The ability to quickly and accurately predict key PK properties based solely on chemical structure can aid in several tasks.

Multicriteria Decision Aiding in the service of Drug Discovery
Drug discovery is inherently a multicriteria optimization problem.

Predicting dose-dependent fraction absorbed via a mechanistic absorption model and machine learning
Drug dissolution and absorption are crucial in oral drug delivery.

Pemvidutide, a glucagon-like peptide 1/glucagon dual receptor agonist, improves metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis activity and fibrosis in a clinical quantitative systems pharmacology model
Elevated liver fat content (LFC) is the primary pathophysiologic driver of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). In prior clinical trials, pemvidutide...

Evaluation of the Dissolution Behavior of the Lysosomotropic Drug Amlodipine using Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM)
Amlodipine (AML) is a weak base drug (pKa 9.1, lop=2.96) belonging to class I of the BCS and therefore a candidate for biowaiver.

Evaluation of the Dissolution Behavior of Etodolac Tablers Using Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) Approach
Etodolac is a non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory, acidic molecule (pKa 4.65) with pH-dependent solubility and classified as a BCS class II drug [1].

Best of Both Worlds: An Expansion of the State of the Art pKa Model with Data from Three Industrial Partners
In a unique collaboration between Simulations Plus and several industrial partners, we were able to develop a new version 11.0 of the previously published1 in silico pKa model, S+pKa, with considerably improved prediction accuracy.

A Biomarker-Focused QSP Model of Complement Alternative and Terminal Pathways to Evaluate Potential Targets for Therapeutic Impact in Complement-Associated Diseases: Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) as a Case Study
Complement overactivity has been implicated in multiple diseases, including PNH...

Framework for Classifying Chemicals for Repeat Dose Toxicity using NAMs
Initially all chemicals are of High concern. Reassessment is based on accumulating evidence to potentially move chemicals to Medium or Low concern.

Evaluating Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Liver Toxicity in a Biomimetic Liver Microphysiology Model
The prominence of biologic drugs has rapidly gained traction and has delivered life-changing...

Investigating the Potential Hepatotoxicity of ORM-48824 in a Quantitative Systems Toxicology Platform for Liver Safety, DILIsym®
ORM-48824 is a transient receptor potential Ankyrin-1 (TRPA1) antagonist and was initially being developed for patients with diabetic neuropathic pain...

Prediction of Multidrug Resistance Protein 3 (MDR3) Inhibition-mediated Cholestatic Drug-induced Liver Injury (DILI) Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Modeling
DILI is a primary cause of acute liver failure and reason for the termination of drug development programs...

Modeling and Simulation of Acetaminophen Pharmacokinetics and Hepatic Biomarkers After Overdoses of Extended-Release and Immediate-Release Formulations with DILIsym, a Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Software Platform
The analgesic/antipyretic acetaminophen (APAP) has multiple formulations including immediate-, modified-, and extended-release preparations...
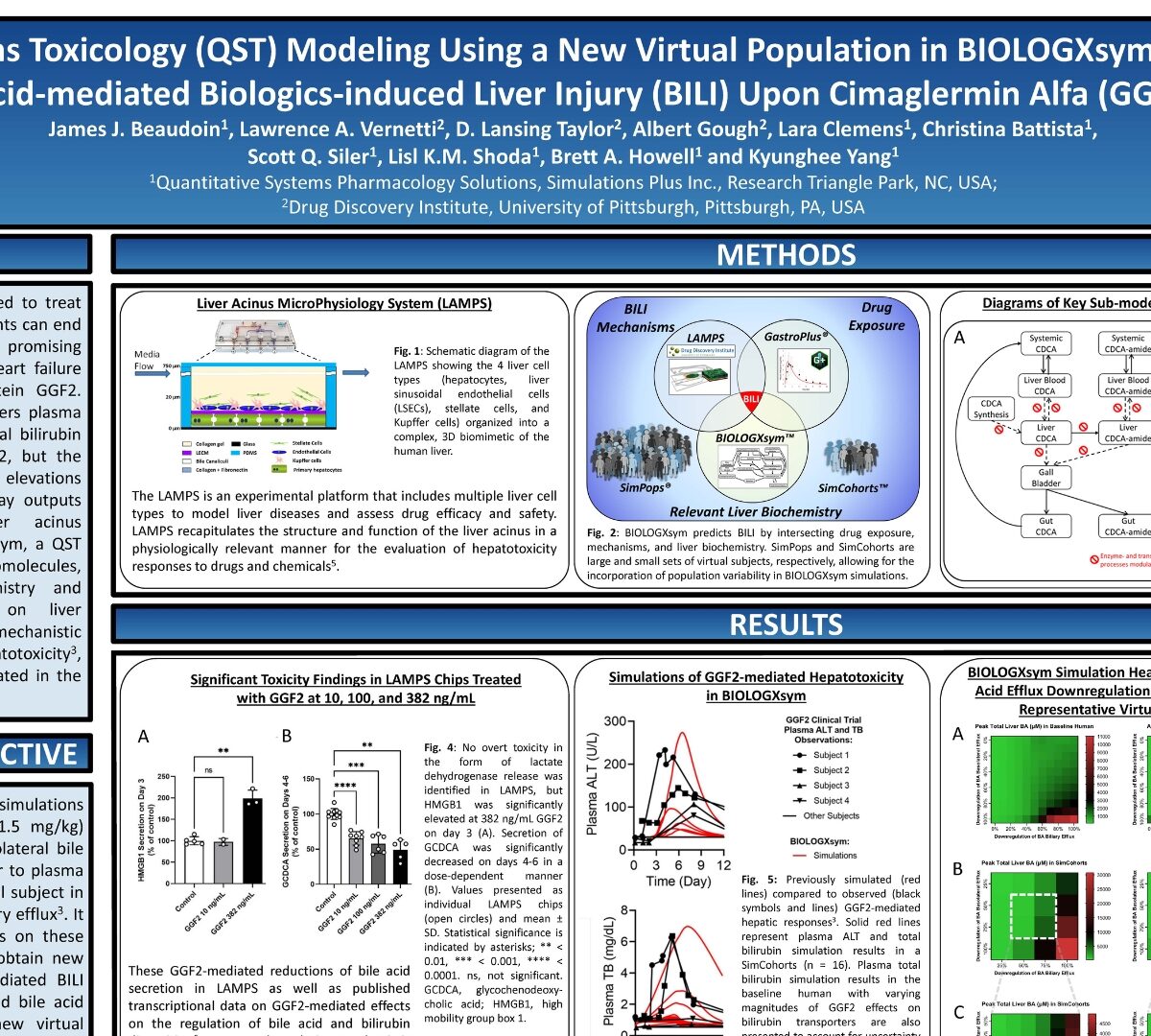
Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) Modeling Using a New Virtual Population in BIOLOGXsym Offers Mechanistic Insights Into Bile Acid-mediated Biologics-induced Liver Injury (BILI) Upon Cimaglermin Alfa (GGF2) Administration
Biopharmaceuticals are increasingly used to treat various medical conditions, but BILI events can end...
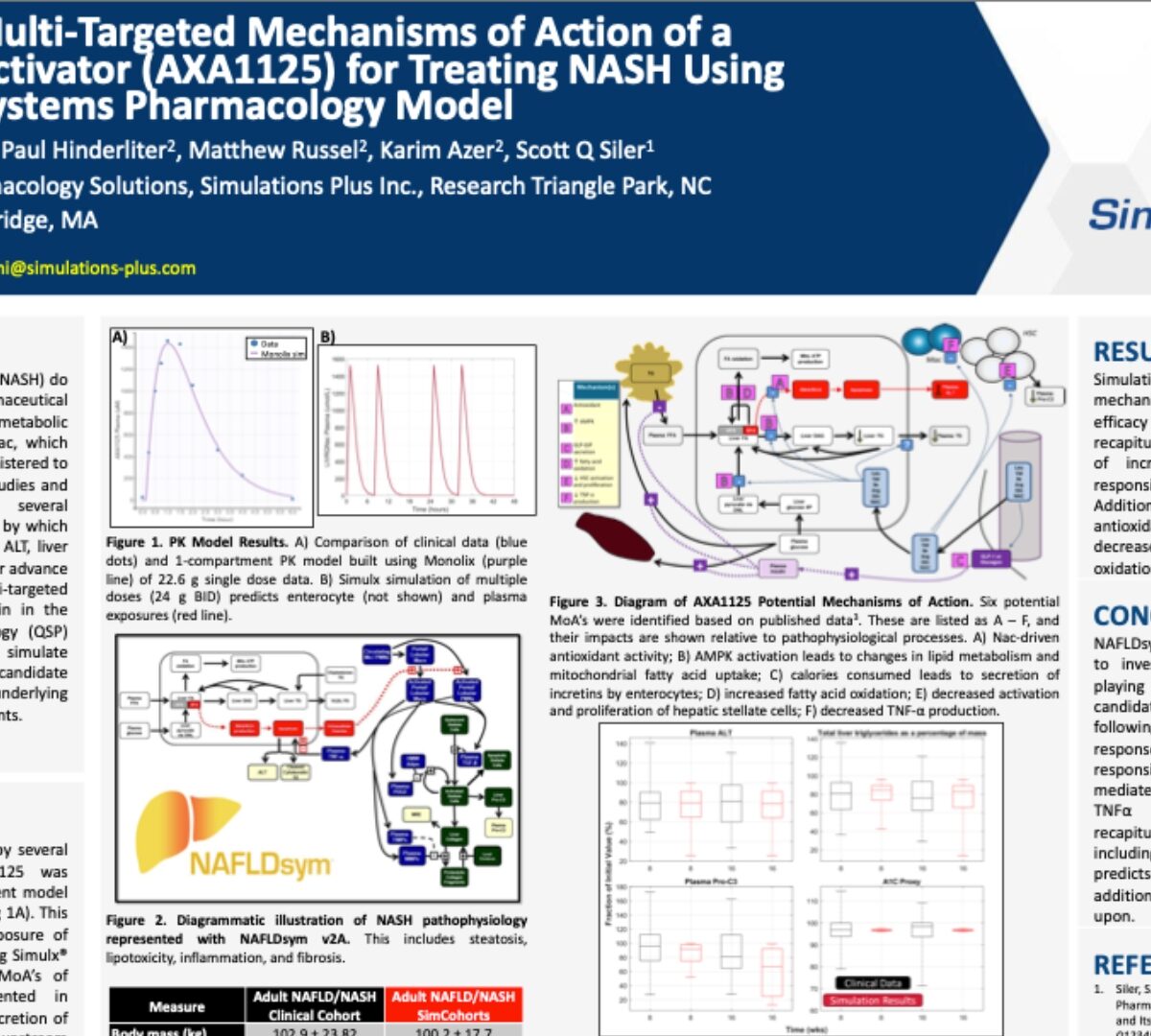
Advancing the Multi-Targeted Mechanisms of Action of a Mitochondrial Activator (AXA1125) for Treating NASH Using a Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Model
Patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) do not currently have options for pharmaceutical...
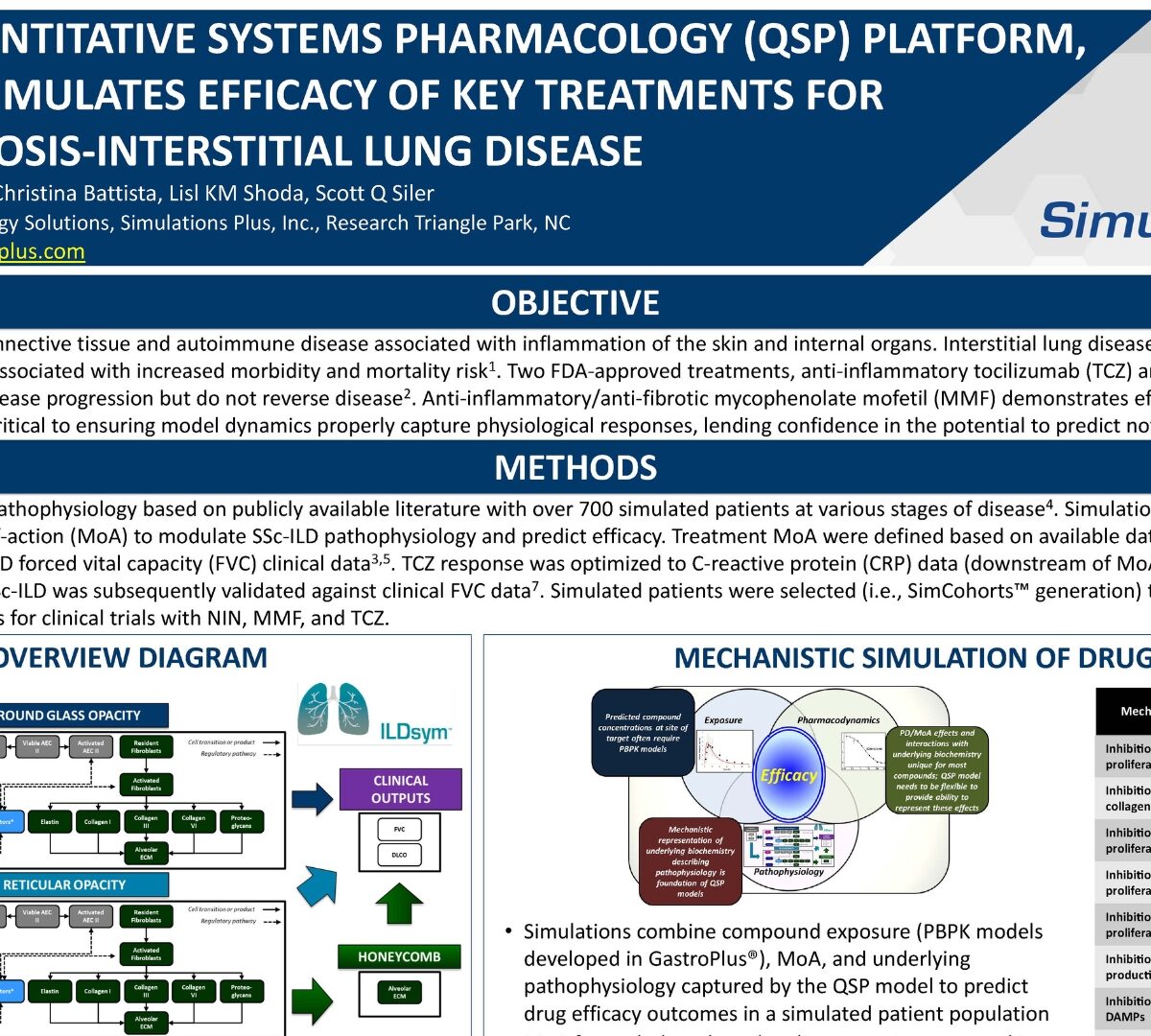
ILDSYM®, A Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP) Platform, Successfully Simulates Efficacy of Key Treatments for Systemic Sclerosis-Interstitial Lung Disease
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a rare connective tissue and autoimmune disease associated with inflammation of the skin and internal organs. Interstitial lung disease (ILD), a frequent complication of SSc with highly variable course, is associated with increased morbidity and mortality risk¹. Two FDA-approved treatments, anti-inflammatory tocilizumab (TCZ) and anti-fibrotic nintedanib (NIN)...
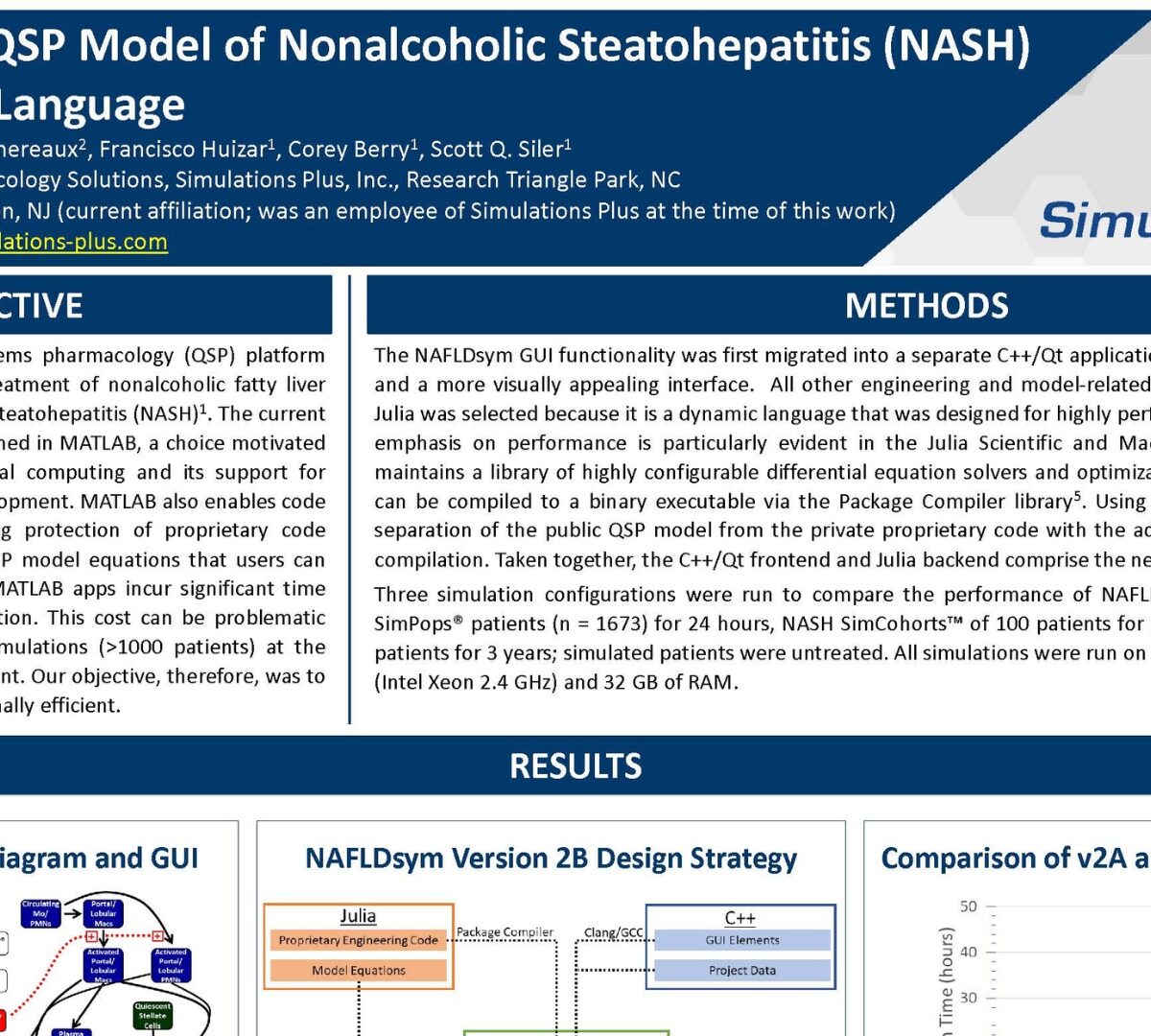
Accelerating a QSP Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Using the Julia Language
NAFLDsym® is a quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) platform that simulates progression and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver...

Mechanistic Representation of NAG Release in Relation to Renal Proximal Tubular Cellular Injury
Novel Acute kidney injury (AKI) biomarkers enhance disease understanding and aid...
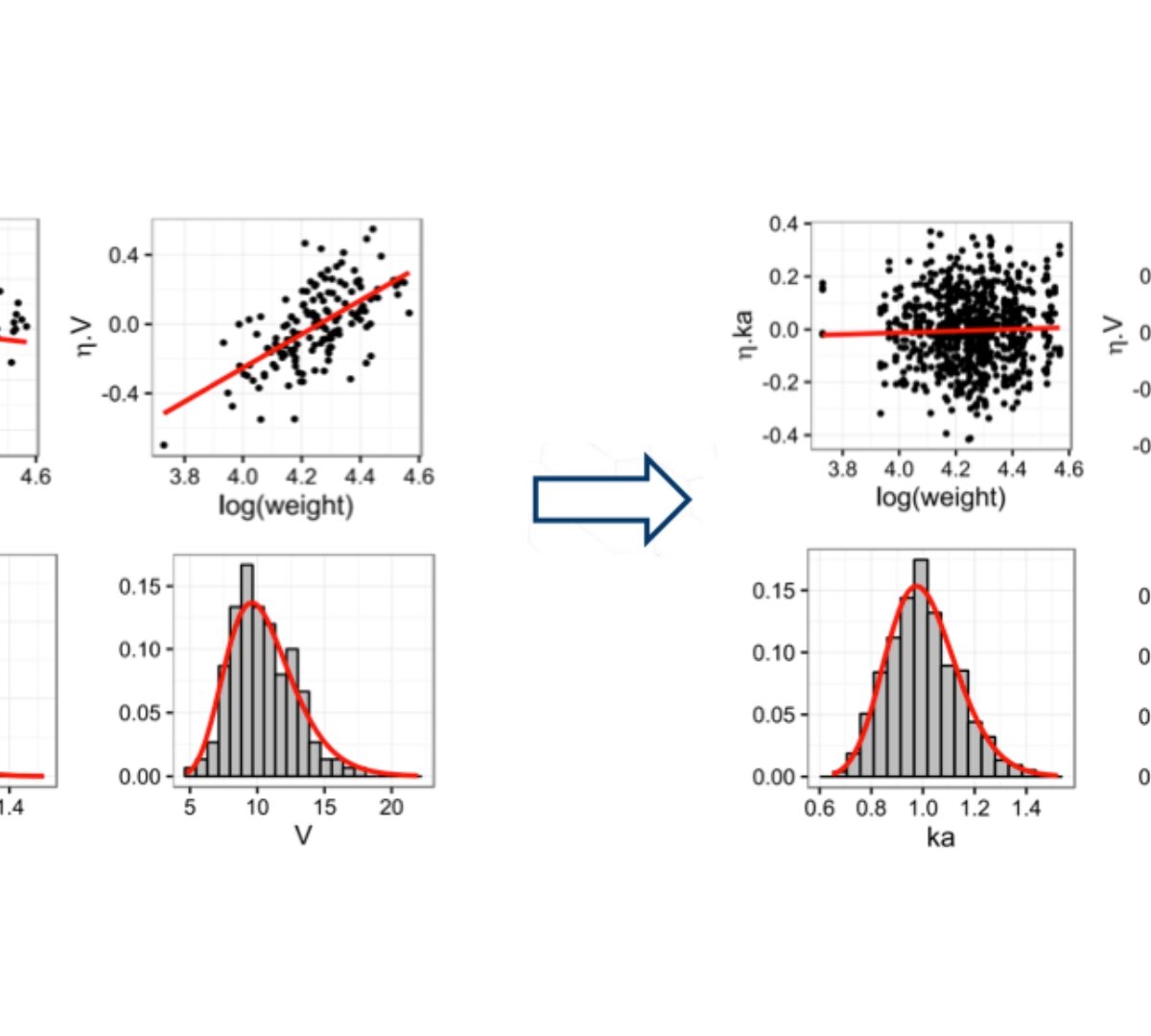
Automated covariate selection: SAMBA and COSSAC algorithms
COSSAC Conditional Sampling use for Stepwise Approach based on Correlation tests
SAMBA Stochastic Approximation for Model Building Algorithm
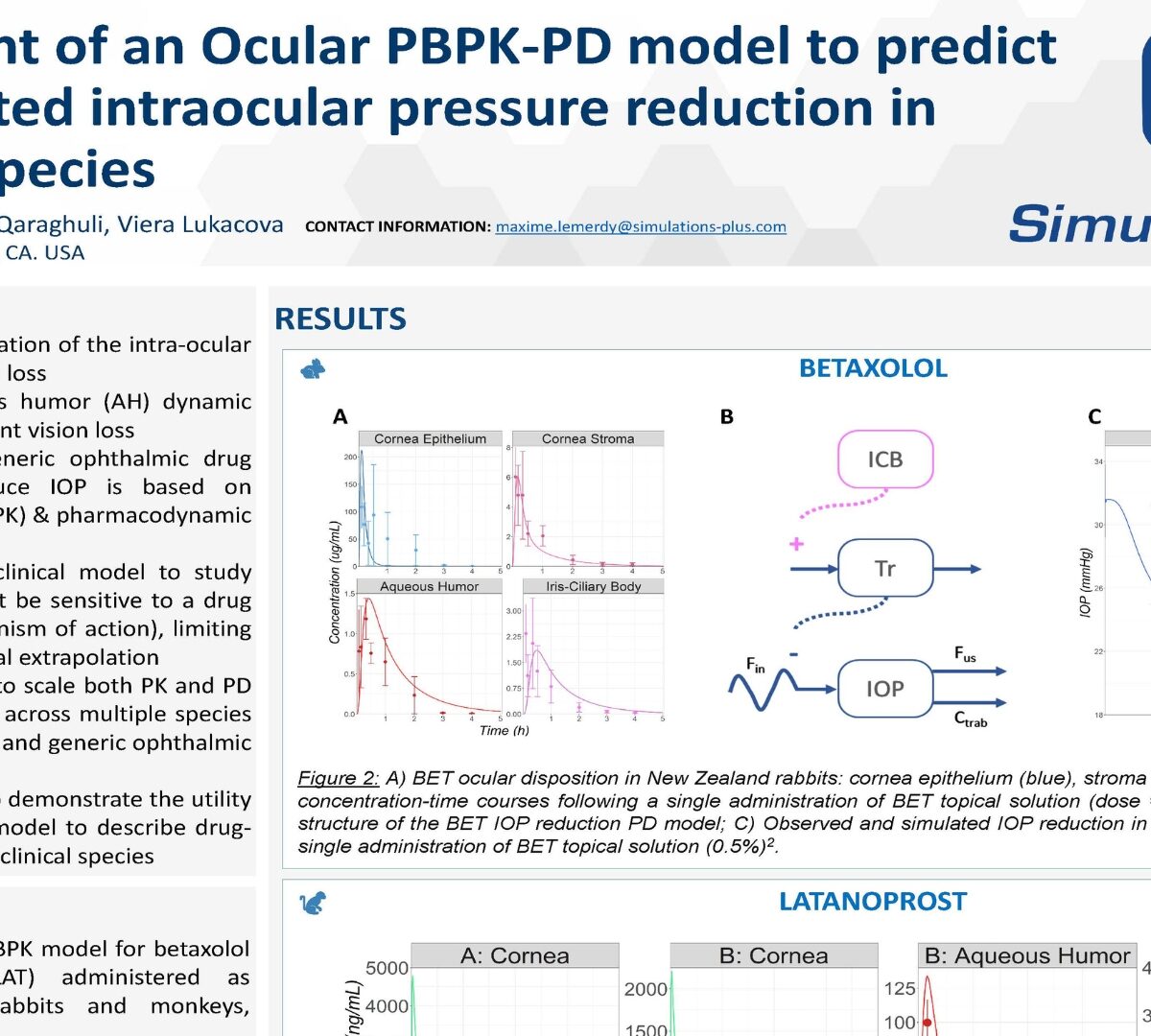
Development of an Ocular PBPK-PD model to predict drug-mediated intraocular pressure reduction in preclinical species
Glaucoma, caused by an elevation of the intra-ocular pressure (IOP), leads to vision loss
