The FGFR1/beta-klotho receptor (FGFR1/KLB) in adipose has been demonstrated to be a...

Reduction of daily moderate alcohol intake predicted to decrease fibrosis stage in patients with non-alcholic steatohepatitis
Several recently completed clinical trials in NASH patients have included fibrosis stage reductions in...

Mathematical Representation of Drug-Induced Crystal Nephropathy Using a Quantitative Systems Toxicology Approach
Drugs may cause crystal nephropathy by precipitating within kidney tubules or inducing...

Mathematical Modeling of Renal Sodium, Potassium, and Glucose Dynamics in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Simulated Populations
Type 2 diabetic (T2D) patients often exhibit reduced systolic and diastolic functions, which can place them at...

Representation of Fibrosis Stage Within Mechanistic Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)/Non-Alchoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Aligns with Histologic Assessments
NAFLD encompasses a histological spectrum of liver pathophysiology ranging from steatosis to NASH and may result in cirrhosis and ultimately liver failure. A reduction in fibrosis stage, which...

Proof-of-concept that Variable Onset and Severity of T cell-mediated Drug-Induced Liver Injury is Reproduced in a Simulated Human Population
Idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury (iDILI) is a rare, but often serious, adverse reaction that can compromise drug development. For some iDILI compounds¹, the...

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Rifampicin and Its Application for Drug-Drug Interaction with Midazolam in Adults
Rifampicin (RIF) is an essential part of tuberculosis therapy and the pharmacokinetics (PK) of RIF has been of interest due to its non-linear and auto-induction behavior

Clinical Ocular Exposure Extrapolation Using PBPK Modeling and Simulation: Gatifloxacin Solution Case Study
Development of generic ophthalmic drugs has been extremely challenging due to the complexity of the ocular system and a lack of sensitive testing tools to evaluate its interplay with ophthalmic formulations.
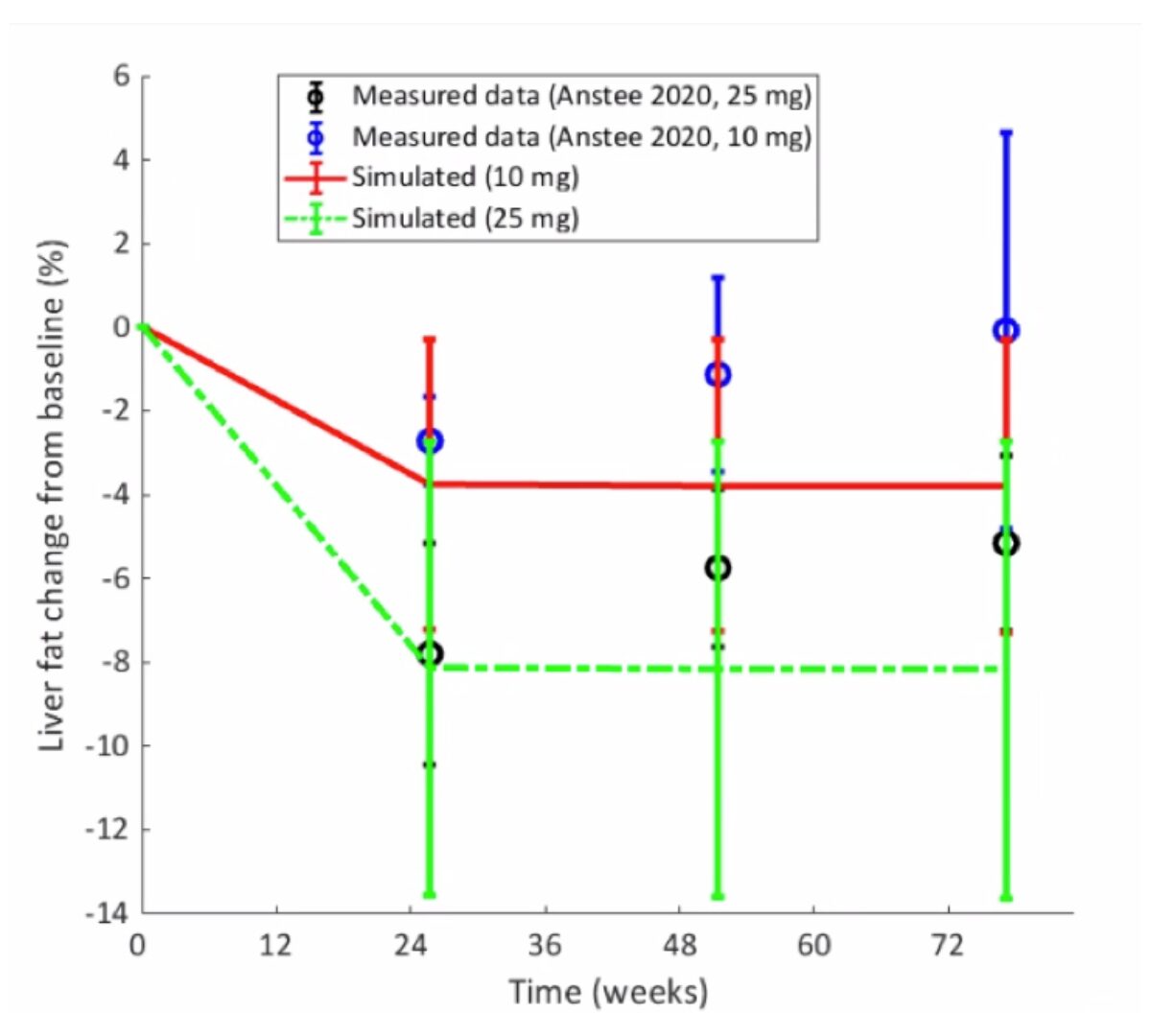
Predicting the Efficacy of Obeticholic Acid Treatment for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Using NAFLDsym, a Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Obeticholicacid (OCA), a bile acid analog and agonist of the farnesoidX receptor (FXR), is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).

Establishment of preclinical mechanistic in vitro-in vivo correlations for long-acting injectable suspensions
Long acting injectable (LAI) formulations administered through subcutaneous (SC) or intramuscular (IM) routes provide sustained drug release over an extended period.
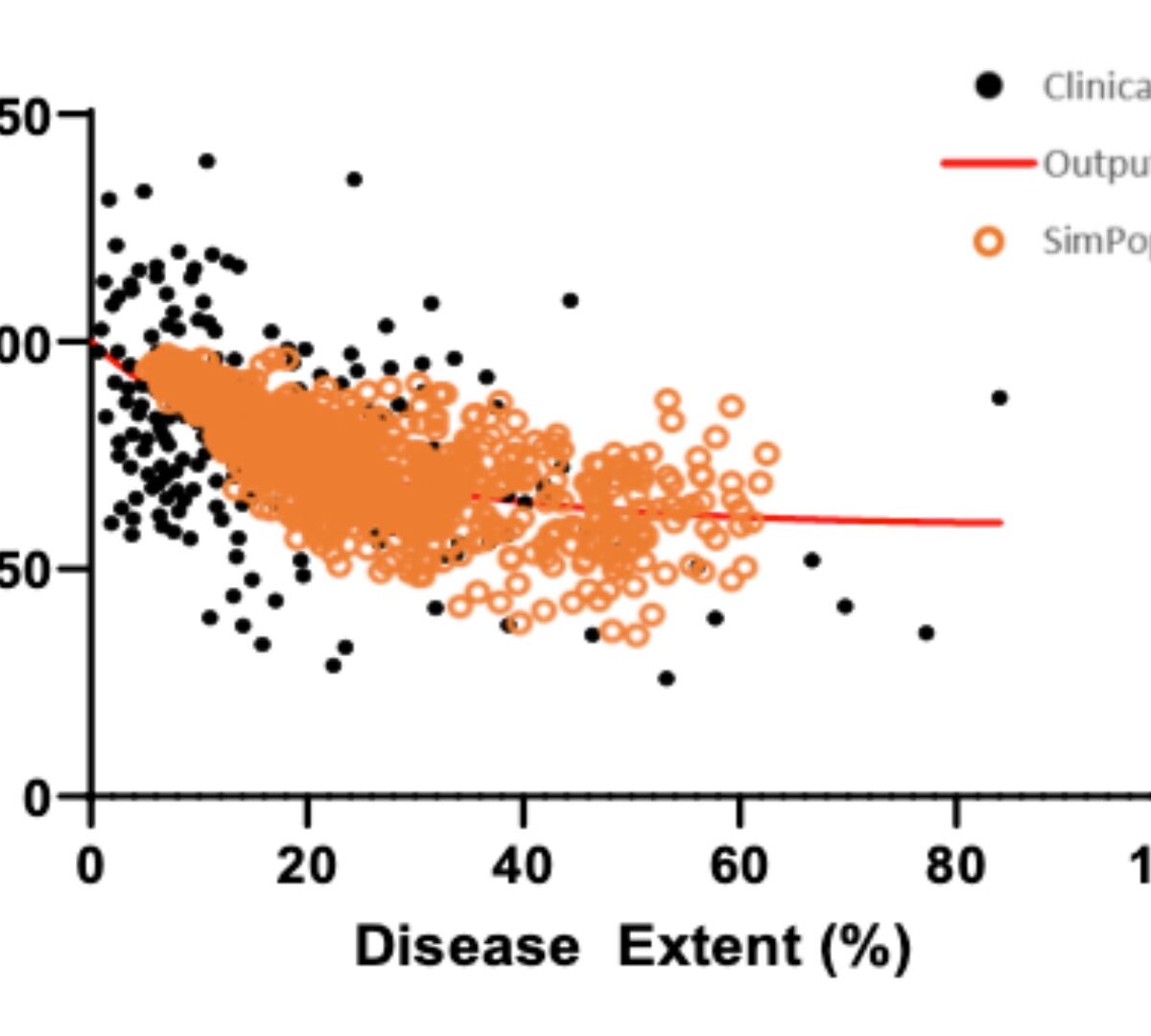
ILDsym®, a Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP) Platform, Successfully Simulates the Pathophysiology of Systemic Sclerosis-Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD) and Inter-patient Variability
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a rare connective tissue and autoimmune disease associated with inflammation of the skin and internal organs.

Use of Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) to Identify Potential Intrinsic Mechanisms of Toxicity
BAY1128688, a selective inhibitor of aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3), was in clinical trials as a potential therapy to provide pain relief for women with endometriosis.

Delineating the Complex Interplay of Enzymes and Transporters Governing the Absorption and Disposition of Atorvastatin and the Metabolites Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling
Atorvastatin (ATS) is widely used to treat high cholesterol and potentially lower the risk of cardiac complications.

A phase 1b dose escalation study of CD137 mAb agonist OC-001 as monotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic cancer
OC-001 is a CD137 mAb agonist designed to show differential agonistic activity from that of competitor
antibodies. OC-001 provided T cell activation that

Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Pyrotinib to Understand the Impact of Interplay Between CYP3A4 and P-GP on its DDIs with CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Inducers
To develop a PBPK model for pyrotinib and qualify it with the in vivo data obtained after oral administrations.

Implementation of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach to Predict Disease-Related Changes in Drug Pharmacokinetics in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Conference name: International Society for the Study of Xenobiotics (ISSX)-Microsomes and Drug Oxidations (MDO) Joint Meeting
Introduction: Understanding disease-related changes in the pharmacokinetics of drugs in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is of clinical importance...

Absence of association between abatacept exposure levels and initial infection in patients with RA: a post hoc analysis of the randomized, placebo-controlled AVERT-2 study
Infections are the most commonly reported AEs in patients with RA treated with immunosuppressive therapies, and

Clinical Ocular Exposure Extrapolation Using PBPK Modeling and Simulation: Moxifloxacin Solution Case Study
Development of generic ophthalmic drug products is challenging due to the complexity of the ocular system and a lack of sensitive...

Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) simulations and modeling of botanical constituents
Botanicals have broad use as traditional medicines, natural health products, and dietary supplements around the world.

Modeling of Cyclosporine A-Induced Acute Kidney Injury with RENAsym®
Cyclosporine A (CsA) is an immunosuppressant commonly used to prevent organ rejection and can be used to treat other diseases such as...
