Presented by Zack Kenz at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Clinical Track: 2023 DDI Standards Model Update
Presented by Viera Lukacova at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Discovery + Preclinical Track Poster Presentation: QST – Prediction of the Liver Safety Profile of a First-in-Class Myeloperoxidase Inhibitor (Verdiperstat) Using Quantitative Systems Toxicology Modeling
Presented by Jeff Woodhead at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Clinical Track: A Physiologically Pharmacokinetic Model Based Approach for Predicting Dose of Long-Acting Lenacapavir
Presented by Naveed Shaik, Gilead at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Discovery + Preclinical Track: Introduction to COMPLEMENTsym
Presented by Lisl Shoda at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Clinical Track: Update on MIDD Program within the FDA
Presented by Dr. Rajanikanth Madabushi, U.S. FDA at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Discovery + Preclinical Track: Formulation: Using In Silico PK Simulations for Early Formulation Development of Amorphous Solid Dispersions
Presented by Deanna Mudie, Lonza at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Clinical Track: Towards a flexible model-informed precision dosing software solution using MonolixSuite™
Presented by Manuel Ibarra & Laura Gonzalez, University of the Republic Uruguay at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Discovery + Preclinical Track: Evaluation of ADMET Predictor in Early Discovery Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics
Presented by Ylva Terelius, ADMEYT AB at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Clinical Track: From Preclinical to Clinical Drug Product Development: A Path for Smooth Transition
Presented by Sandra Suarez-Sharp at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Discovery + Preclinical Track: High-Throughput Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation to Inform Early Drug Discovery
Presented by Andrés Olivares-Morales, Roche at MIDD+ 2023 on Wednesday, February 15th.

Career Center Open House
Now Hiring! Submit your CV and application directly to our Human Resource and hiring team!

Welcome to the MIDD+ 2023 Scientific Conference
Welcome by Director of Business Development, Arlene Padron.
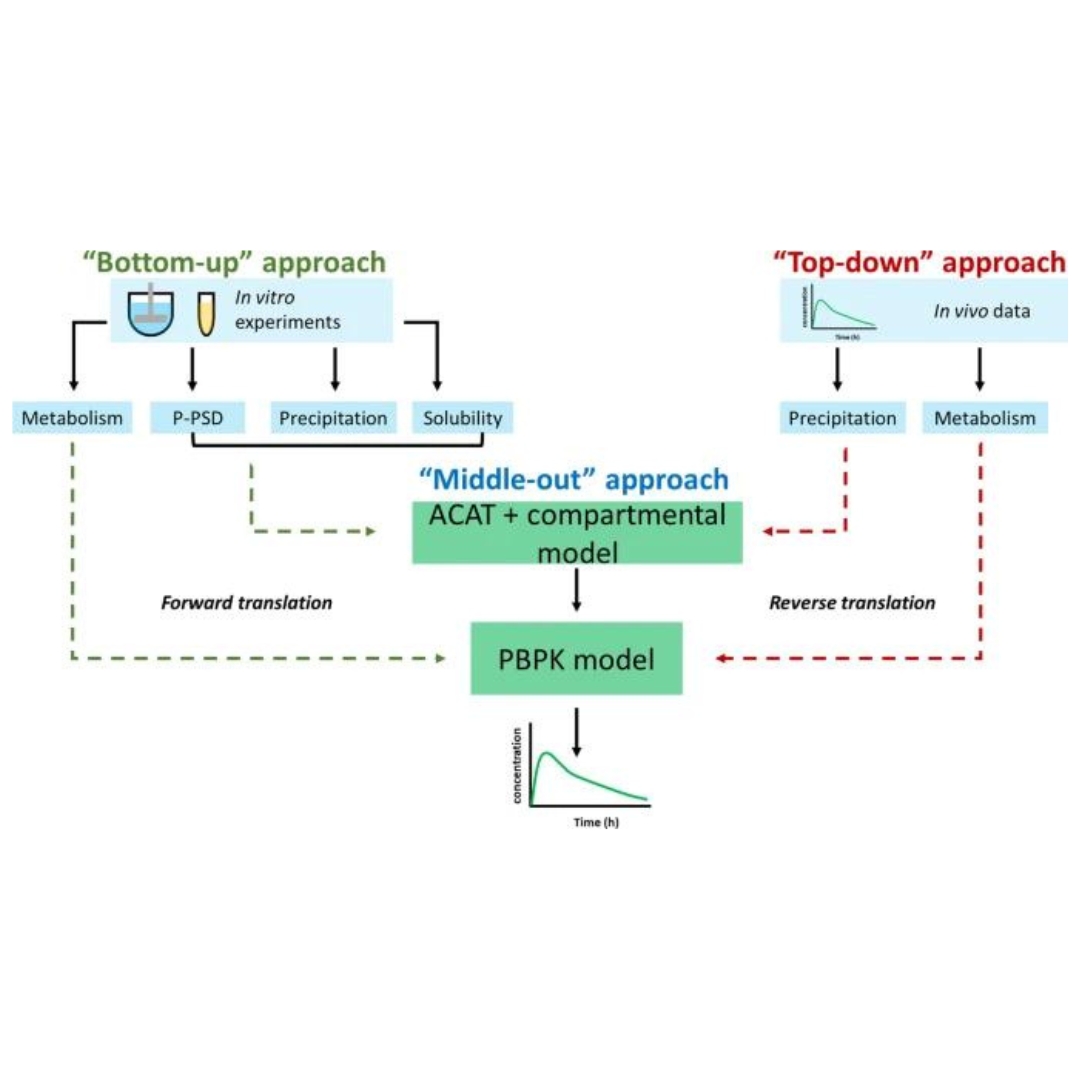
Integrating Forward and Reverse Translation in PBPK Modeling to Predict Food Effect on Oral Absorption of Weakly Basic Drugs
Ketoconazole and posaconazole are two weakly basic broad-spectrum antifungals classified as Biopharmaceutics Classification System class II drugs, indicating that they are...
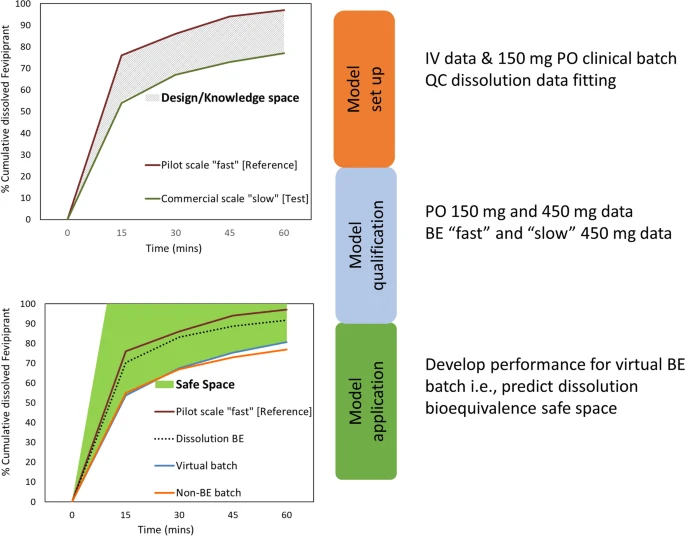
Establishing the Safe Space via Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling. Case Study: Fevipiprant/QAW039
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic and absorption modeling has increasingly been implemented for biopharmaceutics applications to define the safe space for drug...

February 2023 GastroPlus Newsletter
Exciting news from the world of GastroPlus®!
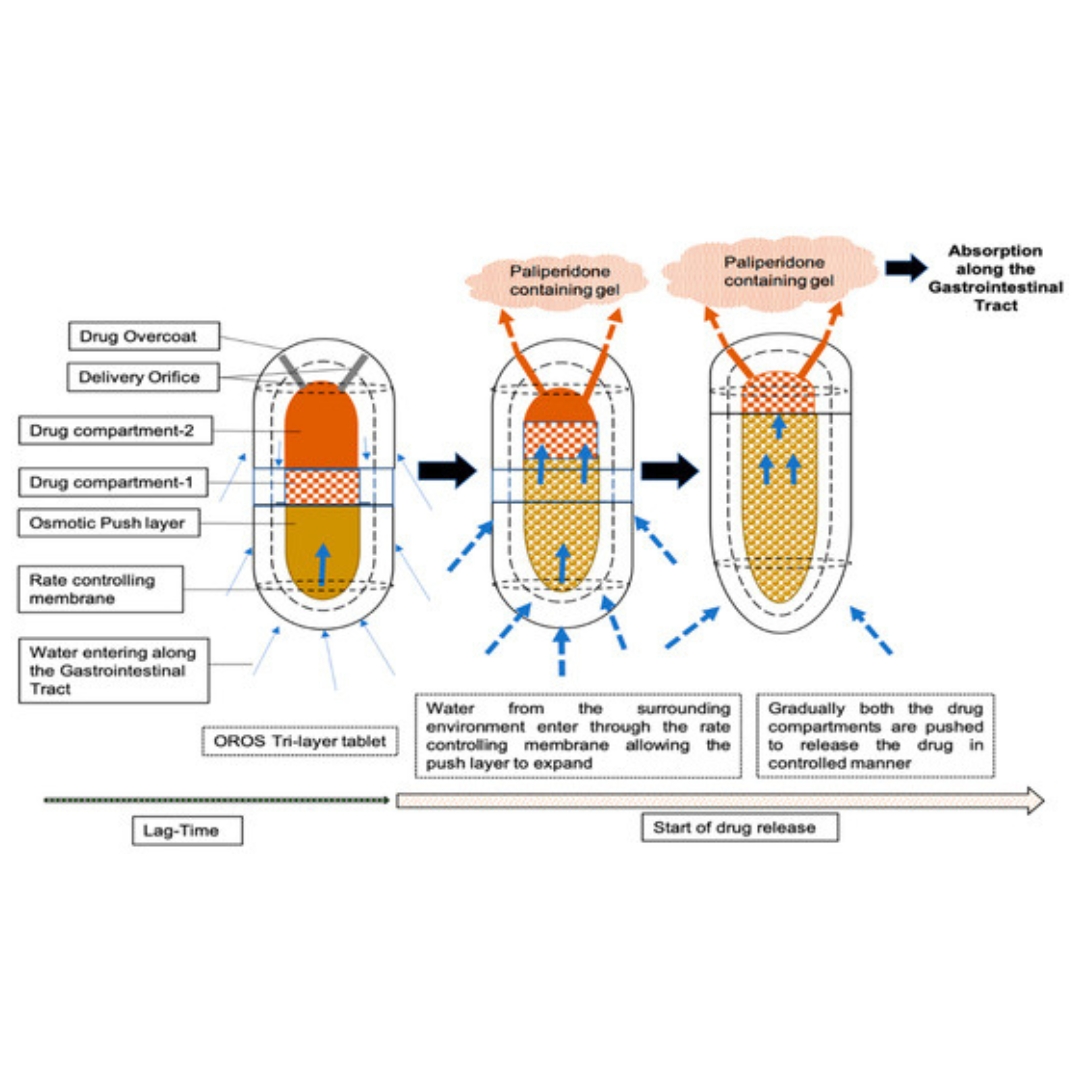
Leveraging Physiologically Based Modelling to Provide Insights on the Absorption of Paliperidone Extended-Release Formulation under Fed and Fasting Conditions
Paliperidone was approved by the US FDA in 2006 as an extended-release (ER) tablet (Invega®) for the once-daily treatment of schizophrenia. This osmotic-controlled...

Regulatory Requirements for the Development of Second-Entry Semisolid Topical Products in the European Union
The development of second-entry topical products is hampered by several factors.
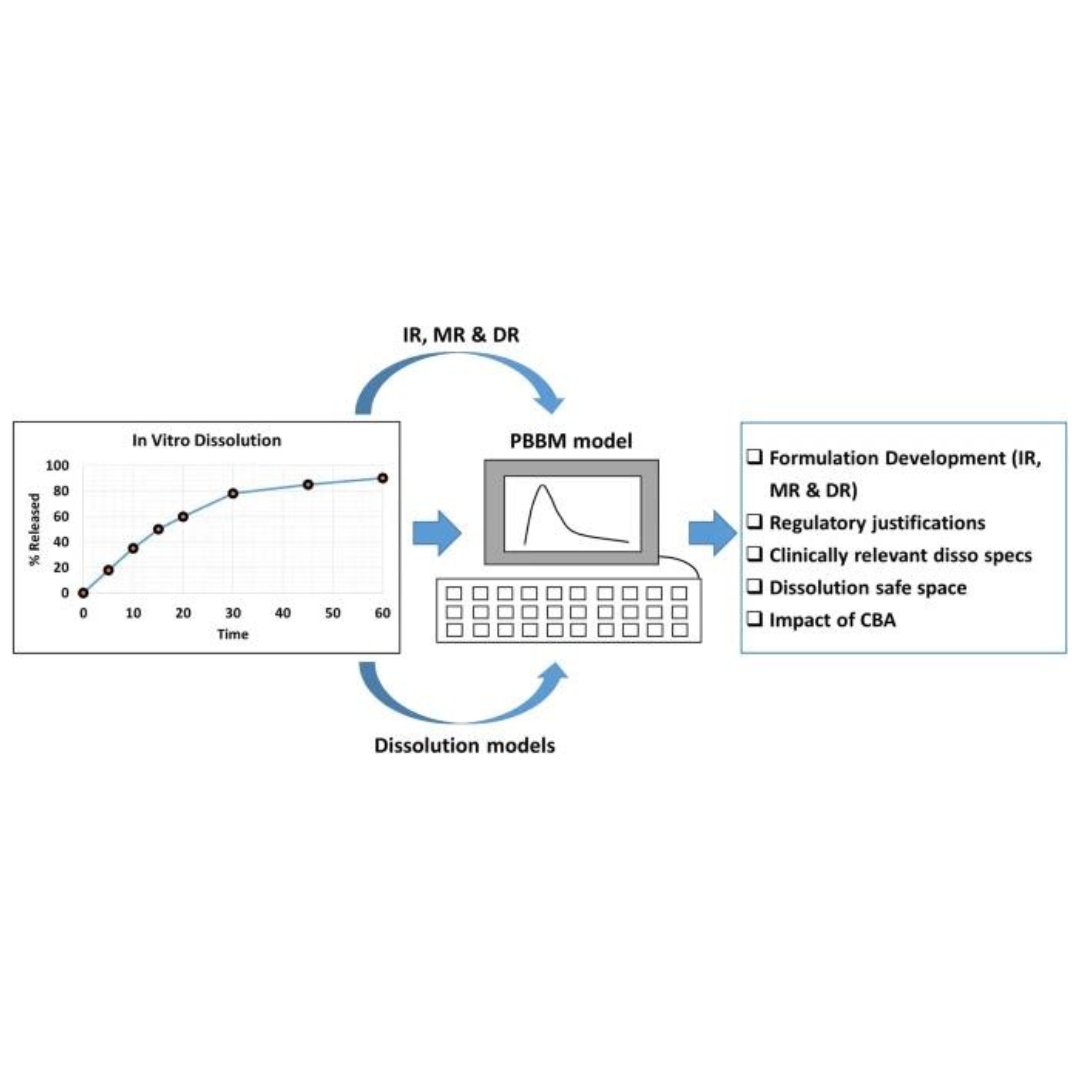
Best Practices for Integration of Dissolution Data into Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Models (PBBM): A Biopharmaceutics Modeling Scientist Perspective
Dissolution is considered as a critical input into physiologically based biopharmaceutics models (PBBM) as it governs in vivo exposure. Despite many workshops, initiatives...

Simulations Plus Releases Redesigned NAFLDsym® QSP Software Tool
NAFLDsym v2B Beta represents the first release in the faster, sleeker Julia infrastructure
