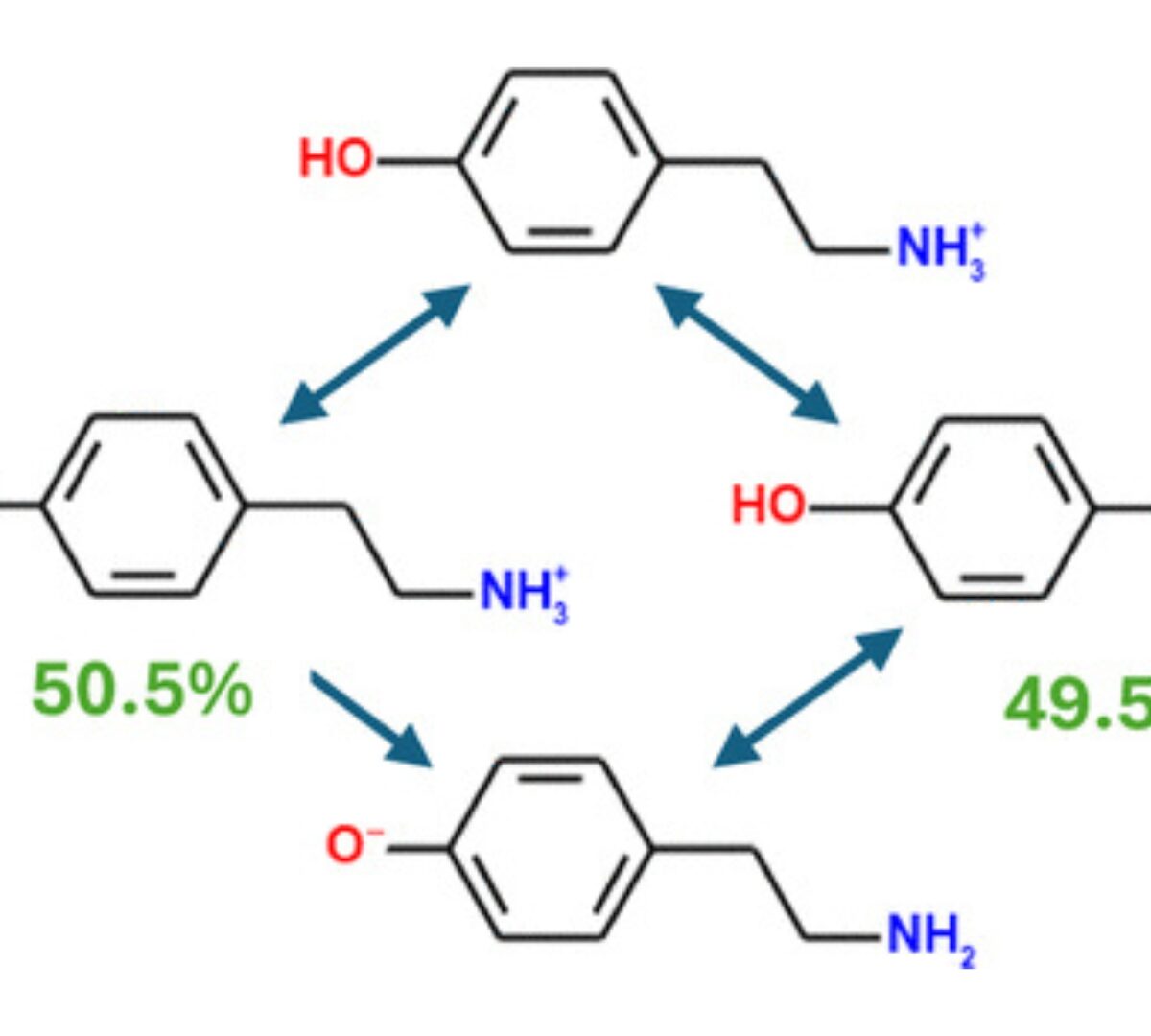
What, This “Base” Is Not a Base? Common Misconceptions about Aqueous Ionization That May Hinder Drug Discovery and Development
The challenges of modern medicinal chemistry increase with the complexity of the chemical compounds studied.
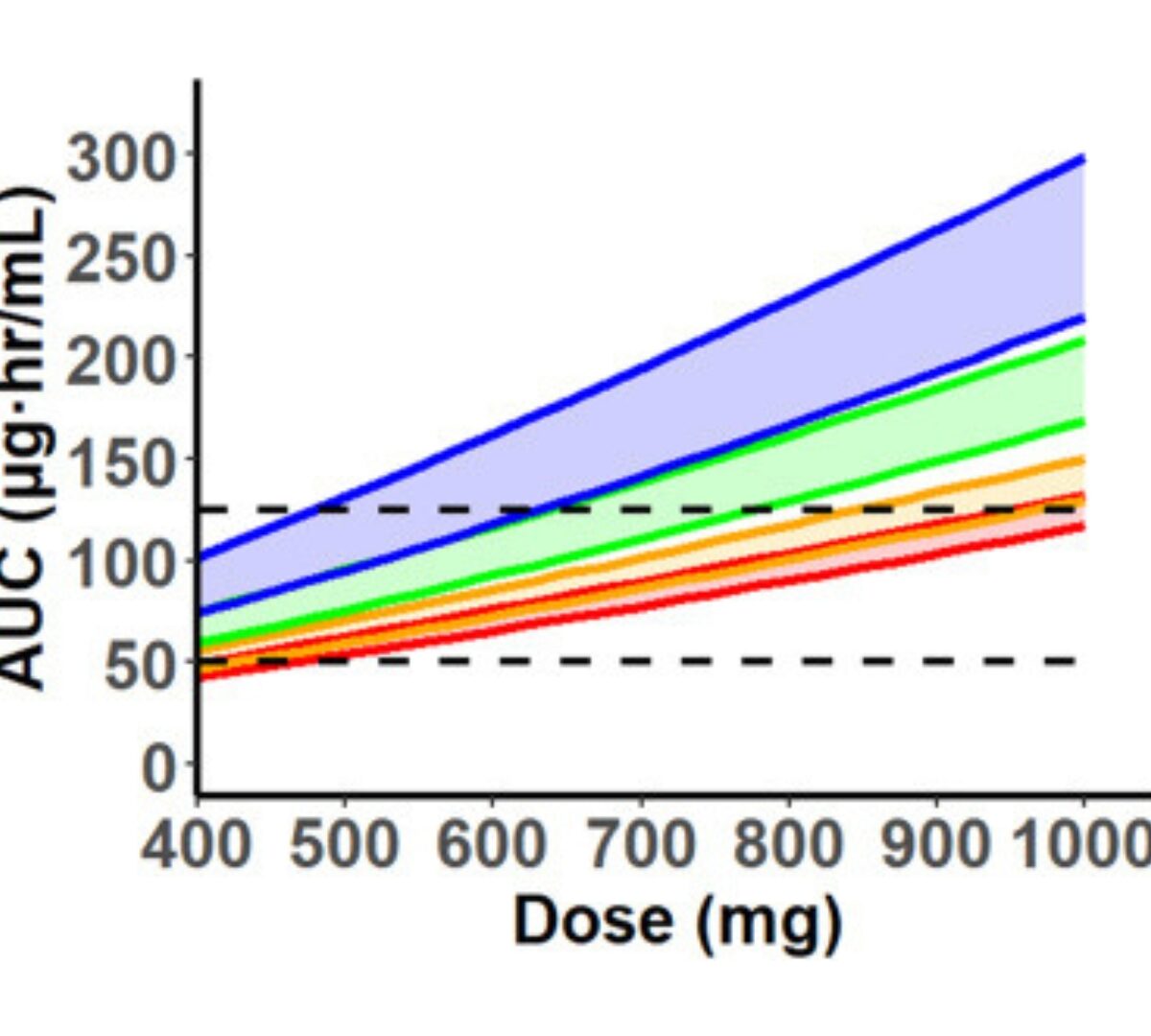
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Hydroxyurea: Implications for Dose Adjustment in Patients with Renal Insufficiency
Hydroxyurea is widely used in the management of sickle cell anemia.
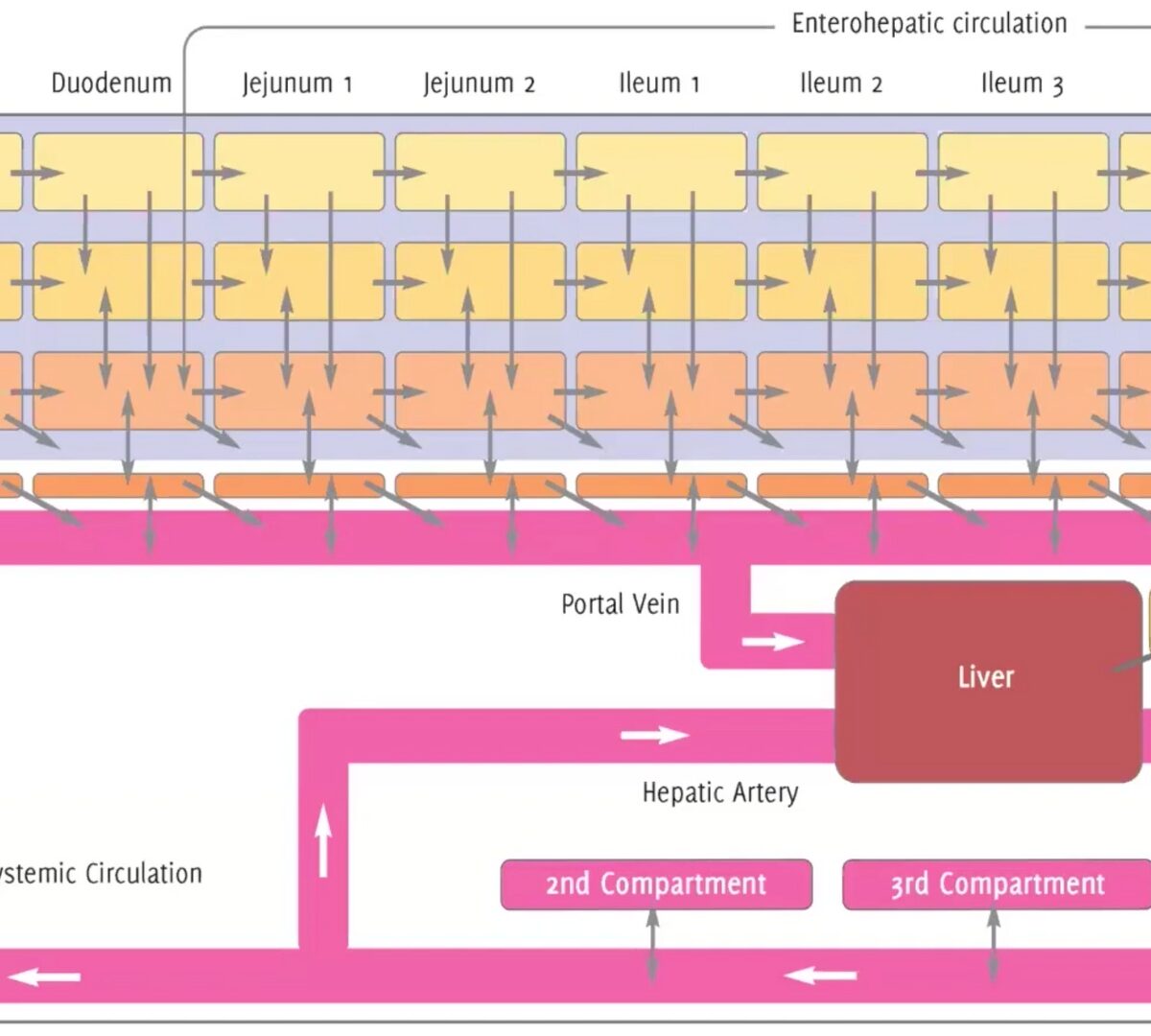
Pharmacomicrobiomics
Oral medications encounter gut commensal microbes that participate directly and indirectly in drug effects through metabolism, interactions with drug metabolites, or production of substrates that compete with drugs for drug-metabolizing enzymes, consequently influencing drug pharmacokinetics.

Becoming a Better Scientist with AI: How Tools Like GastroPlus X.2 and GastroPlusGPT Support Modelers
Learn how AI-powered tools--specifically GastroPlusGPT--can help physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelers work more efficiently, focus on deeper analysis, and ultimately be better scientists.
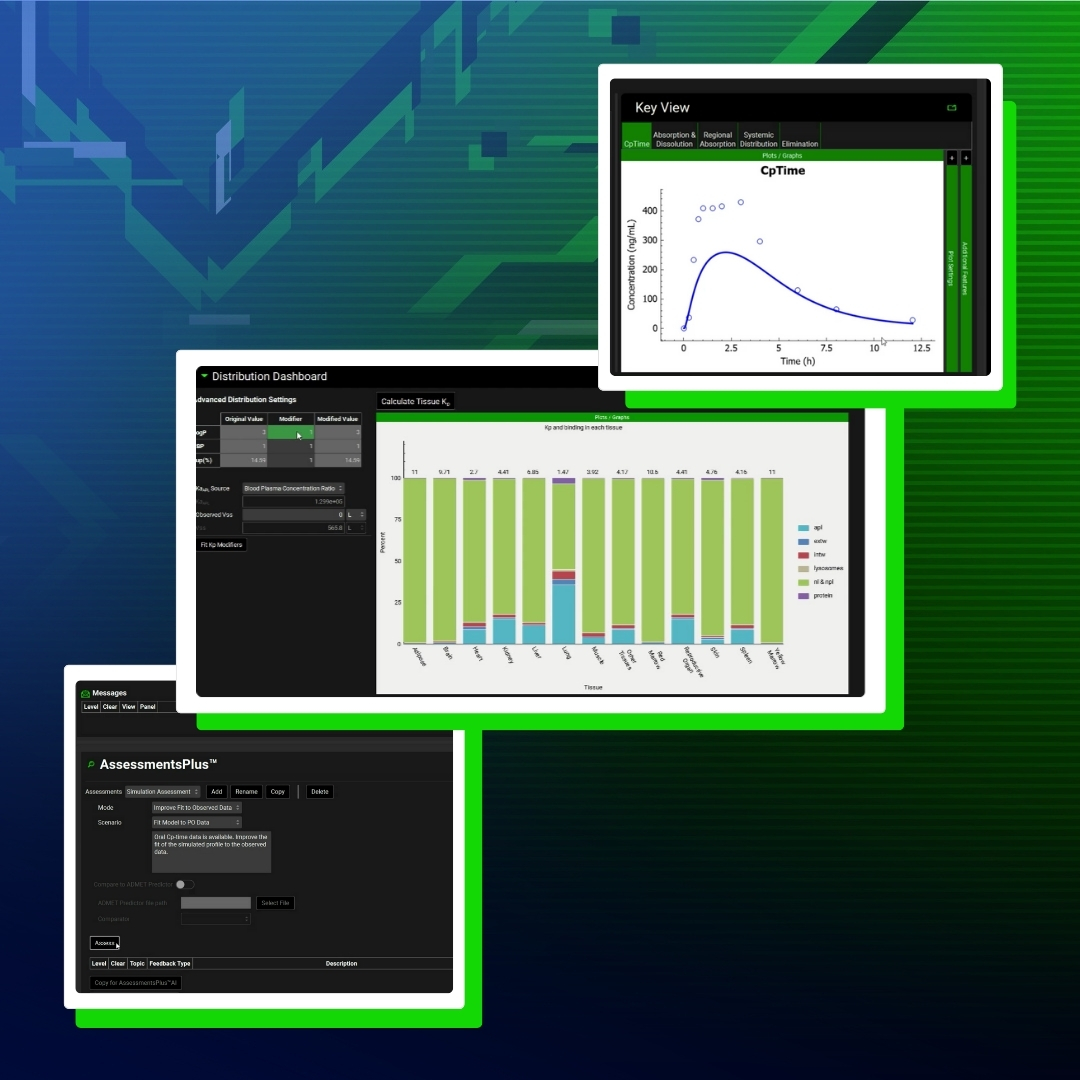
Introducing GastroPlus X.2: AI, Automation, Insights & More
Get a first look at game-changing new functionality that will revolutionize your PBPK/PBBM modeling.
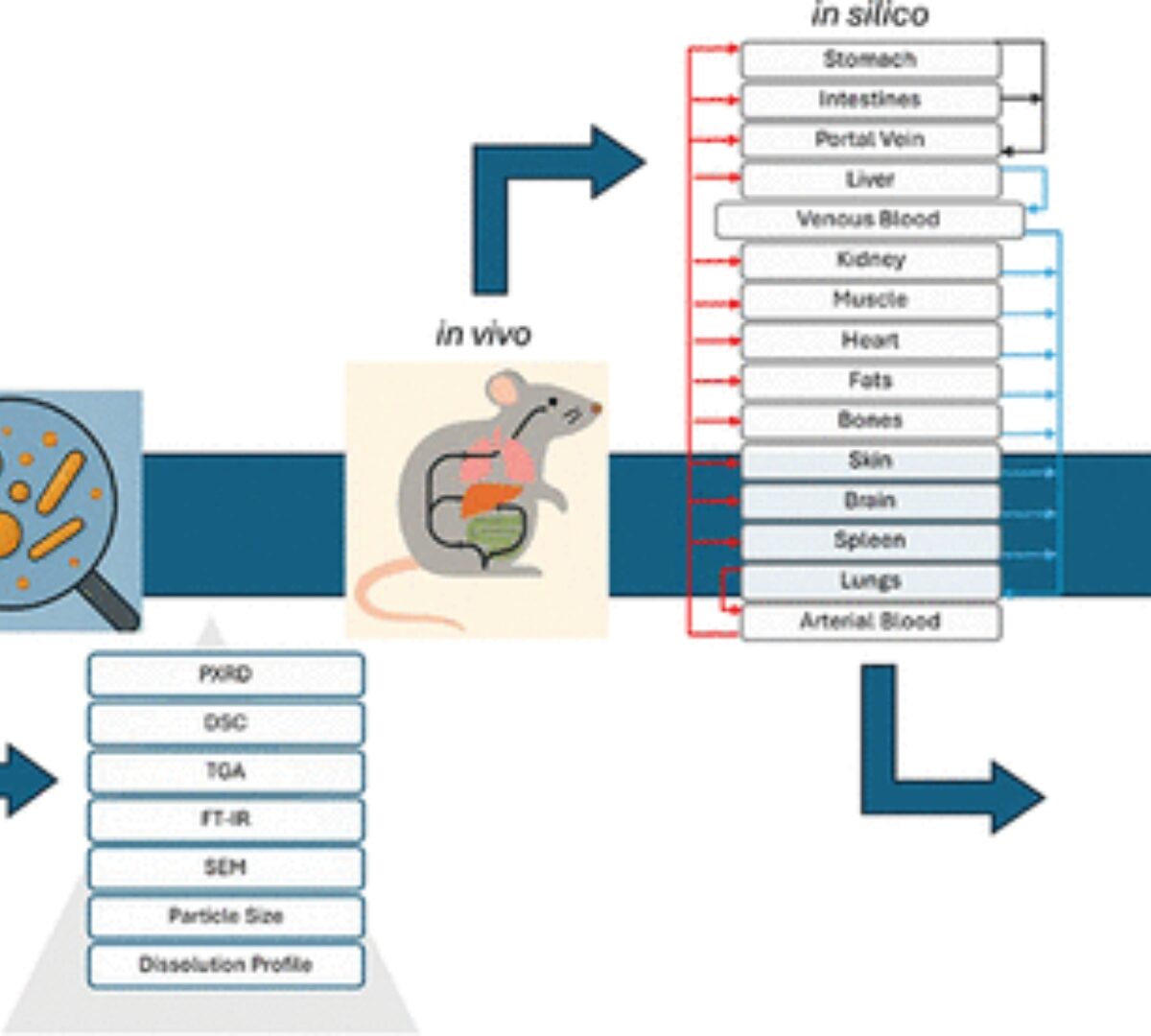
Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Efavirenz Nanoparticles: from Animal Model to Human Extrapolation
The present work aims to establish a formulation-specific, physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for efavirenz (EFV) nanocrystals that have shown increased dissolution and were produced ...
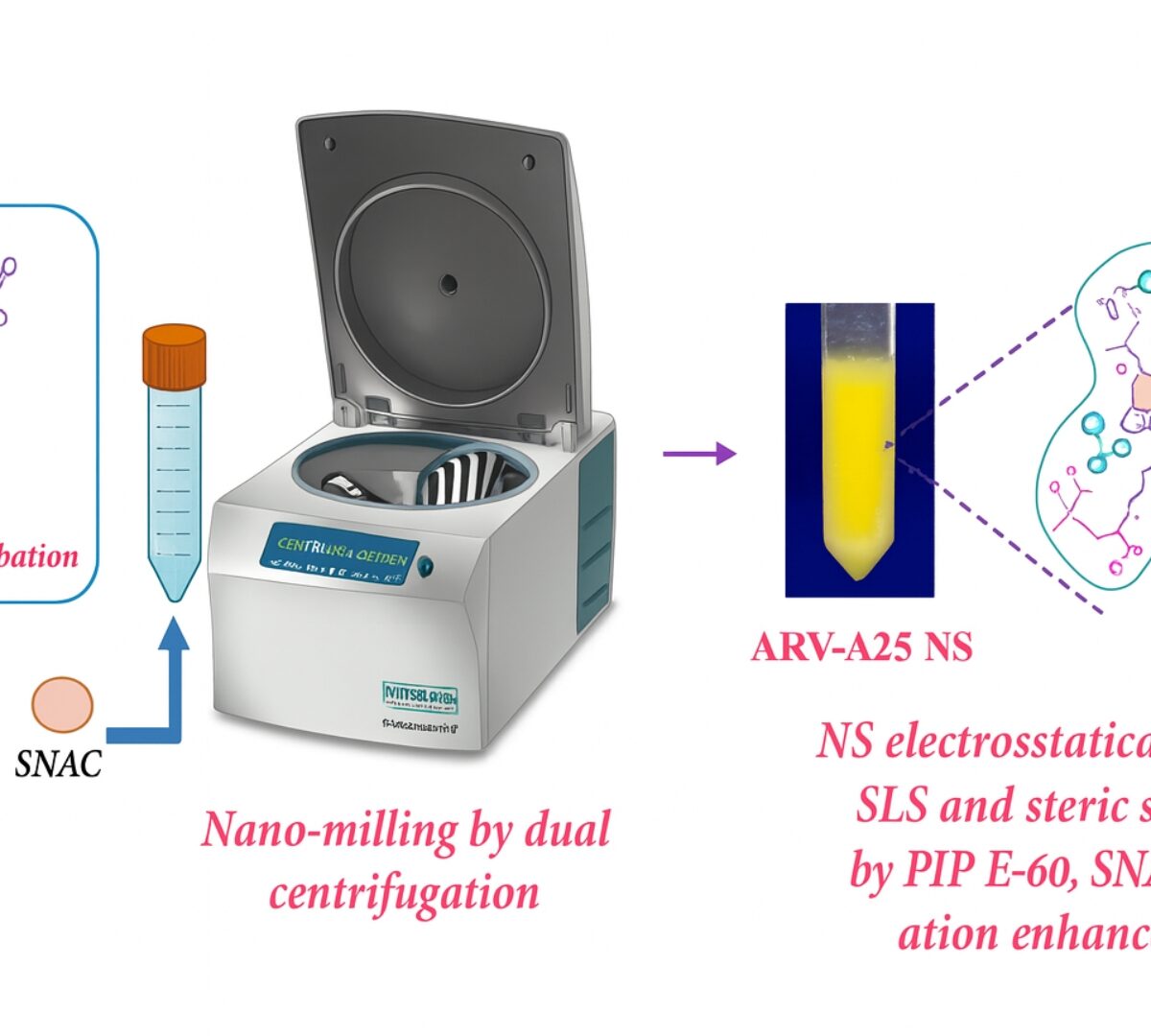
Permeability Enhancer Incorporated Oral Nanosuspension of ARV-825 PROTAC for Glioblastoma Treatment
Glioblastoma(GBM) is an aggressive brain tumor with dismal prognosis, necessitating innovative therapeutic strategies.

Indirect Modeling of Post-Prandial Intestinal Lymphatic Uptake of Halofantrine Using PBPK Approaches: Limitations and Implications
Despite the recognized importance and distinctive characteristics of the intestinal lymphatic pathway in drug absorption, its pharmacokinetic modeling remains largely unexplored.